11
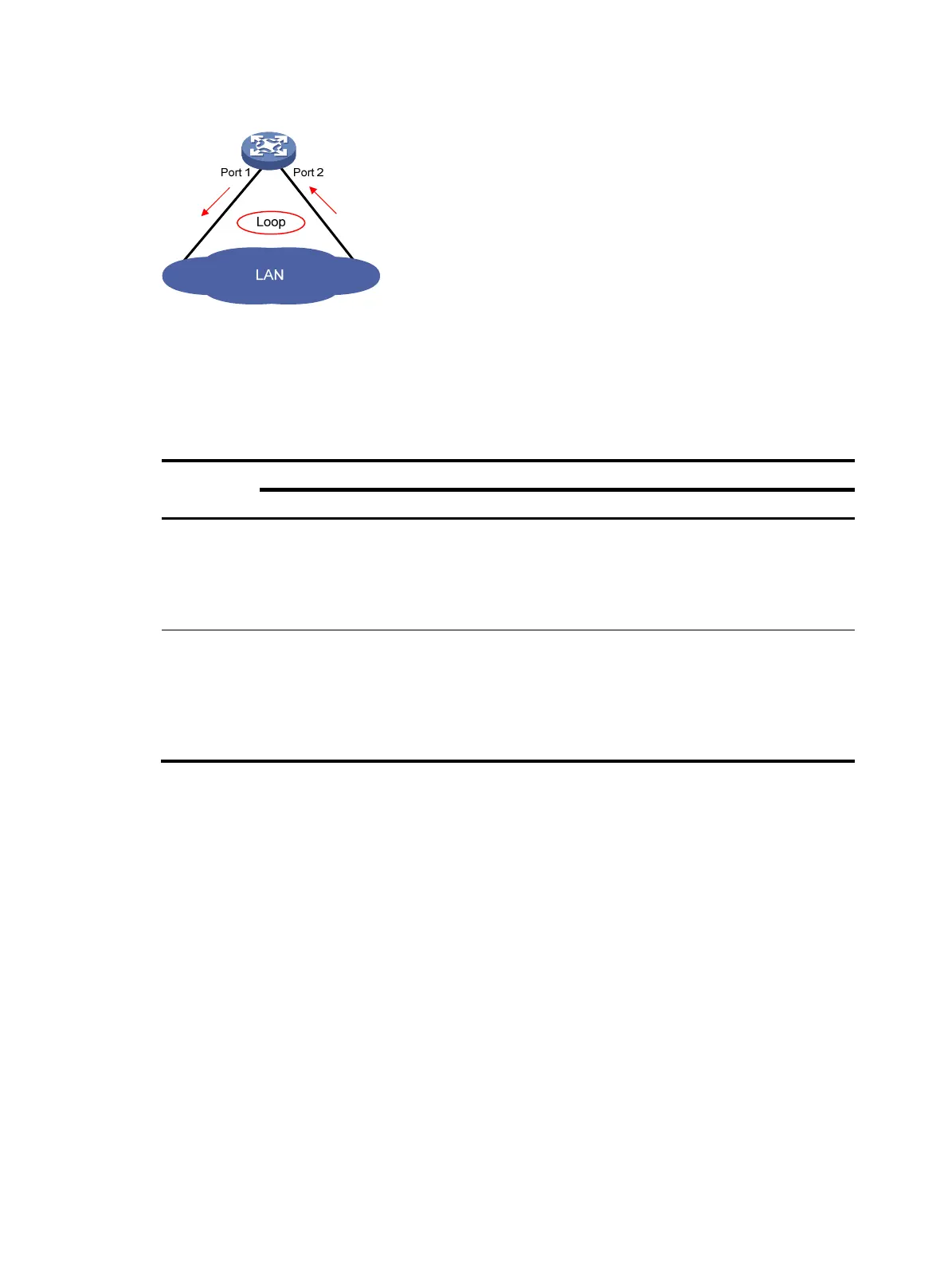
Figure 4 Multi-port loop
You can enable loopback detection to detect loops on an interface and, if the interface supports the
loopback-detection action command, configure the protective action to take on the receiving interface
when a loop is detected, for example, to shut down the interface. Depending on whether a protective
action is configured, the switch takes the actions in Table 1 to
alleviate the impact of the loop condition.
Table 1 Actions to take upon detection of a loop condition
Port type
Actions
No
rotective action is confi
ured
A
rotective action is confi
ured
Access port
• Place the receiving interface in controlled mode.
The interface drops the incoming packets and
correctly sends packets.
• Generate traps and log messages.
• Delete all MAC address entries of the interface.
• Perform the configured protective
action.
• Generate traps and log messages.
• Delete all MAC address entries of the
interface.
Hybrid or
trunk port
• Generate traps and log messages.
• If loopback detection control is enabled, place
the receiving interface in controlled mode. The
interface does not receive or send packets.
• Delete all MAC address entries of the interface.
• Generate traps and log messages.
• If loopback detection control is
enabled, take the configured
protective action on the interface.
• Delete all MAC address entries of the
interface.
Configuration restrictions and guidelines
• To use loopback detection on an Ethernet interface, you must enable the function both globally and
on the interface.
• When the multi-port loopback detection function is enabled, the function can also detect single-port
loops.
• To disable loopback detection on all interfaces, run the undo loopback-detection enable command
in system view.
• To enable a hybrid or trunk port to take the administratively specified protective action, you must use
the loopback-detection control enable command on the port.
• When you change the link type of an Ethernet interface by using the port link-type command, the
switch removes the protective action configured on the interface. For more information about the
port link-type command, see Layer 2—LAN Switching Command Reference.

 Loading...
Loading...











