DGS-3100 Series Gigabit Stackable Managed Switch User Manual
Defining ARP Spoofing Prevention Settings
Classic Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a TCP/IP protocol that translates IP addresses into MAC addresses.
ARP Spoofing Prevention eliminates man-in-the-middle attacks, where false ARP packets are inserted into the subnet. ARP
requests and responses are inspected, and their MAC Address to IP Address binding is checked. Packets with invalid ARP
Spoofing Prevention Bindings are logged and dropped. If the incoming packet's source IP address is not one of the gateways
defined in the ARP Spoofing prevention database, the packet is forwarded.
The Arp Spoofing Prevention Page provides parameters for enabling and setting global ARP Spoofing Prevention
param
e
ters, as well as defining ARP Spoofing Prevention Log parameters. Up to 240 entries can be defined.
To define ARP Spoofing Prevention:
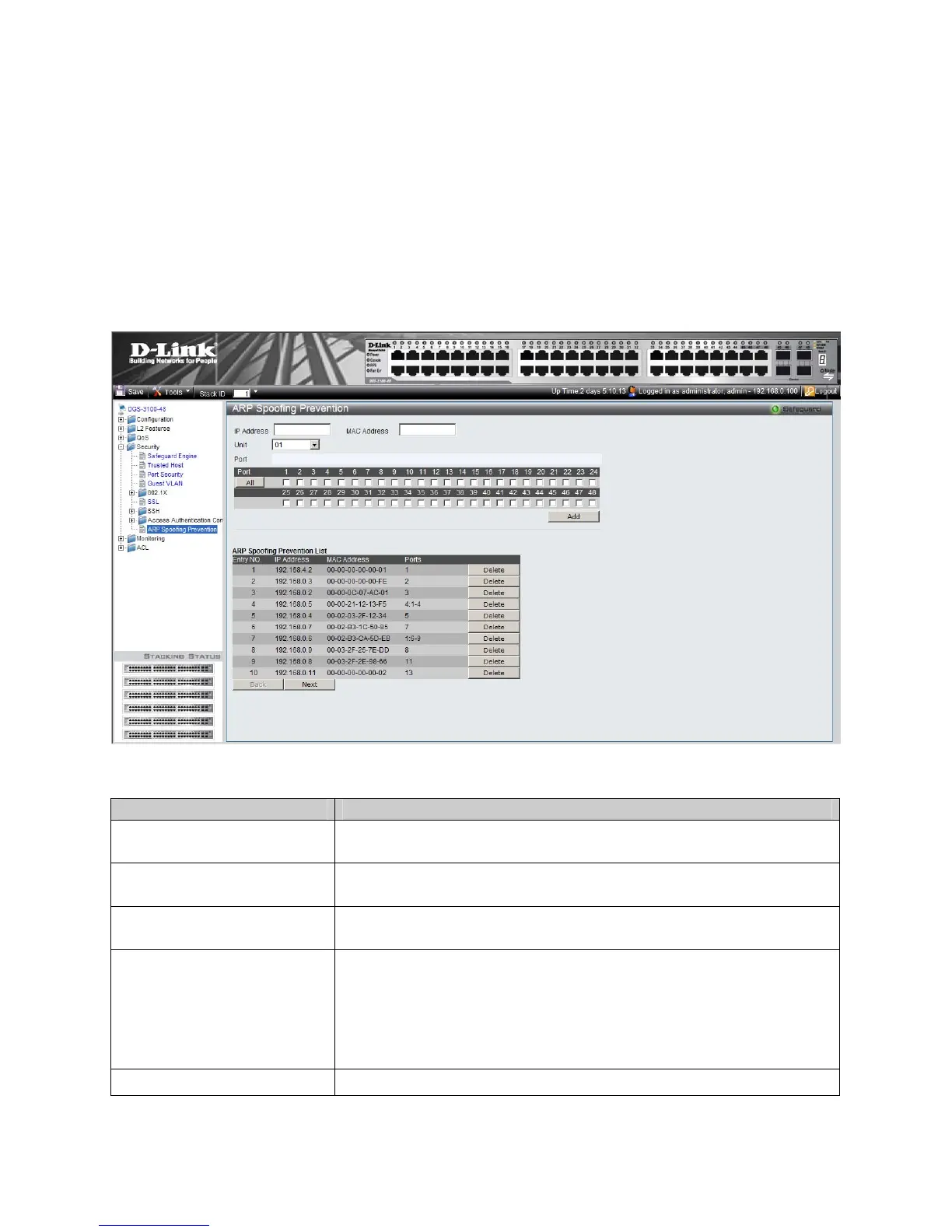
1. Click Security > Arp Spoofing Prevention. The Arp Spoofing Prevention Page opens:
Figure 5-16 Arp Spoofing Prevention Page
The Arp Spoofing Prevention Page contains the following fields
Field Description
IP Address
Specifies IP addresses included in ARP Binding Lists that are checked against
ARP requests.
MAC address
Specifies MAC addresses included in ARP Binding Lists that are checked against
ARP requests.
Unit
Displays the stacking member for which the ARP Spoofing Prevention is
displayed.
Port
Defines the Port Settings Mode. The possible field values are:
Checked Ports — Indicates that a packet received on the port needs to be
checked for a match with the ARP Spoofing Prevention database.
Unchecked Ports — Indicates that the port is not selected for ARP
Spoofing (trusted port). ARP packets that are received on unchecked
interfaces are forwarded.
Port
Specifies IP addresses included in ARP Binding Lists that are checked against
169

 Loading...
Loading...











