xStack
®
DGS-3400 Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Managed Switch
112
forwarded to the port for transmission, the port will add an 802.1Q tag using the PVID to write the
VID in the tag. When the packet arrives at its destination, the receiving device will use the PVID to
make VLAN forwarding decisions. If the port receives a packet, and Ingress filtering is enabled, the
port will compare the VID of the incoming packet to its PVID. If the two are unequal, the port will
drop the packet. If the two are equal, the port will receive the packet.
Double VLANs
Double or Q-in-Q VLANs allow network providers to expand their VLAN configurations to place customer VLANs within a
larger inclusive VLAN, which adds a new layer to the VLAN configuration. This lets large ISP's create L2 Virtual Private
Networks and also create transparent LANs for their customers, which will connect two or more customer LAN points without
over-complicating configurations on the client's side. Not only will over-complication be avoided, but also now the administrator
has over 4000 VLANs in which over 4000 VLANs can be placed, therefore greatly expanding the VLAN network and enabling
greater support of customers utilizing multiple VLANs on the network.
Double VLANs are basically VLAN tags placed within existing IEEE 802.1Q VLANs which we will call SPVIDs (Service
Provider VLAN IDs). These VLANs are marked by a TPID (Tagged Protocol ID), configured in hex form to be encapsulated
within the VLAN tag of the packet. This identifies the packet as double-tagged and segregates it from other VLANs on the
network, therefore creating a hierarchy of VLANs within a single packet.
Here is an example Double VLAN tagged packet.
Destination Address Source Address SPVLAN (TPID +
Service Provider
VLAN Tag)
802.1Q CEVLAN Tag
(TPID + Customer VLAN
Tag)
Ether Type Payload
Consider the example below:
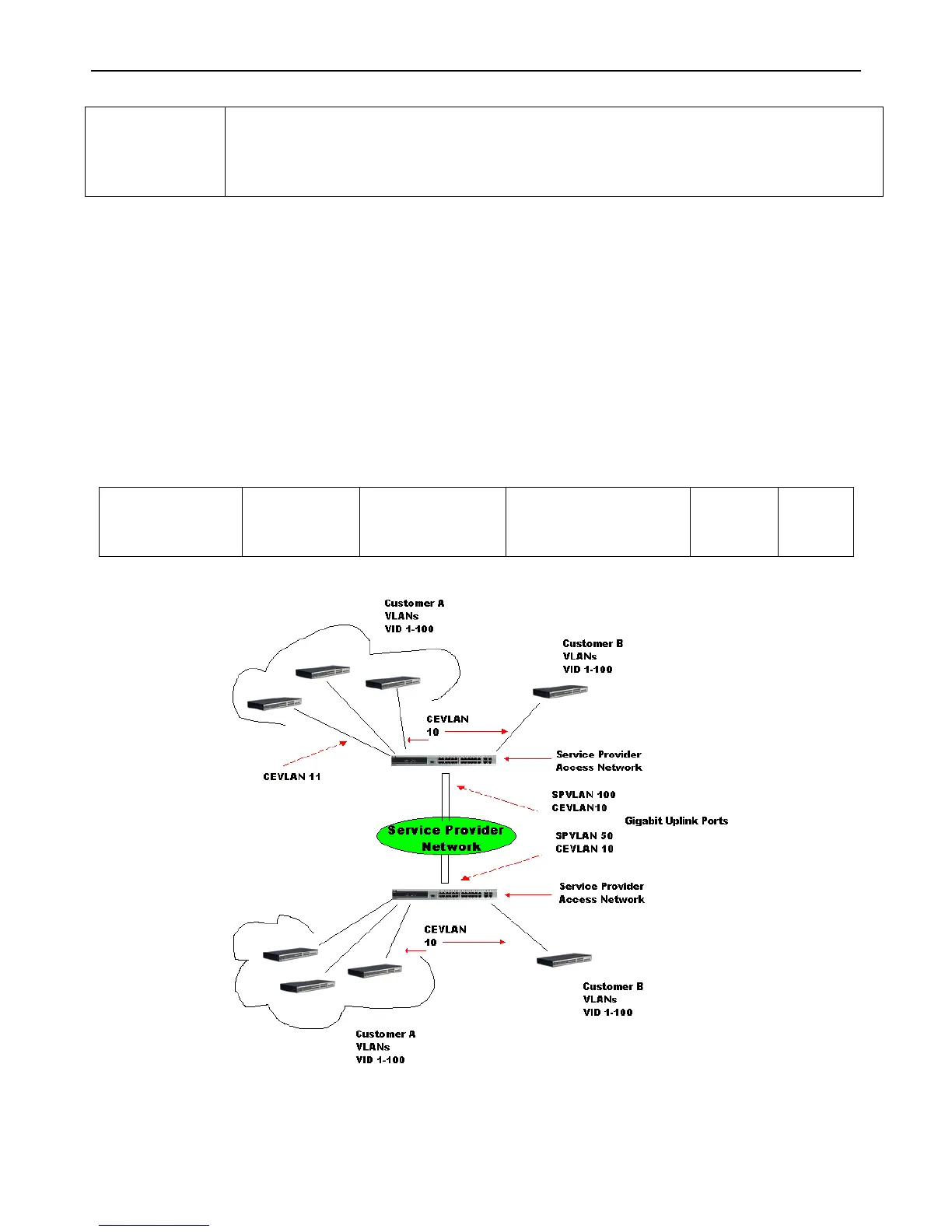
Figure 3 - 8 Double VLAN Example
In this example, the Service Provider Access Network switch (Provider edge switch) is the device creating and configuring
Double VLANs. Both CEVLANs (Customer VLANs) 10 and 11, are tagged with the SPVID 100 on the Service Provider Access
 Loading...
Loading...











