Balance System SD (with v4.X software) 125
Appendix A: Data Definitions and Interpretation
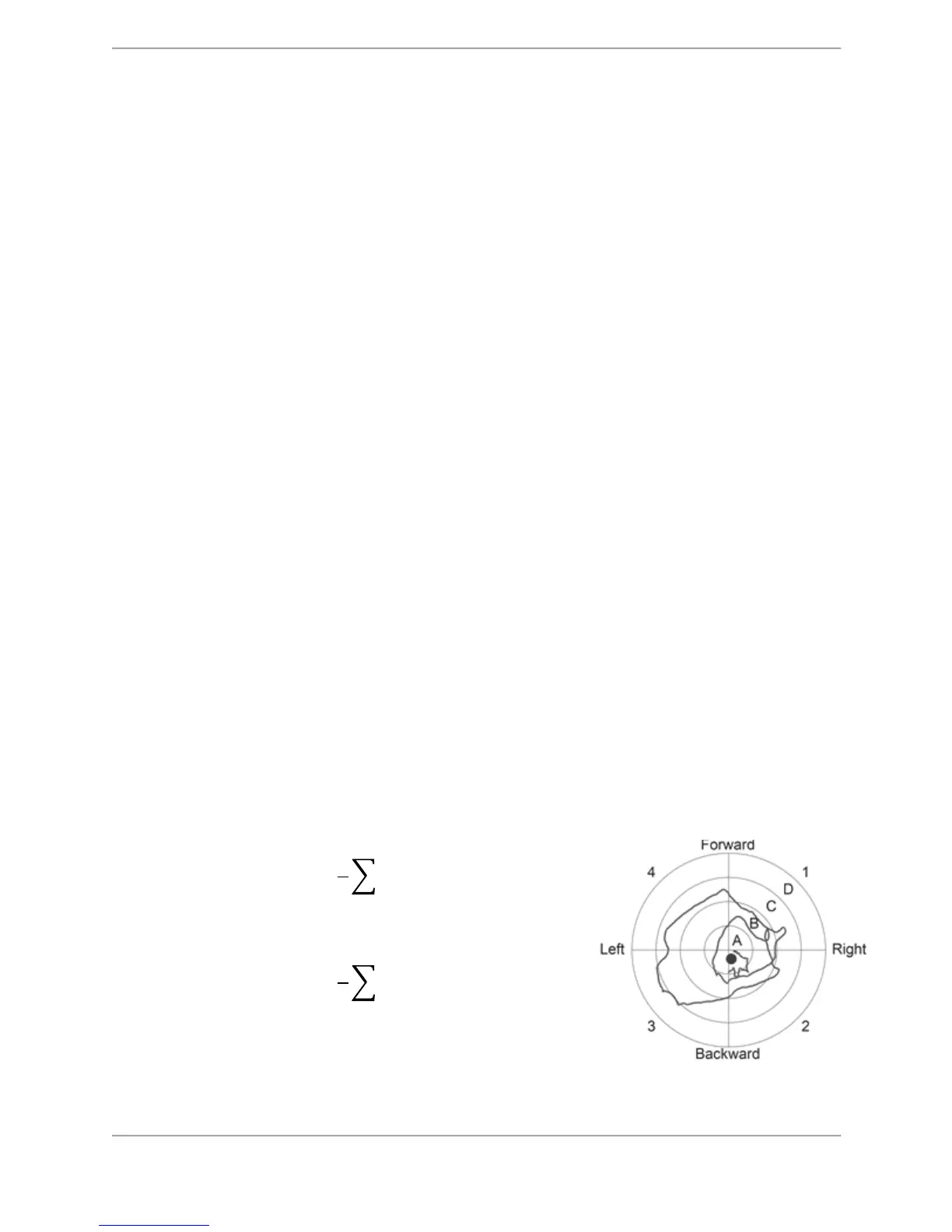
Calculation of Limits of Stability Direction Control
In this Appendix, the terms and metrics used in both training and testing protocols are defined.
Different tests within the Balance System SD use different scoring methods. It can be
summarized as follows:
1. Sway Index – CTSIB, BESS, Postural Stability, Bilateral Test.
2. Stability Index - Postural Stability Test.
3. Angle – Limit of Stability Test.
4. Direction Efficiency % - Motor Control Test.
5. Sway Velocity Index/ Z Score – Fall Risk Test.
Sway Index: Sway Index calculation is from a static measure, when information is collected by
positioning the patient on a static force plate and then sampling and recording patient
movement. The system employs a series of strain gauges to determine variation in the subject’s
resultant center of pressure (COP). The center of pressure is the patient’s center of gravity
projection on the platform resulting from sway angle and the patient height. Data is sampled at
the rate of 20Hz. Each recorded sample consists of a (X, Y) coordinates. What is displayed is the
sway angle derived from the position of the COG from zero and the height of the patients COG
taken as .55 times the patient height.
This data is recorded for later analysis and also displayed, in real time on, an LCD display
observable by the patient. The resultant movement results in a ‘spaghetti plot’ as shown below.
This plot indicates patient movement from one sample to the next.
Essentially, the database consists of an array of (X, Y) coordinates defining the calculated COP.
The data can be interpreted as an ordered series of sequential vectors from point to point.
The Score, or Sway Index, is the Root Mean Squared distance (RMS distance) of the X,Y
coordinates.
For a 2D position represented by X,Y, the calculation would be:
For the mean position X:
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!!!
For the mean position Y:
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!!!
!
 Loading...
Loading...