UG-570 AD9361 Reference Manual
| Page 36 of 128
GAIN CONTROL THRESHOLD DETECTORS
The AD9361 uses detectors to determine if the received signal is
overloading a particular block or if the signal has dropped below
programmable thresholds. LMT and ADC overload detectors
(also referred to as peak detectors) react to nearly instantaneous
overload events. In contrast, a power measurement in the
AD9361 occurs over 16 or more Rx samples. Figure 18 shows
where these detectors are located in signal path.
LMT OVERLOAD DETECTOR
The LNA/mixer/transimpedance amplifier (LMT) overload
detector is an analog peak detector used to determine if the
received signal is overloading the blocks before the analog low-
pass filter. If an LMT overload occurs but the ADC does not
overload, it may indicate that an out-of-band interfering signal is
resulting in the overload condition.
There are two different LMT overload thresholds, one used to
indicate larger overloads and one used to indicate smaller
overloads. Both thresholds are programmable and are configured
in the ad9361_set_rx_gain_control_mode function. The small
threshold should be set such that it is lower than (or equal to)
the large threshold since the AGC will be affected differently
depending on which threshold is exceeded. In MGC mode, the
BBP can monitor the overload flags via the control output pins.
Equation 15 describes both large and small thresholds.
16mV
5:0 1
(15)
ADC OVERLOAD DETECTOR
The ADC is a highly oversampled sigma-delta modulator (SDM)
with an output ranging from +4 to −4. A particular ADC output
sample does not necessarily represent the input signal at a
particular time. Rather, a positive value indicates that the input
signal is more positive since the last sample and a negative value
indicates that the input signal is more negative since the last
sample. Note that since the ADC is highly oversampled, the ADC
clock is much faster than the receive sample rate. Decimating and
low-pass filtering result in digital samples that represent the
analog signal.
When the ADC is overloaded, the error between its samples and
the input signal will cause the ADC to output more samples with
values of +4 or −4 as it struggles to track the input signal.
Figure 20 shows how the ADC overload detector processes
signals and how the thresholds are used.
Figure 20. ADC Over Range Detection Algorithm
There are two programmable thresholds, both of which are
configured in the ad9361_set_rx_gain_control_mode function.
The thresholds are common to both receivers. The number of
samples to use in the sum-of-squares calculation is also set in the
ad9361_set_rx_gain_control_mode function. The resulting value,
z, shown in the Figure 20 is compared against the two thresholds
and if a particular threshold is exceeded, a flag is set. In MGC
mode, the BBP can monitor the overload flag(s) via the control
output pins.
LOW POWER THRESHOLD
The low power threshold is an absolute threshold measured in
−dBFS with a resolution of 0.5 dBFS per LSB. The range is from
0 dBFS to −63.5 dBFS. The value is programmed with the
ad9361_set_rx_gain_control_mode function. The AD9361 uses
this threshold in the fast attack AGC mode and it can also be used
in MGC mode, both of which are described later in the Fast
Attack AGC Mode section and MGC Overview section. In fast
attack AGC mode, the low power flag does not assert immediately
after the average signal power drops below the low power
threshold. The flag only asserts once the signal power has
remained below the low power Threshold for a time equal to the
increment time. The increment time value is measured in ClkRF
cycles (the clock used at the input of the receive FIR filter). In
MGC mode, the increment time value is not used and the low
power flag asserts as soon as the power drops below the low
power threshold.
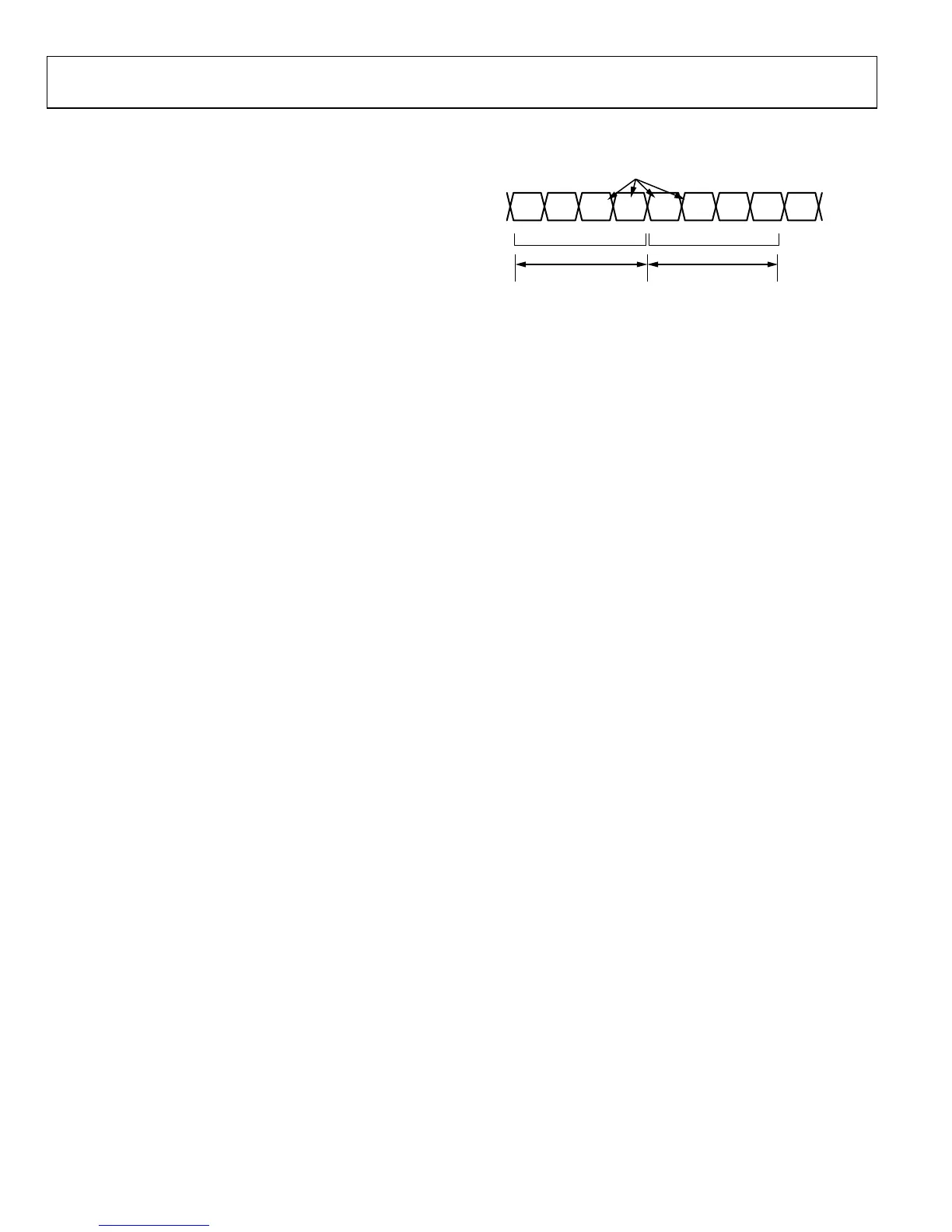
AVERAGE SIGNAL POWER
When measuring power (such as for low power threshold), the
measurement is an average of a certain number of samples set by
the decimated power measurement duration, which is set in the
ad9361_set_rx_gain_control_mode function. The duration is
common to both receivers. At the end of each measurement
period, the average signal power value updates. The actual
duration in Rx sample periods is per Equation 16.
abcdabcd
a
2
+ ++ +++
= z = z
DC SAMPLE VALUES
b
2
c
2
d
2
a
2
b
2
c
2
d
2
11668-021
 Loading...
Loading...