EW50 Industrial LTE Cellular Gateway
202
5.1.5 GRE
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) is a tunneling protocol developed by Cisco Systems that encapsulates a
wide variety of network layer protocols inside virtual point-to-point links over an Internet Protocol
internetwork.
Deploy an M2M gateway for a remote site and establish a virtual private network with control center by using
GRE tunneling. Then, all client hosts behind M2M gateway can make data communication with server hosts
behind control center gateway.
GRE Tunneling is similar to IPsec Tunneling, with the client requesting the tunnel establishment with the
server. Both the client and the server must have a Static IP or a FQDN. Any peer gateway can be worked as
either a client or a server, even using the same set of configuration rules.
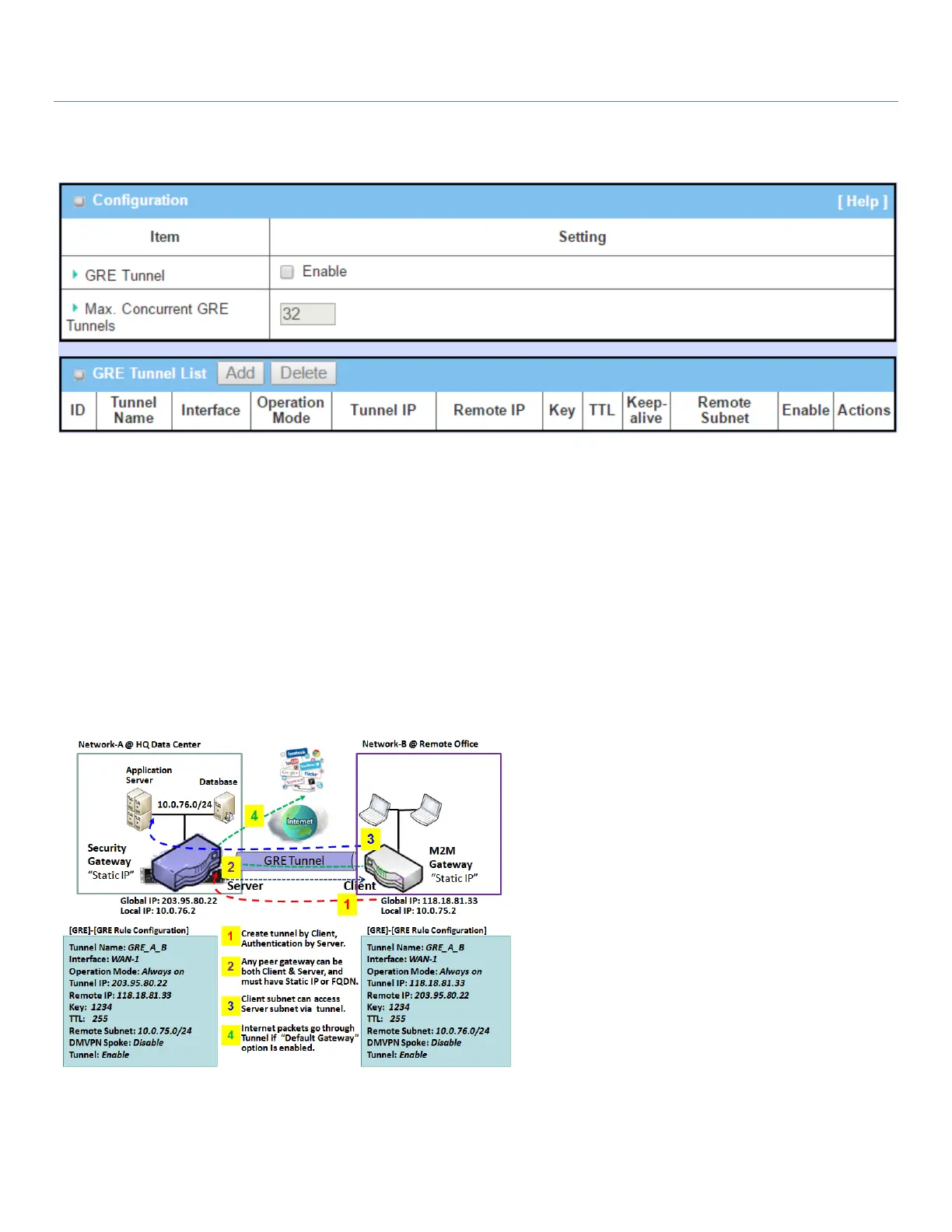
GRE Tunnel Scenario
To setup a GRE tunnel, each peer needs to
setup its global IP as tunnel IP and enter the
other's global IP as remote IP.
Each peer must further specify the Remote
Subnet item for the Intranet of GRE server peer.
At GRE client peer, the packets whose
destination is in the dedicated subnet will be
transferred via the GRE tunnel. Others will be
transferred based on current routing policy of
the gateway at GRE client peer. But, if 0.0.0.0/0
is entered in the Remote Subnet field, it will be
treated as a "Default Gateway" setting for the
GRE client peer, and all packets, including the
Internet accessing of GRE client peers, will go
through the established GRE tunnel. That
means the remote GRE server peer controls the flow of any packets from the GRE client peer.
If the GRE server supports DMVPN Hub function, like Cisco router as the VPN concentrator, the GRE client can
 Loading...
Loading...