System Bus Design Guidelines
R
Intel
®
815 Chipset Platform Design Guide 51
5.3 Electrical Differences for Universal PGA370
Designs
There are several electrical changes between previous PGA370 designs and the universal PGA370
design, as follows:
• Changes to the PGA370 socket pin definitions.
• Addition of VTTPWRGD signal to ensure stable VID selection for future 0.13 micron socket
370 processors.
• Addition of THERMTRIP circuit to allow processor to detect catastrophic overheat.
• Addition of VID[25 mV] signal to support future 0.13 micron socket 370 processors.
• Processor VTT level is switchable to 1.25V or 1.5V, depending on which processor is present
in the socket.
• In designs using future 0.13 micron socket 370 processors, the processor does not generate
V
CMOS
_REF.
5.3.1 THERMTRIP Circuit
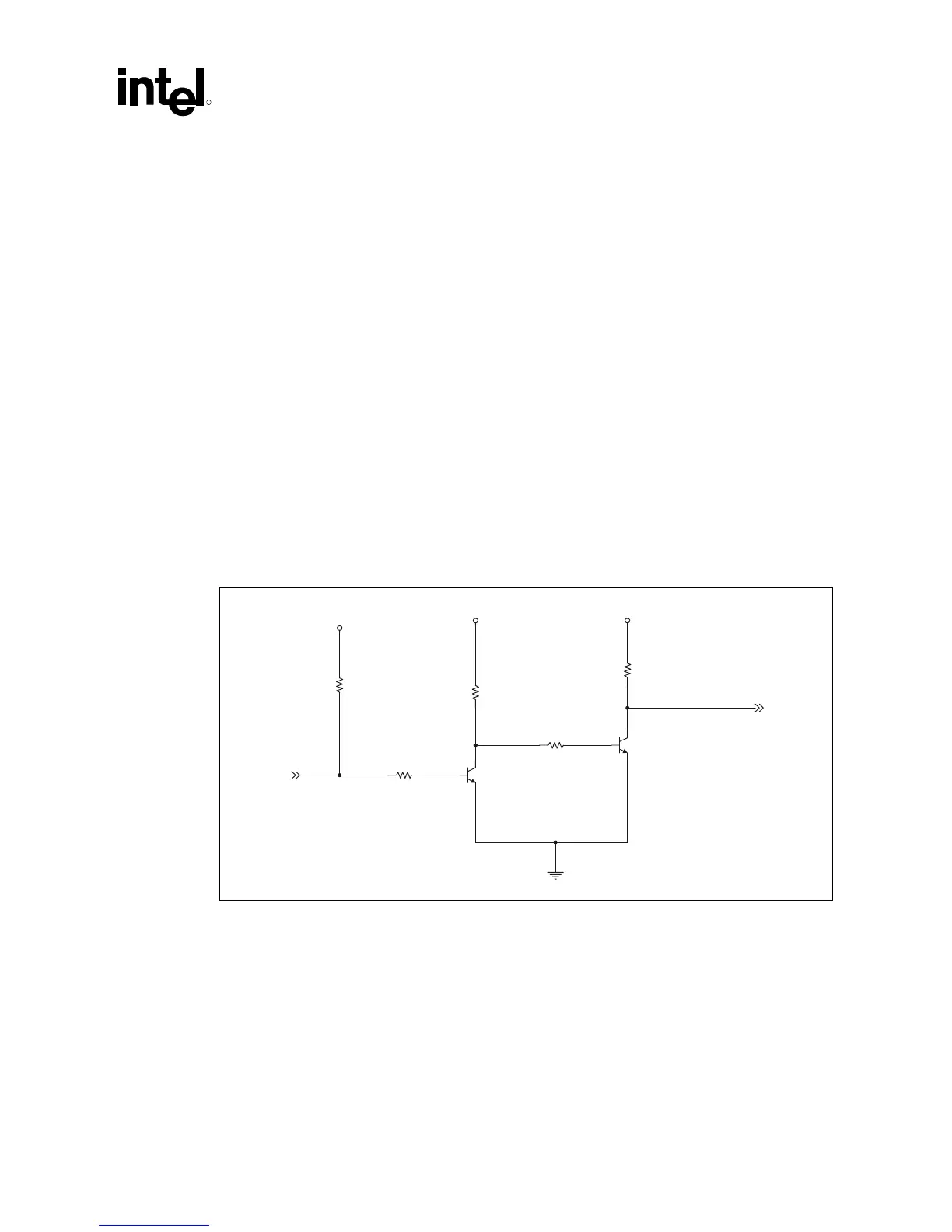
Figure 22. Example Implementation of THERMTRIP Circuit
VCC1_8SB
VCC1.8
VCC3_3SB
Thermtrip#
SW_ON#
2
1
R8
1.6 K
Ω
21
Q3
Q2N3904
Q2
Q2N3904
2
1
2
1
R10
1 K
Ω
2
1
Can Use MBT3904
Dual XSTR Part
Connect to ICH
R11
1 K
Ω
R9
1 K
Ω
R12
22 K
Ω
Thermstrip
5.3.1.1 THERMTRIP Timing
When the THERMTRIP signal is asserted, both the VCC and VTT supplies to the processor must
be turned off to prevent thermal runaway of the processor. The time required from THERMTRIP
asserted to VCC rail at ½ nominal is 5 sec and THERMTRIP asserted to VTT rail at ½ nominal is
5 sec. System designers must ensure that the decoupling scheme used on these rails does not
violate the THERMTRIP timing specifications.

 Loading...
Loading...