2-18
Cisco ONS 15310-MA SDH Troubleshooting Guide, Release 9.0
78-18663-01
Chapter 2 Alarm Troubleshooting
Safety Summary
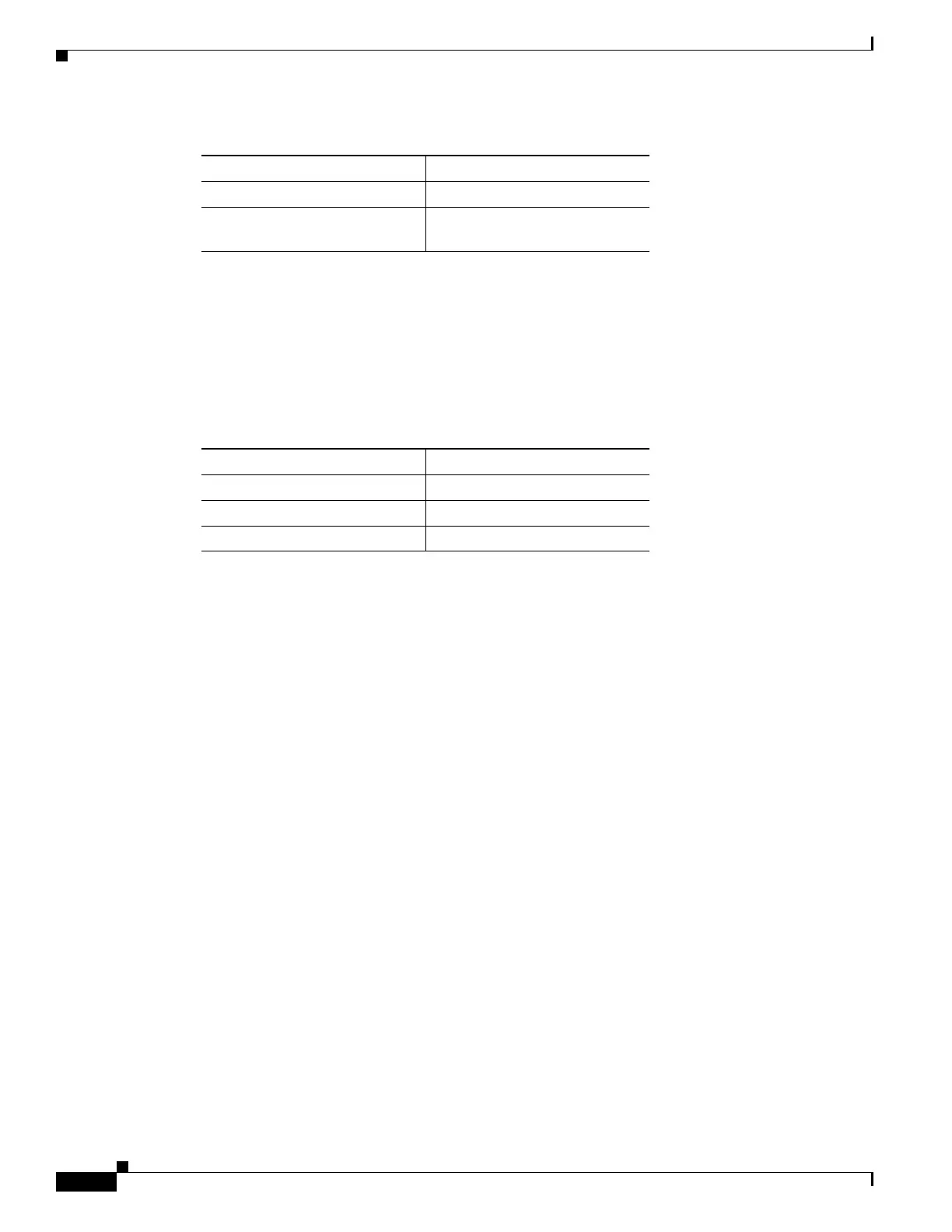
The far-end failure alarm hierarchy is shown in Table 2-12, as given in Telcordia GR-253-CORE.
2.5.5 Service Effect
Service-Affecting (SA) alarms—those that interrupt service—could be Critical (CR), Major (MJ), or
Minor (MN) severity alarms. Service-Affecting (SA) alarms indicate service is affected.
Non-Service-Affecting (NSA) alarms always have a Minor (MN) default severity.
2.5.6 States
The State column on the Alarms or History tabs indicates the disposition of the alarm or condition as
follows:
• A raised (R) event is one that is active.
• A cleared (C) event is one that is no longer active.
• A transient (T) event is one that is automatically raised and cleared in CTC during system changes
such as user login, logout, loss of connection to node view, etc. Transient events do not require user
action. These are listed in Chapter 3, “Transient Conditions.”
2.6 Safety Summary
This section provides safety considerations designed to ensure safe operation of the
ONS 15310-MA SDH. Do not perform any procedures in this chapter unless you understand all safety
precautions, practices, and warnings for the system equipment. Some troubleshooting procedures
require installation or removal of cards; in these instances pay close attention to the following cautions
and warnings.
— HP-PLM
Lowest DS-N AIS (if reported for
outgoing DS-N signals)
1. Although it is not defined as a defect or failure, all-ones VC pointer relay is also
higher priority than AU-LOP. Similarly, all-ones VC pointer relay is higher
priority than TU-LOP.
2. AU-LOP is also higher priority than the far-end failure HP-RFI, which does not
affect the detection of any near-end failures. Similarly, TU-LOP is higher priority
than LP-RFI.
Table 2-11 Near-End Alarm Hierarchy
Priority Condition Type
Table 2-12 Far-End Alarm Hierarchy
Priority Condition Type
Highest MS-RFI
—HP-RFI
Lowest LP-RFI

 Loading...
Loading...