20-5
Catalyst 2960 and 2960-S Switches Software Configuration Guide, Release 15.0(1)SE
OL-26520-01
Chapter 20 Configuring DHCP and IP Source Guard Features
Understanding DHCP Snooping
In the port field of the circuit-ID suboption, the port numbers start at 3. For example, on a switch with
24 10/100 ports and small form-factor pluggable (SFP) module slots, port 3 is the Fast Ethernet x/0/1
port, port 4 is the Fast Ethernet x/0/2 port, and so forth, where x is the stack member number. Port 27 is
the SFP module slot 0/1, and so forth.
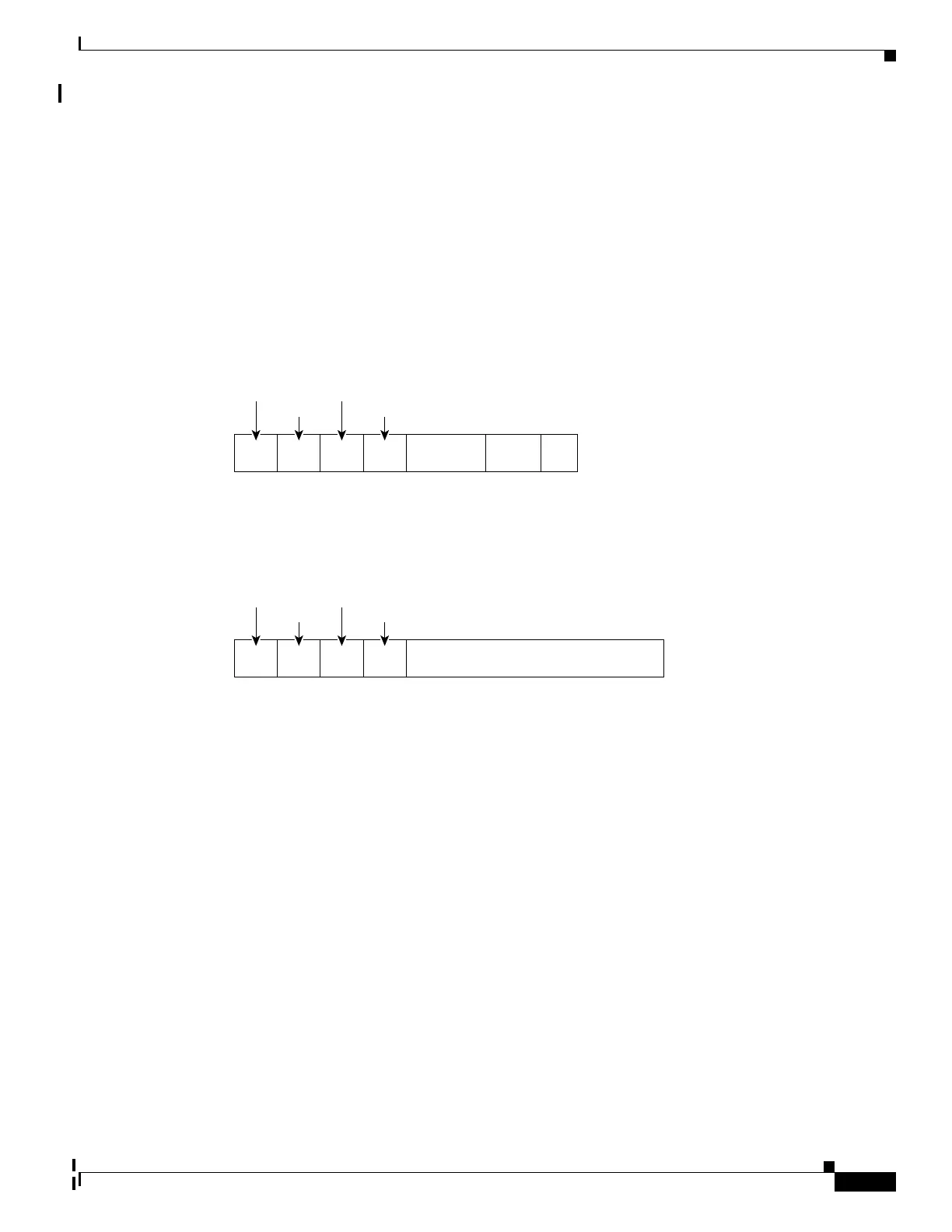
Figure 20-2 shows the packet formats for the remote-ID suboption and the circuit-ID suboption. For the
circuit-ID suboption, the module number corresponds to the switch number in the stack. The switch uses
the packet formats when you globally enable DHCP snooping and enter the ip dhcp snooping
information option global configuration command.
Figure 20-2 Suboption Packet Formats
Figure 20-3 shows the packet formats for user-configured remote-ID and circuit-ID suboptions The
switch uses these packet formats when DHCP snooping is globally enabled and when the ip dhcp
snooping information option format remote-id global configuration command and the ip dhcp
snooping vlan information option format-type circuit-id string interface configuration command are
entered.
The values for these fields in the packets change from the default values when you configure the
remote-ID and circuit-ID suboptions:
• Circuit-ID suboption fields
–
The circuit-ID type is 1.
–
The length values are variable, depending on the length of the string that you configure.
• Remote-ID suboption fields
–
The remote-ID type is 1.
–
The length values are variable, depending on the length of the string that you configure.
Length Length
Circuit
ID type
Suboption
type
Circuit ID Suboption Frame Format
Remote ID Suboption Frame Format
6 bytes
MAC address
1 byte 1 byte 1 byte
Suboption
type
1 byte
Length Length
Remote
ID type
1 byte 1 byte 1 byte1 byte
116300
4061
6082
Module Port
1 byte 1 byte2 bytes
VLAN
 Loading...
Loading...
















