Engineering manual - UniSAB III 1.10.8
001930 en 2021.06
91/346
Compressor control and surveillance
3.2.2 Standard limiters
The standard limiting function is based on the user selected high/low shutdown limit, high/low alarm limit
and the limiting zone (Lz). In the particular case of the high motor current/kW limiter, the value of Lz is
5% for both screw and reciprocating compressors. In all other cases, Lz is calculated as half the differ-
ence between the shutdown limit and the alarm limit. Fig. 17 illustrates how a standard limiter works with
the high discharge pressure limiter as example.
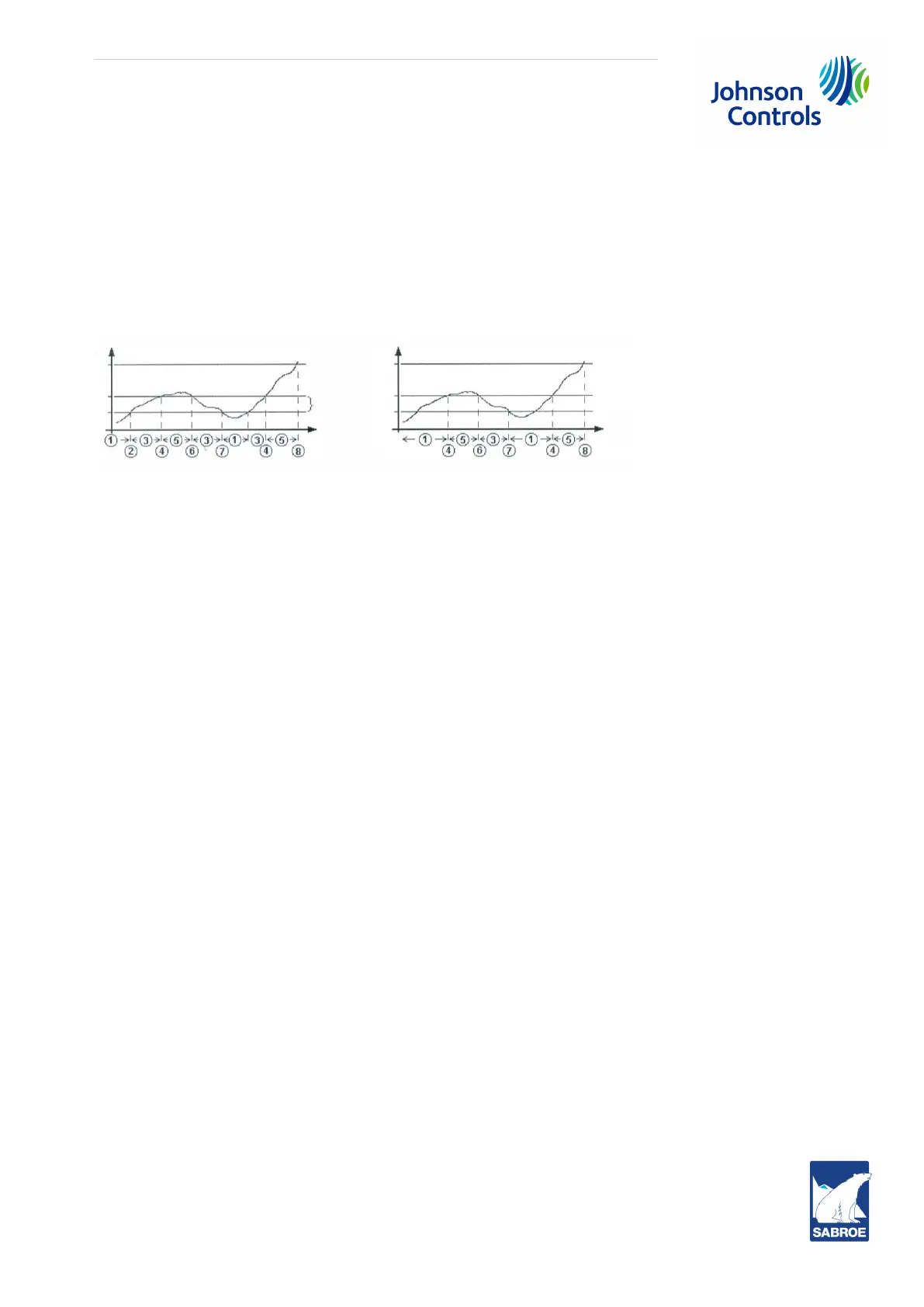
Fig. 17: Limiting sequence
Pos. numbers
1. Limiter is watching. Normal control, capacity can increase or decrease. If compressor is not in
operation, it can be started.
2. Limiter changes from watching to passive.
3. Limiter is passive. Capacity cannot be increased. Capacity is not reduced by limiter, but possibly
by regulator. If compressor is not running, it cannot be started and will be in Pause state.
4. Limiter becomes active. Capacity is reduced at once and timer begins to count.
5. Limiter is active. At each timeout, capacity is reduced and timer restarted, until compressor
stops at low capacity. If compressor is not running, it cannot be started and will be in Pause
state.
6. Limiter changes from active to passive.
7. Limiter changes from passive to watching.
8. Compressor has stopped immediately (shutdown).
In the example, the shutdown limit for high discharge pressure has been set for 16 bar, while the alarm
limit is 14 bar. As indicated, the size of the limiting zone (Lz) is then (16-14) / 2 = 1 Bar. The limit of the
limiting zone is thus alarm limit - Lz = 14 -1 = 13 bar.
Note: The limitation is calculated in °C/R. Therefore, never set the low shutdown for suction pressure to
-1 bar as -1 bar equals -273°C/R when using ammonia.
Example:
Low alarm -0.9 bar ~ -71.7 °C/R.
Low shutdown -1 bar ~ -273 °C/R.
In this case the limitation starts at -71.9 + (273-71.9)/2 = 28.65°C/R.
Obviously, the suction pressure can never reach that value and the plant will never start! As shown in
Fig. 17, most reciprocating compressor limiters differ from the corresponding screw compressor limiters
in the way that when the measured value is within the limiting zone, the state of the limiter depends on
whether the limiter has been watching or active. If the limiter has been watching, it will remain watching
in the limiting zone. If the limiter has been active, it will become passive for as long as it remains within
the limiting zone.
16
14
13
ALARM
Limiting zone
SHUTDOWN
Discharge press. [bar]
Screw compressors (all limiters) and
reciprocating compressors (motor current
limiter)
Time
Reciprocating compressors
(All limiters except motor current
limiter)
Discharge press. [bar]
Time

 Loading...
Loading...