Chapter 2 Specifications
PAGE 2-5
2-4-2. Fastening Method
(1) Torque Method (Angle Monitor)
Fastening is performed up to a preset standard torque.
The fastening operation is performed with the preset torque as the target, and high limit/low limit
judgment of the angle value is enabled.
The number of fastenings steps is selectable among 1 step, 2 steps, and 3 steps.
(2) Angle Method (Torque Monitor)
Fastening is performed up to a preset standard angle.
The fastening operation is performed with the preset angle as the target, and high limit/low limit
judgment of the torque value is enabled.
Generally when a handheld tool is used, the angular precision may vary according to the state in
which the tool is held during fastening. Use in combination with the reaction force receiver jig etc.,
is recommended.
The number of fastenings steps is selectable among 1 step, 2 steps, and 3 steps.
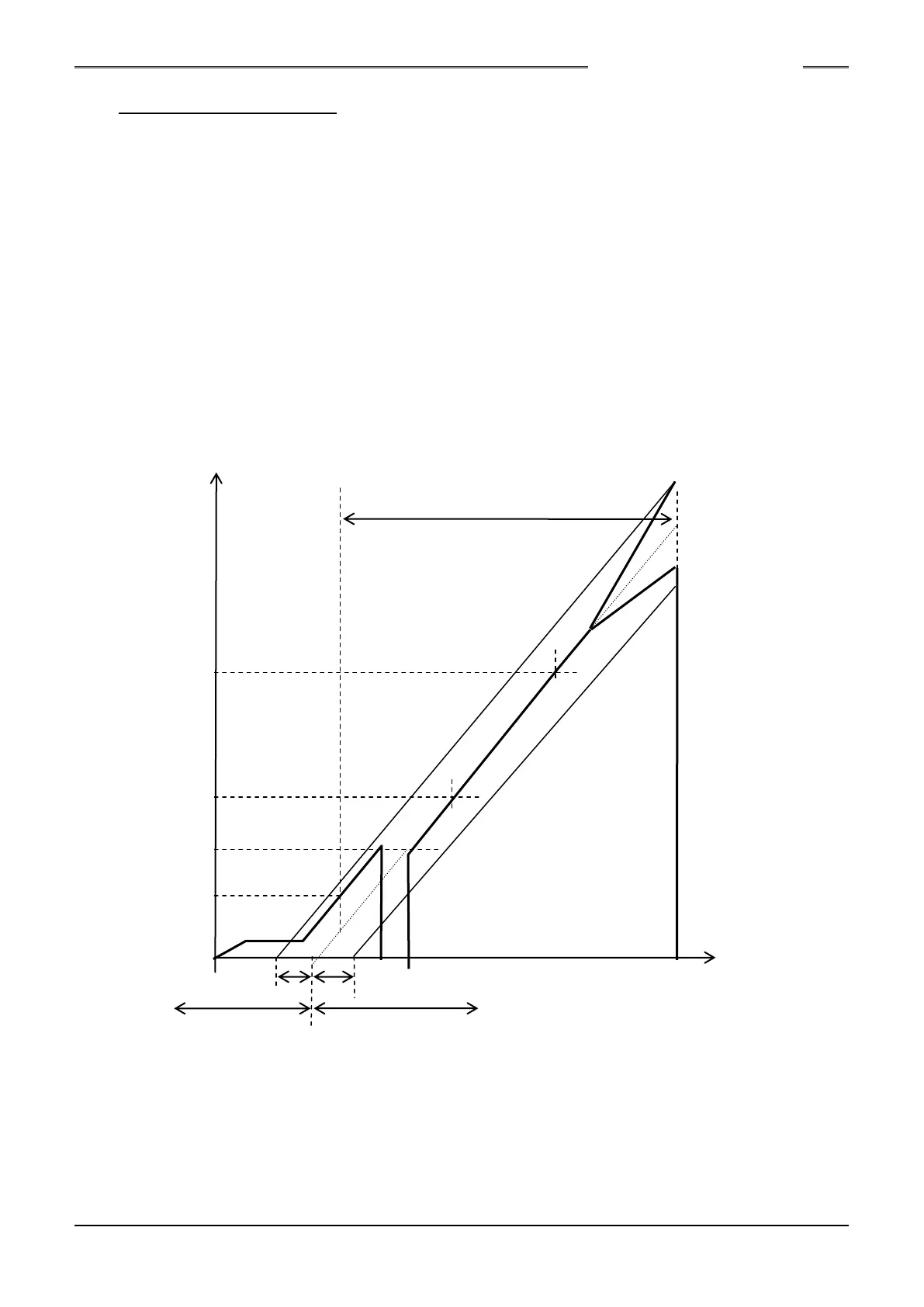
(3) Differential Angle Check Method
Torque
Standard Angle
Rate 2 End Torque
Rate 2 Start Torque
1st Torque
Snug Torque
Differential Angle (fastening result) Angle
Differential Low Limit (-) Angle Differential High Limit (+) Angle
Seating point calculated from the value of rate 2
Fastening is performed from the Snug torque (angle measurement start torque) to the standard
angle value (or the standard torque value).
After completion of fastening, the seating point is calculated from the value of rate 2.
The differential angle is then calculated from the final torque value and the value of rate 2, and
judgment is performed if differential angle check is available.
The rate 2 is calculated from the rate 2 start torque and the rate 2 end torque.
S0140185-H
 Loading...
Loading...