4
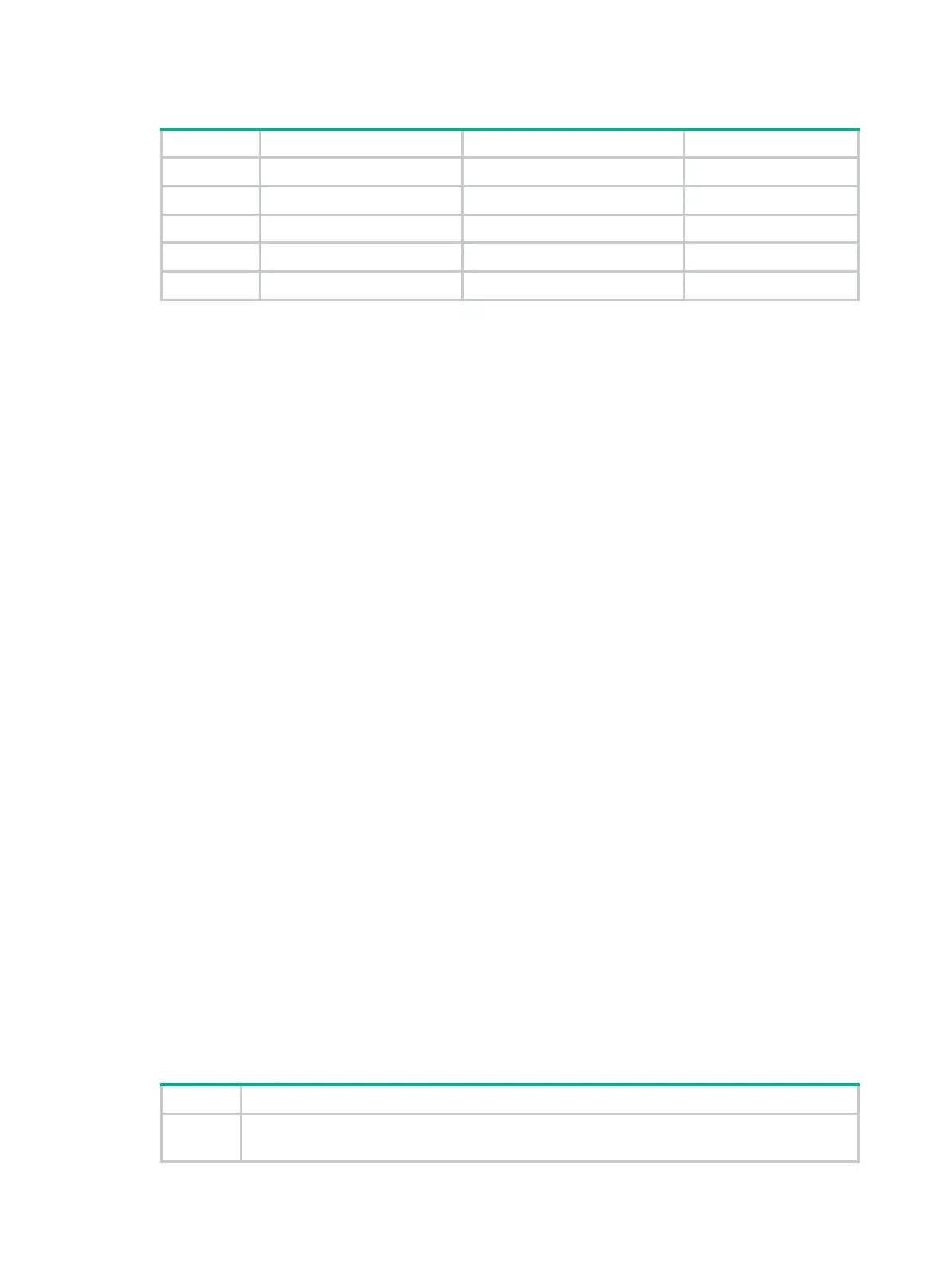
Table 1 STP port states
State Receives/sends BPDUs Learns MAC addresses Forwards user data
Disabled No No No
Listening Yes No No
Learning Yes Yes No
Forwarding Yes Yes Yes
Blocking Receive No No
Path cost
Path cost is a reference value used for link selection in STP. To prune the network into a loop-free
tree, STP calculates path costs to select the most robust links and block redundant links that are less
robust.
Calculation process of the STP algorithm
In STP calculation, a device compares the priorities of the received configuration BPDUs from
different ports, and elects the root bridge, root ports and designated ports. When the spanning tree
calculation is completed, a tree-shape topology forms.
The spanning tree calculation process described in the following sections is an example of a
simplified process.
Network initialization
Upon initialization of a device, each port generates a BPDU with the following contents:
• The port as the designated port.
• The device as the root bridge.
• 0 as the root path cost.
• The device ID as the designated bridge ID.
Root bridge selection
The root bridge can be selected in the following methods:
• Automatic election—Initially, each STP-enabled device on the network assumes itself to be
the root bridge, with its own device ID as the root bridge ID. By exchanging configuration
BPDUs, the devices compare their root bridge IDs to elect the device with the smallest root
bridge ID as the root bridge.
• Manual assignment—You can configure a device as the root bridge or a secondary root bridge
of a spanning tree.
{ A spanning tree can have only one root bridge. If you configure multiple devices as the root
bridge for a spanning tree, the device with the lowest MAC address is selected.
{ You can configure one or multiple secondary root bridges for a spanning tree. When the root
bridge fails or is shut down, a secondary root bridge can take over. If multiple secondary root
bridges are configured, the one with the lowest MAC address is selected. However, if a new
root bridge is configured, the secondary root bridge is not selected.
Root port and designated ports selection on the non-root bridges
Step Description
1
A non-root-bridge device regards the port on which it received the optimum configuration BPDU
as the root port. Table 2 descr
ibes how the optimum configuration BPDU is selected.

 Loading...
Loading...