4
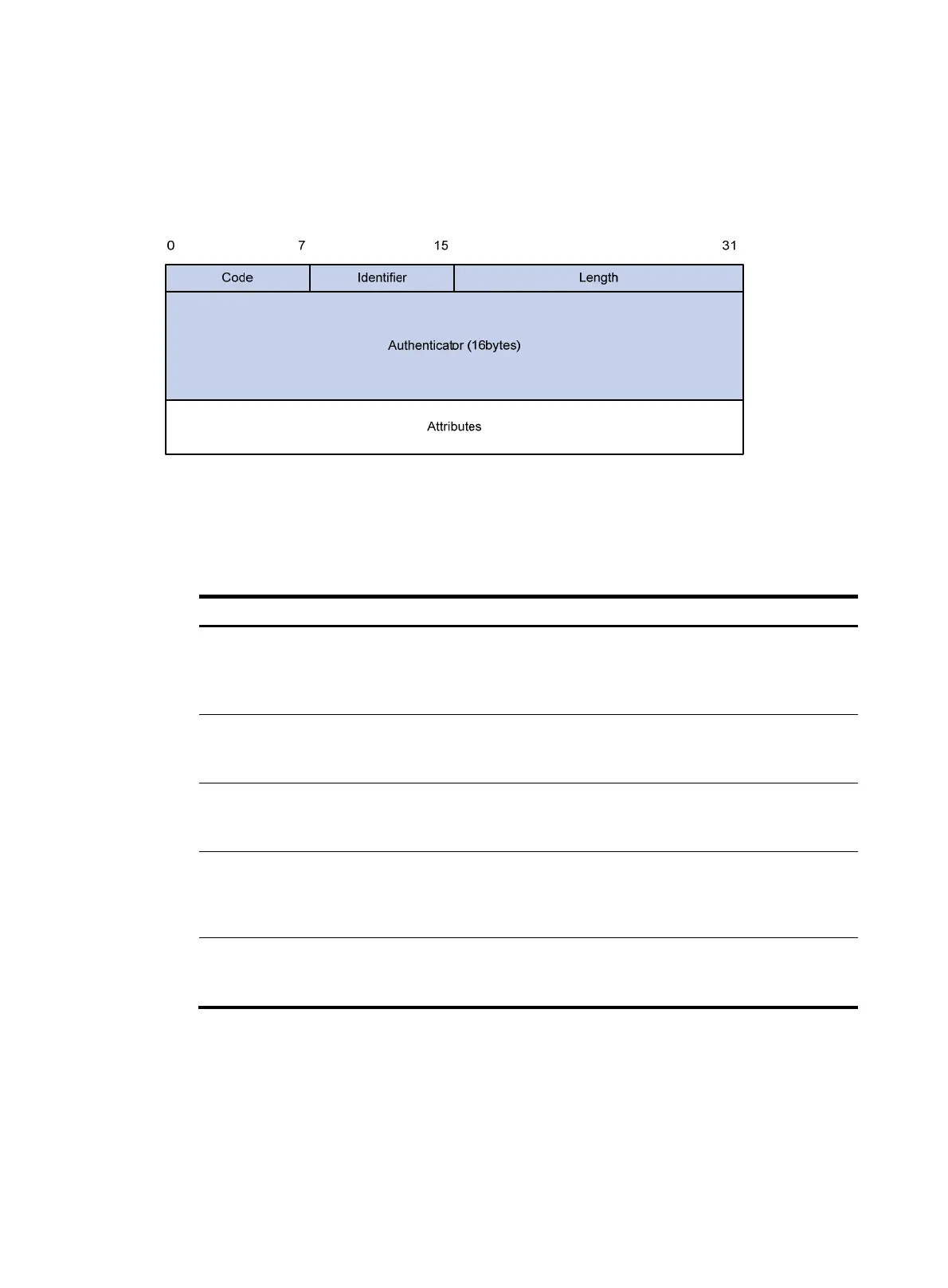
RADIUS packet format
RADIUS uses UDP to transmit packets. To ensure smooth packet exchange between the RADIUS server
and the client, RADIUS uses a series of mechanisms, including the timer mechanism, the retransmission
mechanism, and the backup server mechanism. Figure 4 sho
w
s the RADIUS packet format.
Figure 4 RADIUS packet format
Descriptions of the fields are as follows:
• The Code field (1 byte long) indicates the type of the RADIUS packet. Table 1 gives the main values
and the
ir meanings.
Table 1 Main values of the Code field
Code Packet type Description
1 Access-Request
From the client to the server. A packet of this type includes user
information for the server to authenticate the user. It must contain the
User-Name attribute and can optionally contain the attributes of
NAS-IP-Address, User-Password, and NAS-Port.
2 Access-Accept
From the server to the client. If all attribute values included in the
Access-Request are acceptable, the authentication succeeds, and the
server sends an Access-Accept response.
3 Access-Reject
From the server to the client. If any attribute value included in the
Access-Request is unacceptable, the authentication fails, and the server
sends an Access-Reject response.
4 Accounting-Request
From the client to the server. A packet of this type includes user
information for the server to start or stop accounting for the user. The
Acct-Status-Type attribute in the packet indicates whether to start or stop
accounting.
5
Accounting-Respons
e
From the server to the client. The server sends a packet of this type to
notify the client that it has received the Accounting-Request and has
successfully recorded the accounting information.
• The Identifier field (1 byte long) is used to match response packets with request packets and to detect
duplicate request packets. The request and response packets of the same exchange process for the
same purpose (such as authentication or accounting) have the same identifier.
• The Length field (2 bytes long) indicates the length of the entire packet (in bytes), including the Code,
Identifier, Length, Authenticator, and Attributes fields. Bytes beyond this length are considered
padding and are ignored by the receiver. If the length of a received packet is less than this length,
the packet is dropped.
 Loading...
Loading...





