44 Biodex Medical Systems, Inc. © 2017
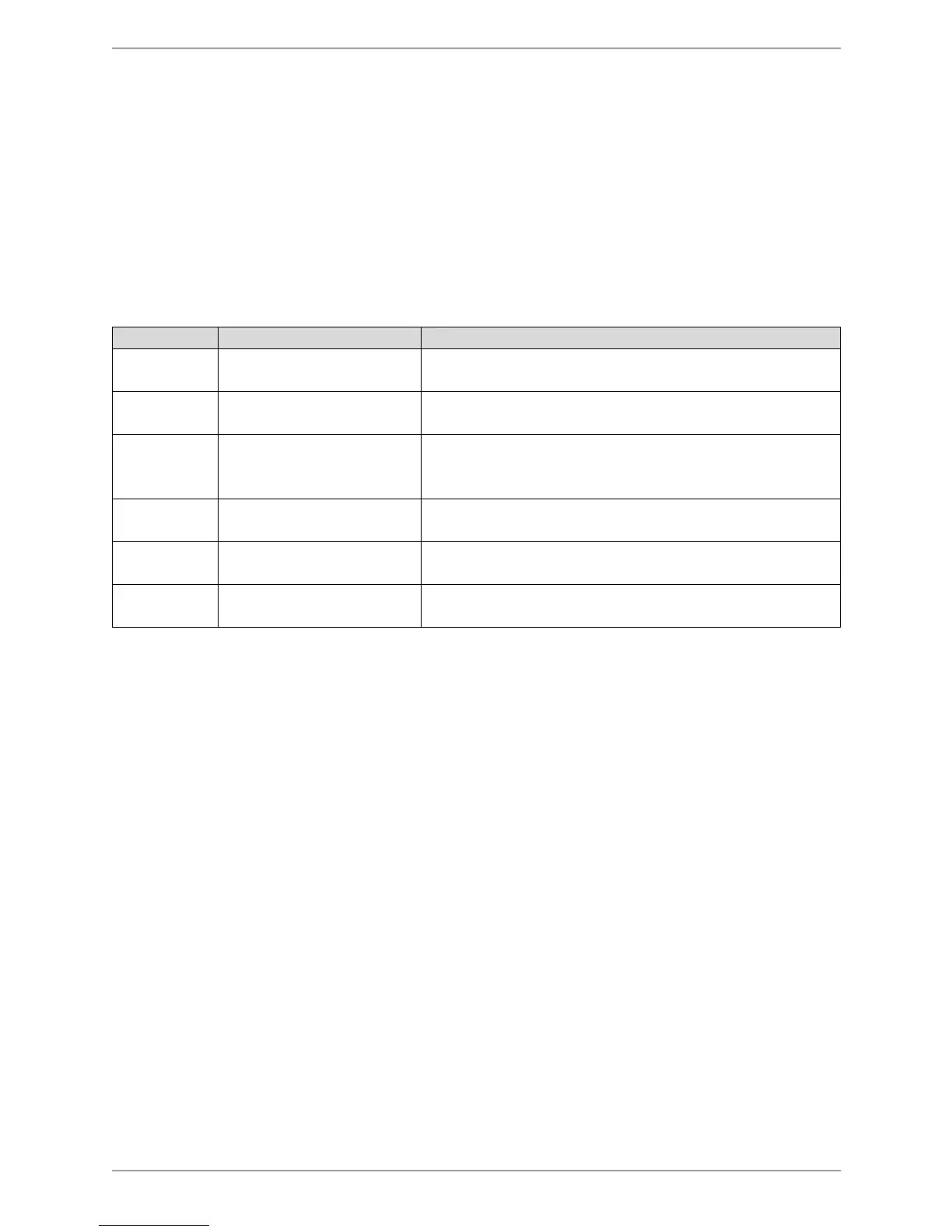
Table 7.1 Clinical Test of Sensory Interaction and Balance (CTSIB).
Clinical Test of Sensory Integration and Balance – CTSIB or m-
CTSIB (Modified CTSIB)
The Clinical Test of Sensory Interaction and Balance (CTSIB) is a standardized test for balance
assessment on a static surface. The CTSIB test protocol is well documented as an effective test
for identifying individuals with mild to severe balance problems. The test provides a
generalized assessment of how well a patient can integrate various sensory conditions during a
balance test. The test accounts for how well the patient compensates when one or more of
those sensory conditions are compromised. The CTSIB consists of six conditions:
Incorporates visual, vestibular and somatosensory
inputs. This is considered the baseline condition.
2 Eyes closed/firm surface Eliminates visual input to evaluate vestibular and
somatosensory inputs.
3 Visual conflict/firm
surface
Some vision input present but information conflicts
with vestibular information. This condition relies on
more vestibular and somatosensory inputs.
4 Eyes open/dynamic
surface
Used to evaluate somatosensory interaction with
visual input.
surface
Used to evaluate somatosensory interaction with
vestibular input.
surface
Used to evaluate the mediation of visual with and
vestibular and somatosensory inputs.
Another version of this test, called the modified CTSIB, or m-CTSIB, is often used. The m-CTSIB
eliminates conditions 3 and 6. Biodex Balance products use the m-CTSIB format of four
conditions (#’s 1, 2, 4, and 5) as the default with the option to include the other two if desired.
A Note Concerning Eye Glasses for the Visual Conflict Condition:
Clinicians who want to perform the Visual Conflict conditions will require some type of glasses
that provide a distorted yet transparent image. Commercially available prism type glasses are
commonly used. Other improvised glasses are: 3D glasses, or clear safety glasses in which the
lenses have been marred or covered with Scotch™ type tape.
The CTSIB test measures a patient’s Sway Index. (See Appendix A for more details.)
The Sway Index is a way of calculating the mean absolute deviation of the patient’s average
position during a test. The higher the Sway Index, the more unsteady the person was during the
test. The Sway Index is an objective quantification of what commonly is performed with a time-
based pass/fail for completing the CTSIB stage in 30 seconds without falling or assigning a
value of 1 to 4 to characterize the sway; 1= minimal sway, 4 = a fall.
If a patient cannot complete a condition, it is noted as DNC (Did Not Complete) on the results
screen and report. Specific information on Stability index can be found in the Appendix.
NOTE: A standardized indexed foam pad that matches the size of the Balance System SD
platform is provided. The foam pad should be used for the dynamic (foam) surface conditions in
the CTSIB test.

 Loading...
Loading...