Communication
98 USER MANUAL FPC 200 - 3/2017
3.2 Protocol IEC60870-5-103
Standard IEC60870-5-103 defines communication between protection equipment and dedicated supervisor devices. The
standard in full form can be obtained from the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
General description
The IEC60870-5-103 protocol is a Slave – Master based
communication protocol. An information can be
exchanged between master and one or multiple slave
devices. A supervisor or other device is used as master
and the device is always used as a slave station. Multiple
slave stations can be connected to the supervisor
device. Each slave station is identified by unique
address.
The following application functions can be accessed or
executed using this protocol:
Time synchronization
Confirmation of alarms
Reading the metering information
Reading the device status and switchgear
diagnostic information
Transmission of remote controls
Acronyms and Terms
Application Service data unit.
Event on bidirectional transition.
Cause of Transmission of ASDU.
The number of the function to which
data belongs.
A General Interrogation marker.
The information number of the basic
data.
Type identification of ASDU.
Rate factor, valid just for measurements.
Reference unit, valid for metering
information.
Table 101 Description of acronyms and terms.
If a BIDI is selected the event is generated on both on
event occurrence and event disappearance. Else event is
generated only on its occurrence.
Protocol data transfer
The standard defines two methods of exchanging
information. First, which is supported, by using
predefined ASDU (Application Service Data Units) data
structures and predefined transmission of standardized
information. Second, non-supported, uses generic
services which defines the transmission of any type of
information. The protocol is using two types of
exchanging information based on its source divided to
control direction and monitoring direction.
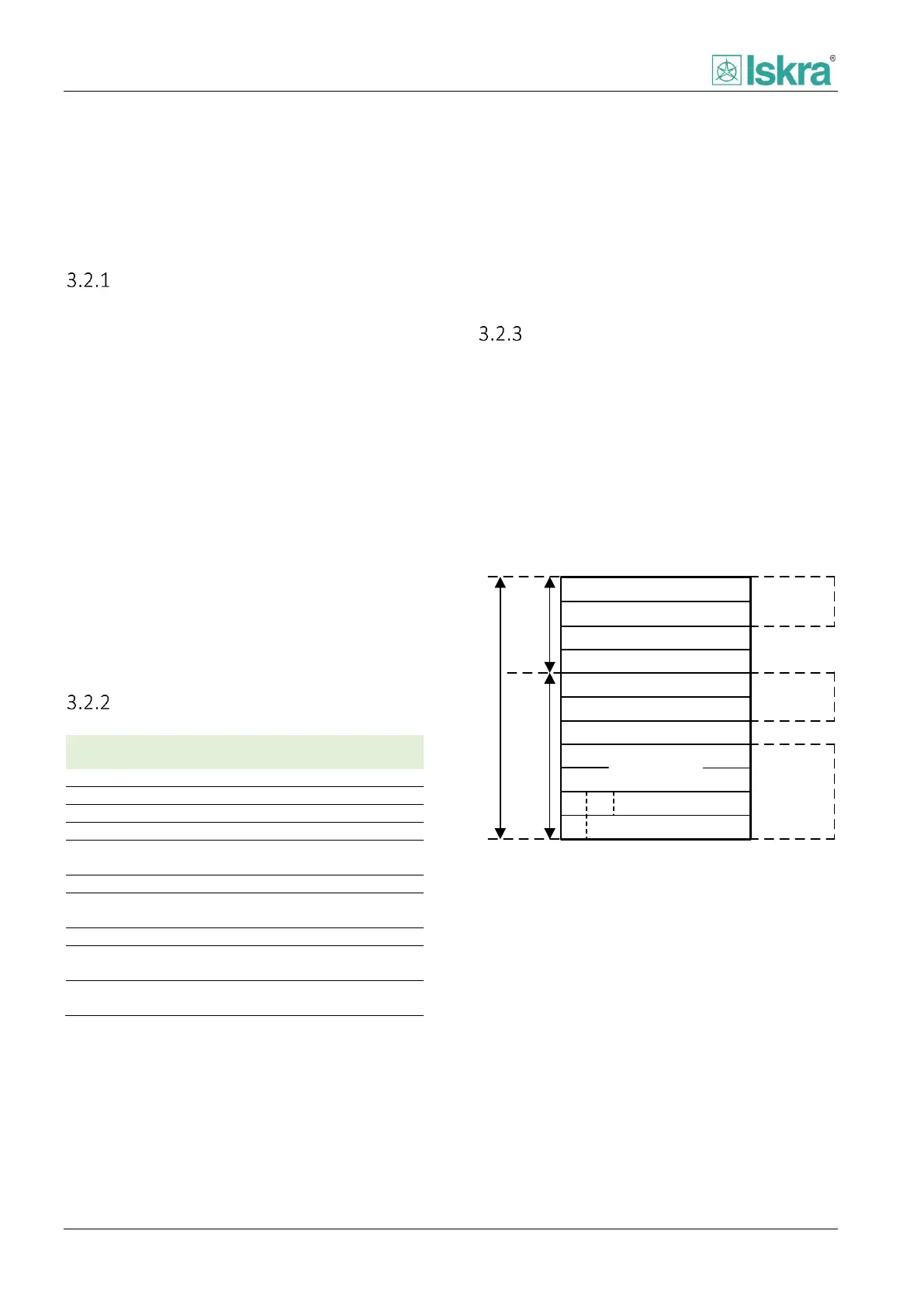
Type identification
Variable structure qualifier
Time tag [ms]
Cause of transmission
Common address of ASDU
Function type
Information number
Set of information elements
Time tag [min]
Time tag [h]
SU
Res
IV
ASDU
Information object
Data unit
indentifier
Data unit
type
Inf. object
identifier
Time tag of
information
object
Table 102 ASDU structure, as presented in the standard
IEC60870-5-103.
 Loading...
Loading...