xStack
®
DGS-3400 Series Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Managed Switch
201
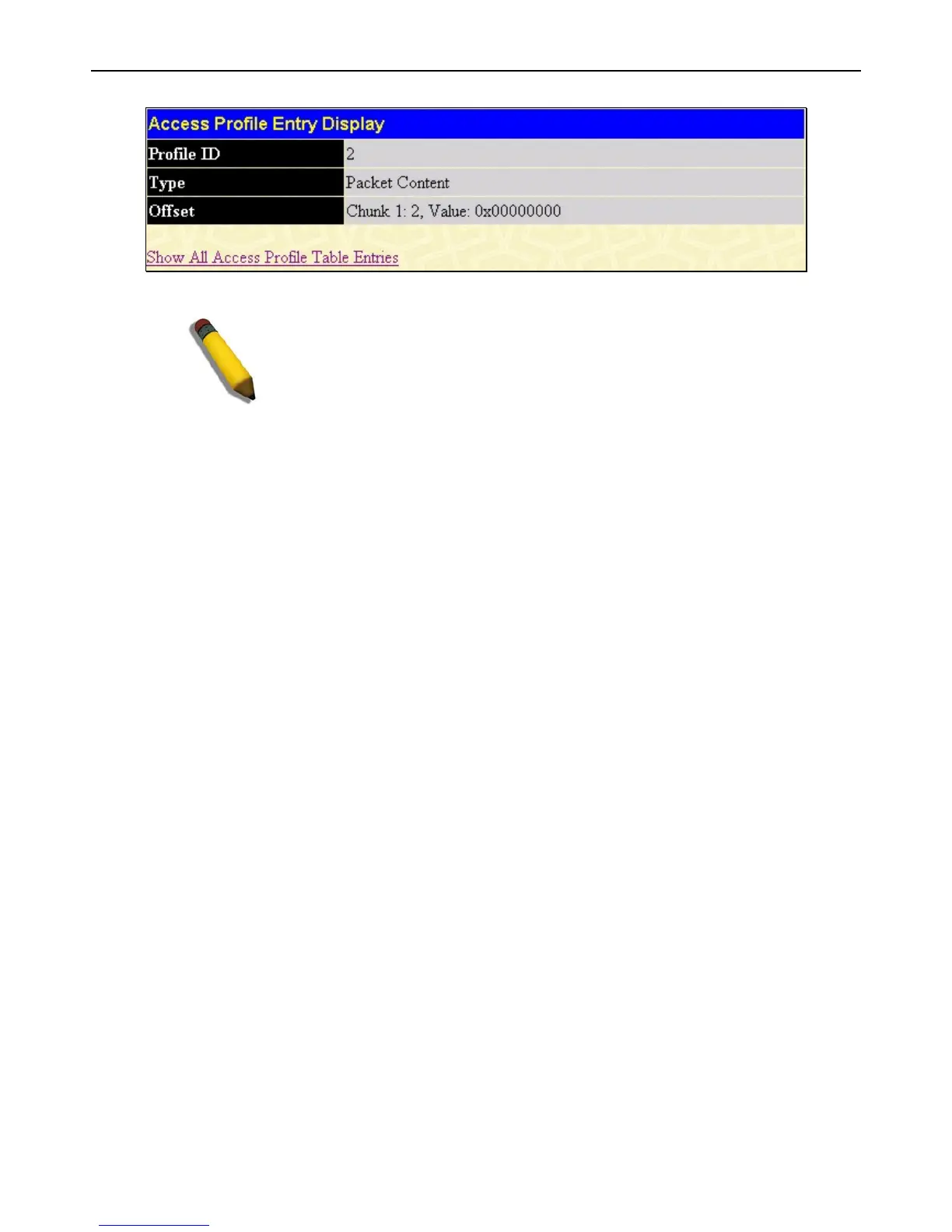
Figure 5 - 22 Access Profile Entry Display window (Packet Content Mask)
NOTE: When using the ACL Mirror function, ensure that the Port Mirroring
function is enabled and a target mirror port is set.
ACL Flow Meter
Before configuring the ACL Flow Meter, here is a list of acronyms and terms users will need to know.
trTCM – Two Rate Three Color Marker. This, along with the srTCM, are two methods available on the switch for
metering and marking packet flow. The trTCM meters and IP flow and marks it as a color based on the flow’s
surpassing of two rates, the CIR and the PIR.
CIR – Committed Information Rate. Common to both the trTCM and the srTCM, the CIR is measured in bytes
of IP packets. IP packet bytes are measured by taking the size of the IP header but not the link specific
headers. For the trTCM, the packet flow is marked green if it doesn’t exceed the CIR and yellow if it does. The
configured rate of the CIR must not exceed that of the PIR. The CIR can also be configured for unexpected
packet bursts using the CBS and PBS fields.
CBS – Committed Burst Size. Measured in bytes, the CBS is associated with the CIR and is used to identify
packets that exceed the normal boundaries of packet size. The CBS should be configured to accept the
biggest IP packet that is expected in the IP flow.
PIR – Peak Information Rate. This rate is measured in bytes of IP packets. IP packet bytes are measured by
taking the size of the IP header but not the link specific headers. If the packet flow exceeds the PIR, that
packet flow is marked red. The PIR must be configured to be equal or more than that of the CIR.
PBS – Peak Burst Size. Measured in bytes, the PBS is associated with the PIR and is used to identify packets
that exceed the normal boundaries of packet size. The PBS should be configured to accept the biggest IP
packet that is expected in the IP flow.
srTCM – Single Rate Three Color Marker. This, along with the trTCM, are two methods available on the switch for
metering and marking packet flow. The srTCM marks its IP packet flow based on the configured CBS and EBS. A
packet flow that does not reach the CBS is marked green, if it exceeds the CBS but not the EBS its marked yellow,
and if it exceeds the EBS its marked red.
CBS – Committed Burst Size. Measured in bytes, the CBS is associated with the CIR and is used to identify
packets that exceed the normal boundaries of packet size. The CBS should be configured to accept the
biggest IP packet that is expected in the IP flow.
EBS – Excess Burst Size. Measured in bytes, the EBS is associated with the CIR and is used to identify
packets that exceed the boundaries of the CBS packet size. The EBS is to be configured for an equal or
larger rate than the CBS.
DSCP – Differentiated Services Code Point. The part of the packet header where the color will be added. Users may
change the DSCP field of incoming packets.
The ACL Flow Meter function will allow users to color code IP packet flows based on the rate of incoming packets.
Users have two types of Flow metering to choose from, trTCM and srTCM, as explained previously. When a packet
flow is placed in a color code, the user can choose what to do with packets that have exceeded that color-coded rate.
 Loading...
Loading...











