EW50 Industrial LTE Cellular Gateway
230
6.1.3 SNMP
SNMP, the Simple Network Management Protocol, is a protocol designed to give a user the capability to
remotely manage a computer network by polling and setting terminal values and monitoring network events.
In typical SNMP uses, one or more administrative computers, called managers, have the task of monitoring or
managing a group of hosts or devices on a computer network. Each managed system executes, at all times, a
software component called an agent which reports information via SNMP to the manager.
SNMP agents deliver management data to the managed systems as variables. The protocol also permits active
management tasks, such as modifying and applying a new configuration through remote modification of these
variables. The variables accessible via SNMP are organized in hierarchies. These hierarchies, and other
metadata (such as type and description of the variable), are described by Management Information Bases
(MIBs).
The device supports several public MIBs and one private MIB for the SNMP agent. The supported MIBs are as
follow: MIB-II (RFC 1213, Include IPv6), IF-MIB, IP-MIB, TCP-MIB, UDP-MIB, SMIv1 and SMIv2,
SNMPv2-TM and SNMPv2-MIB, and AMIB (ETHERWAN Private MIB)
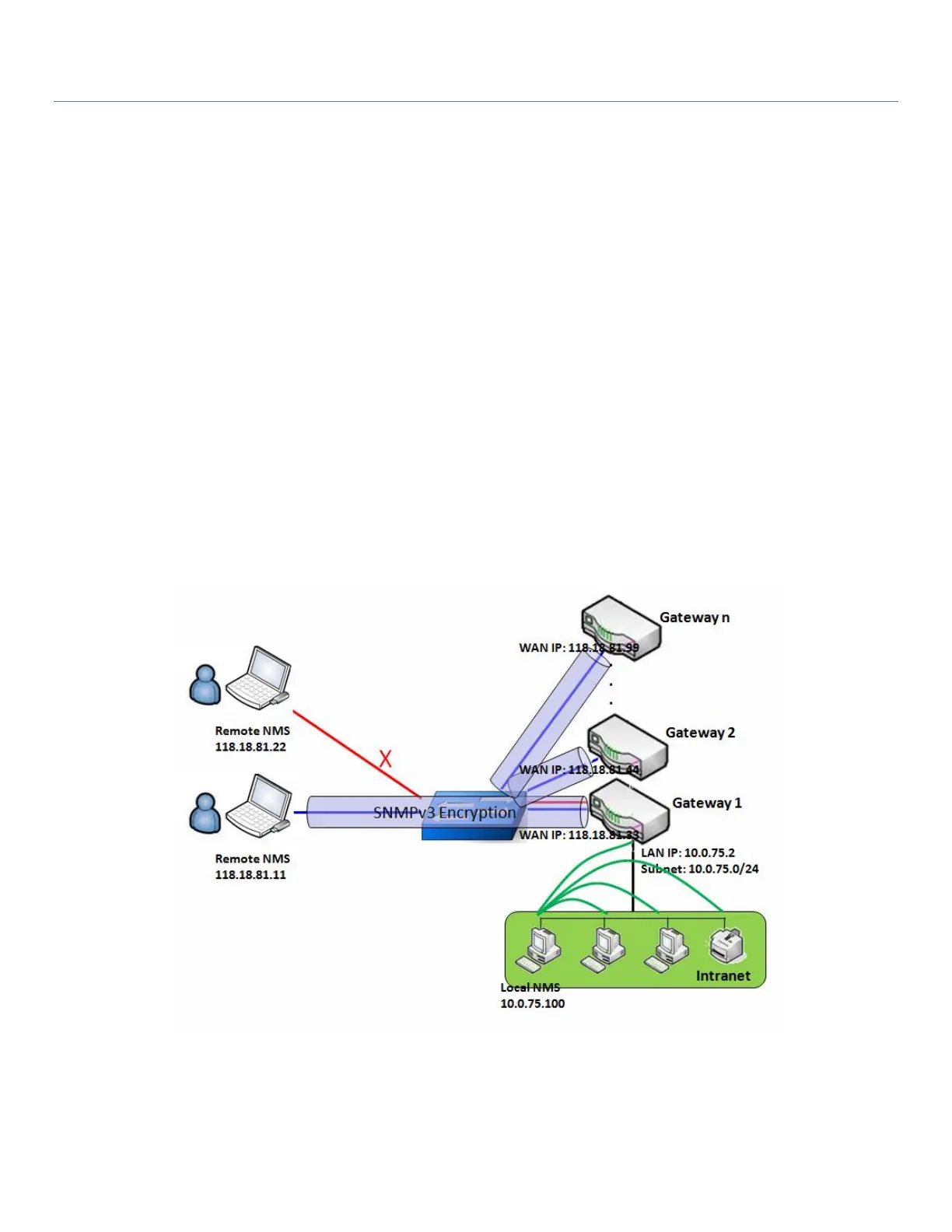
SNMP Management Scenario
There are two application scenarios for SNMP Network Management Systems (NMS). Local NMS is
in the Intranet and manages all devices that support SNMP. Another is using Remote NMS to
manage devices whose WAN interfaces are connected together by a switch or a router with UDP
forwarding.
 Loading...
Loading...