1
Spanning tree protocol overview
Spanning tree protocols eliminate loops in a physical link-redundant network by selectively blocking
redundant links and putting them in a standby state.
The recent versions of STP include the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP), the Per-VLAN
Spanning Tree (PVST), and the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP).
About STP
STP was developed based on the 802.1d standard of IEEE to eliminate loops at the data link layer in
a LAN. Networks often have redundant links as backups in case of failures, but loops are a very
serious problem. Devices running STP detect loops in the network by exchanging information with
one another. They eliminate loops by selectively blocking certain ports to prune the loop structure
into a loop-free tree structure. This avoids proliferation and infinite cycling of packets that would
occur in a loop network.
In a narrow sense, STP refers to IEEE 802.1d STP. In a broad sense, STP refers to the IEEE 802.1d
STP and various enhanced spanning tree protocols derived from that protocol.
STP protocol frames
STP uses bridge protocol data units (BPDUs), also known as configuration messages, as its protocol
frames. This chapter uses BPDUs to represent all types of spanning tree protocol frames.
STP-enabled devices exchange BPDUs to establish a spanning tree. BPDUs contain sufficient
information for the devices to complete spanning tree calculation.
STP uses two types of BPDUs, configuration BPDUs and topology change notification (TCN)
BPDUs.
Configuration BPDUs
Devices exchange configuration BPDUs to elect the root bridge and determine port roles. Figure 1
shows the configuration BPDU format.
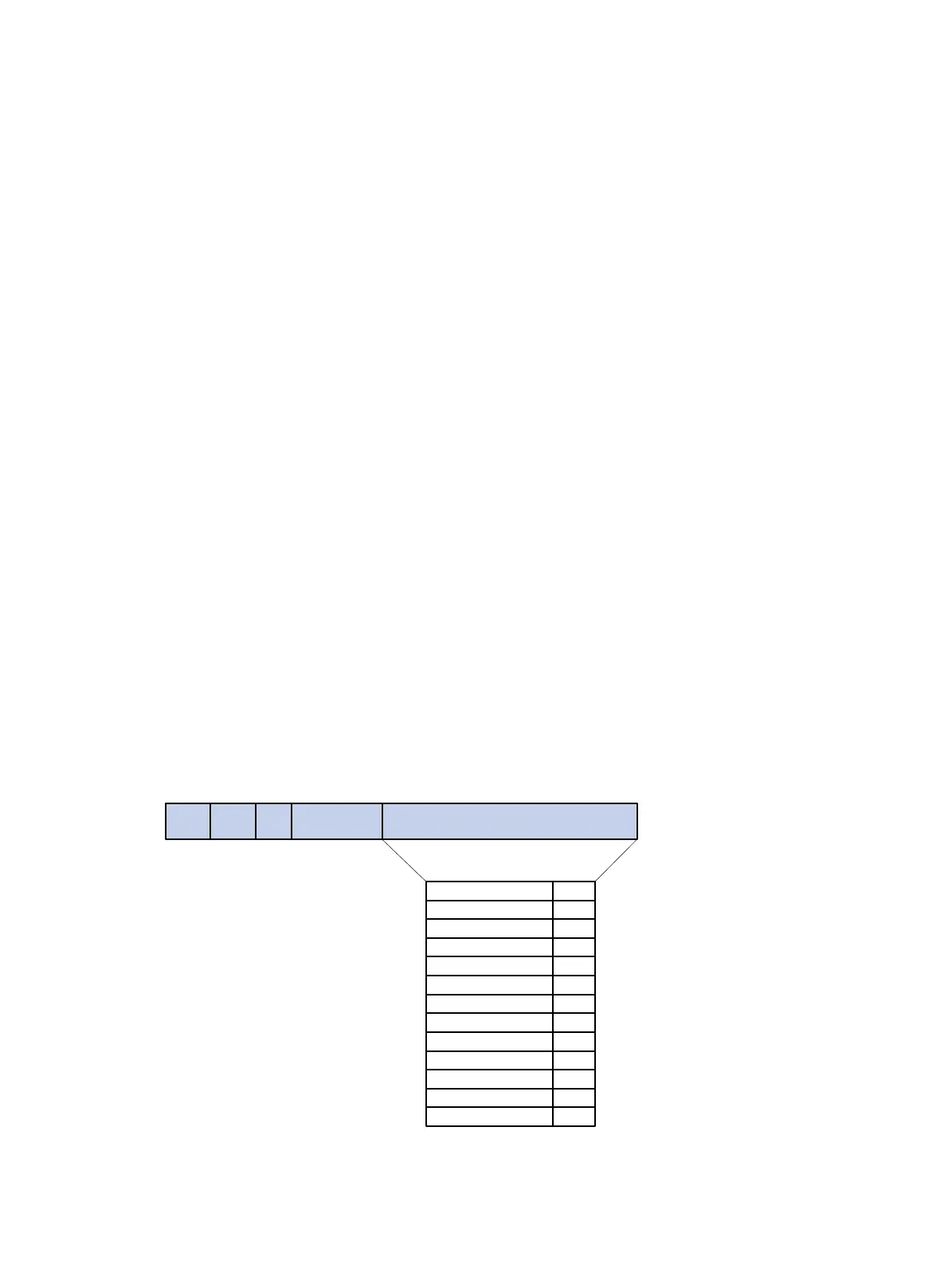
Figure 1 Configuration BPDU format
The payload of a configuration BPDU includes the following fields:
SMA L/T LLC header Payload
Protocol ID
Protocol version ID
BPDU type
Flags
Root ID
Root path cost
Message age
Max age
Hello time
Forward delay
2
1
1
1
8
4
2
2
2
2
Bridge ID 8
Port ID 2
DMA
Fields Byte
DMA: Destination MAC address
SMA: Source MAC address
L/T: Frame length
LLC header: Logical link control header
Payload: BPDU data

 Loading...
Loading...