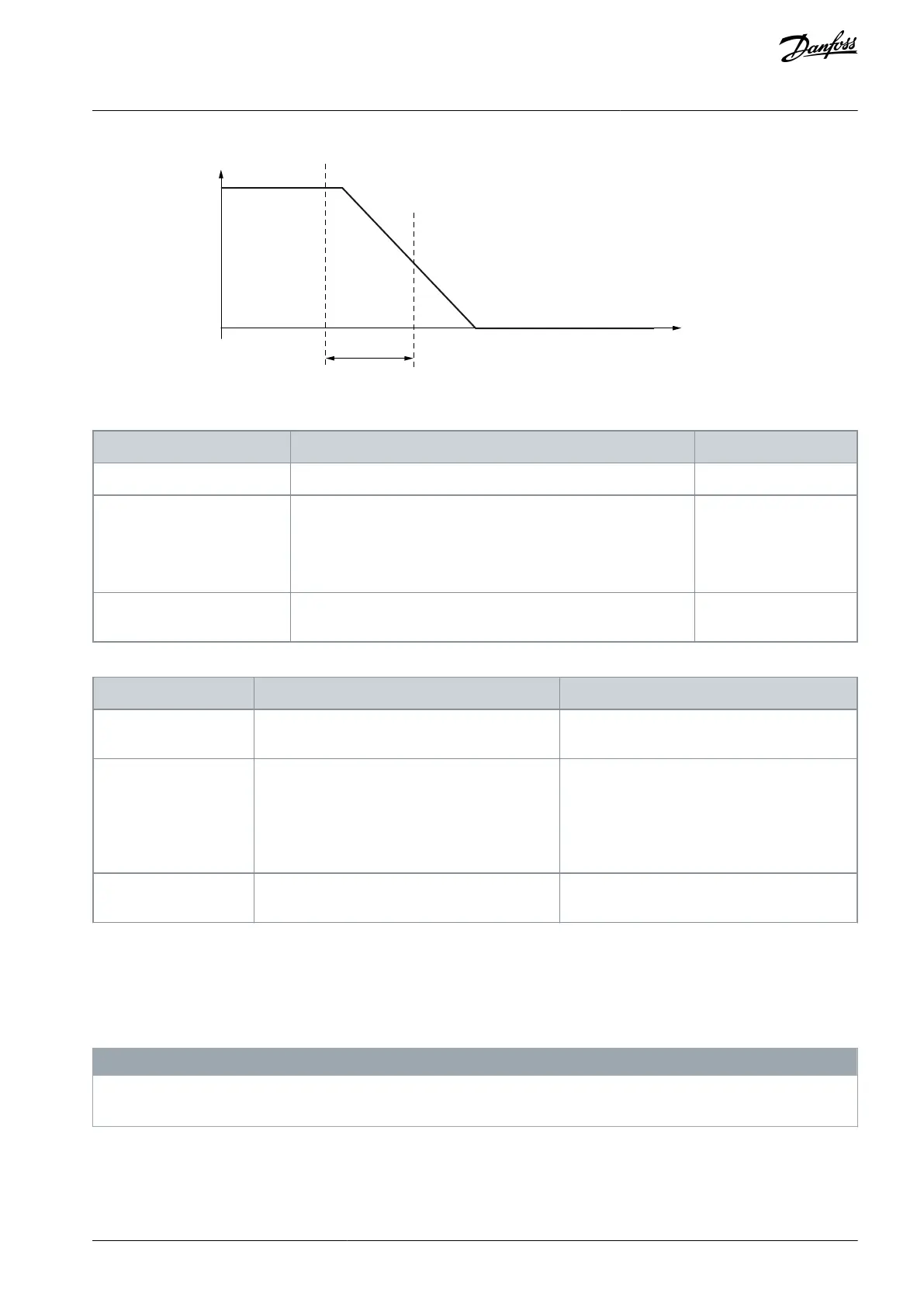
Speed
STO
SBC
SBC t1
t
e30bi389.10
Illustration 31: STO Behaviour with SBC Order = STO First
Table 29: The Behavior of the STO and SBC Functions when SBC Order = STO First
STO at the request. SBC delayed by SBC t1 compared to STO.
The SS1 or SQS-SS1 safety
function
Time monitoring: STO after SQS t1 or SS1 t1.
Zero speed monitoring: STO when speed below zero speed and
SQS td2 or SS1 td2 expires.
SBC delayed by SBC t1 compared to STO.
Violation of SS1, SS2, or SQS or
resettable fault
STO at the fault moment. SBC delayed by SBC t1 compared to STO.
Table 30: The Behavior of the STO and SBC Functions when SBC Order = SBC First
SBC at the request. STO delayed by SBC t1 com-
pared to SBC.
SBC at the request, STO delayed by SBC t1 com-
pared to SBC.
The SS1 or SQS-SS1 safe-
ty function
Time monitoring: SBC after SQS t1 or SS1 t1.
Zero speed monitoring: SBC when speed below
Zero Speed and SQS td2 or SS1 td2 expires.
STO always delayed by SBC t1 compared to SBC.
Time monitoring: SBC after SQS t1/SS1 t1 or
when speed below SBC Speed.
Zero speed monitoring: SBC when speed below
SBC Speed.
STO delayed by SBC t1 compared to SBC.
Violation of SS1, SS2, or
SQS or resettable fault
STO and SBC at the fault moment. SBC t1 not
used.
STO and SBC at the fault moment. SBC t1 not
used.
After acknowledgment or reset, the STO and the SBC functions are deactivated at the same time. Other brake controlling systems
can be used to make sure that sufficient torque has been generated to the motor shaft before the brake is released.
6.2.2.4 The STO and SBC Signals
It is possible that the Active and Reached signals that are mentioned in this chapter are not always available in all interfaces.
N O T I C E
The availability of the signals over safe fieldbus depends on the fieldbus protocol that you use. Refer to chapter Safe fieldbuses
for more information.
AQ319736045637en-000101 / DPD01798 | 69Danfoss A/S © 2021.06
Safety Functions
VACON® NXP Advanced Safety Options
Operating Guide

 Loading...
Loading...











