January 2016 Page 6–9
Chapter 6. Testing Facilities
6
ALARMS
Master Module Remote Module Probable Situation
Major Minor Major Minor
clear clear clear clear All OK
clear clear clear set Weak/noisy line
clear clear set clear Master or line failed
clear clear set set Remote failed
clear set clear clear Weak/noisy line
clear set clear set Weak/noisy line
clear set set clear Weak/noisy line or master failed
clear set set set Remote failed
set clear clear clear Remote or line failed
set clear clear set Remote or line failed
set clear set clear Line failed
set clear set set Remote failed
set set clear clear Master failed
set set clear set Master failed
set set set clear Master failed
set set set set Master and remote failed
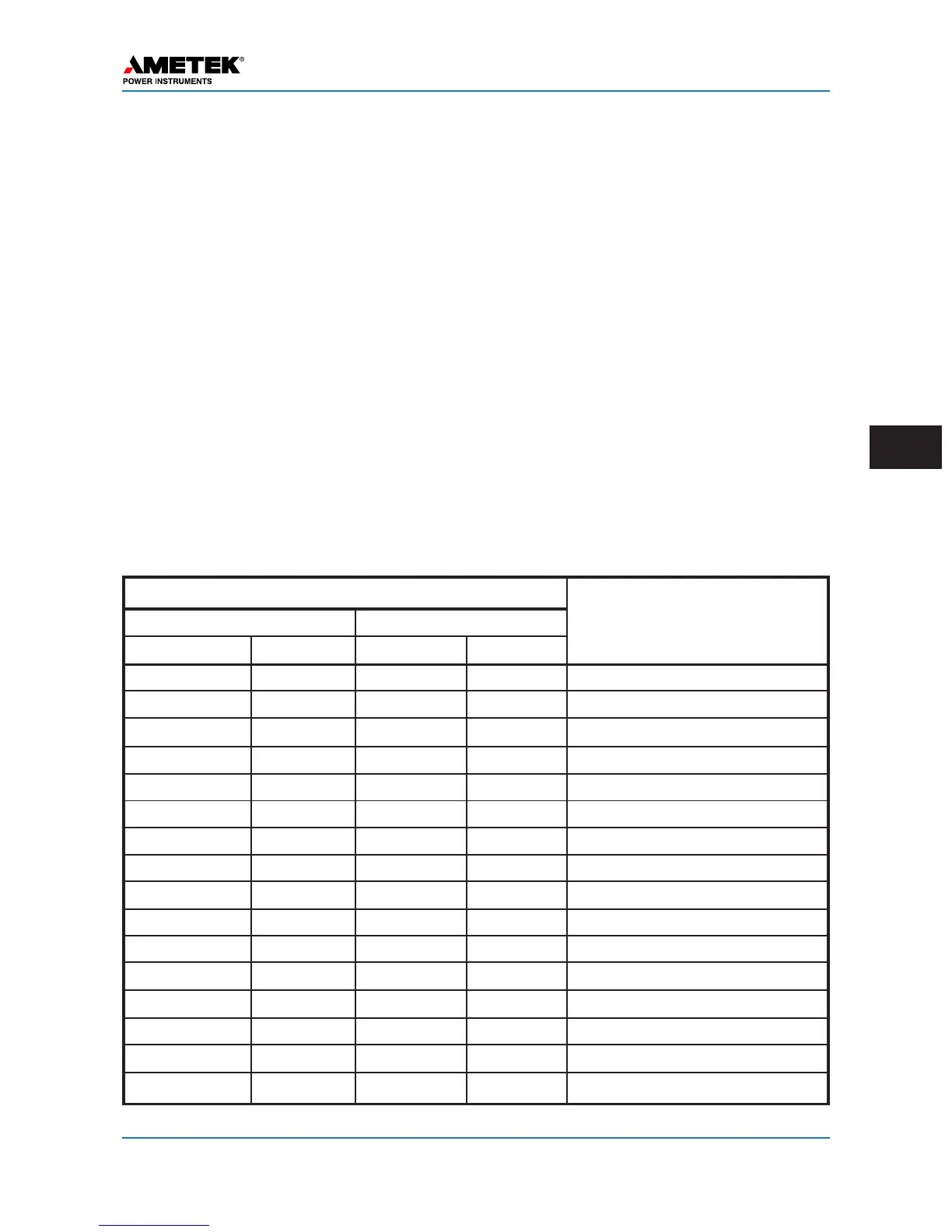
Table 6–3. System Troubleshooting
6.5 System Troubleshooting with
Checkback
You can identify and solve many checkback net-
work problems by examining the major and minor
alarms. If low power checkback tests are enabled in
addition to high power tests, the major and minor
alarms work like this:
• If a unit fails only the low power test, it sets
the minor alarm
• If a unit fails the high power test, it sets the
major alarm
• If a unit fails the high power test and can not
receive its own messages, it sets both major
and minor alarms
Armed with this information, you can usually iden-
tify a failed unit or line problem. The System
Troubleshooting table lists all combinations for a
two-unit system and the probable situation.
To get the complete picture, you must wait long
enough for all remotes to initiate their own check-
back tests. For example, if the master has a major
alarm, but the remote has no alarms, you can not
determine if it failed to receive the command due to
a bad line or because its receiver failed. By waiting
for the remote to initiate a checkback, you can tell
if it is the line (major alarm) or the unit (both
alarms). Some customers use a N.O. Major alarm
and a N.O. Minor alarm output in series to give a
“local” alarm so they can know which end of the
line has a problem. Both Major & Minor alarms
occurring on one UPLC-II™ means that this partic-
ular UPLC-II™ in the system is bad.
 Loading...
Loading...