6.3 Definition of the Used Data Types
This chapter defines the data types that are used. Each data type can be described by bit- sequences. These bit-
sequences are grouped into "Octets” (bytes). The so-called "Little – Endian” format (a.k.a. Intel format) is used
for numerical data types (see also: DS301 Application Layer "General Description of Data Types and Encoding
Rules”).
6.3.1 Basic data types
6.3.1.1 Unsigned Integer
Data in the basic data type UNSIGNEDn define exclusively positive integers.
The value range is from 0 to 2
n
-1. The bit sequence b = b
0
to b
n-1
defines the value
UNSIGNEDn(b) = b
n-1
2
n-1
+ to + b
1
2
1
+ b
0
2
0
Example: the value 266 = 10Ah is transmitted in the data type UNSIGNED16, in the form of two octets (1
st
octet
= 0Ah, 2
nd
octet = 01h).
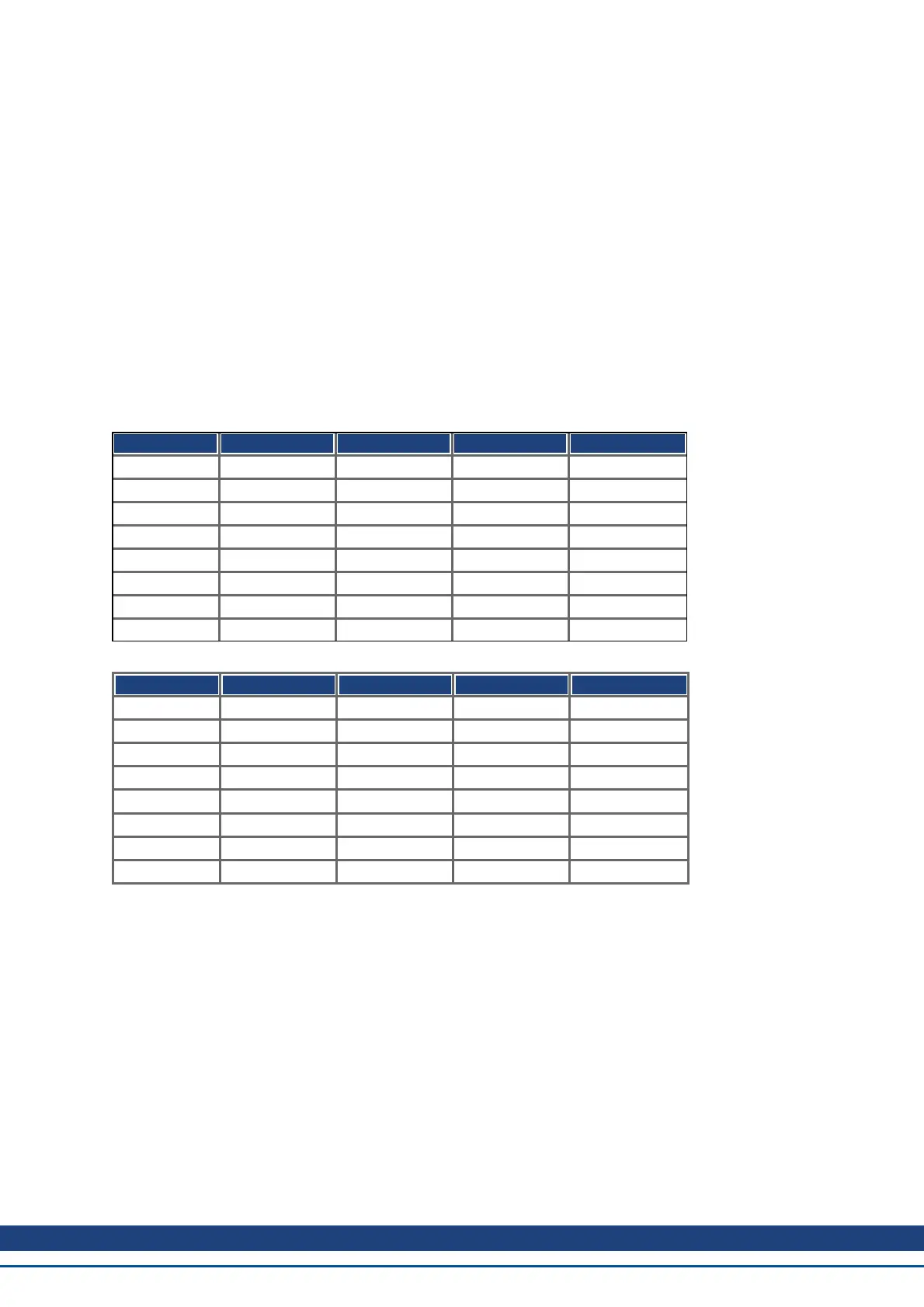
Transmission syntax for the data type UNSIGNEDn
Octet number 1. 2. 3. 4.
UNSIGNED8 b
7
to b
0
UNSIGNED16 b
7
to b
0
b
15
to b
8
UNSIGNED24 b
7
to b
0
b
15
to b
8
b
23
to b
16
UNSIGNED32 b
7
to b
0
b
15
to b
8
b
23
to b
16
b
31
to b
24
UNSIGNED40 b
7
to b
0
b
15
to b
8
b
23
to b
16
b
31
to b
24
UNSIGNED48 b
7
to b
0
b
15
to b
8
b
23
to b
16
b
31
to b
24
UNSIGNED56 b
7
to b
0
b
15
to b
8
b
23
to b
16
b
31
to b
24
UNSIGNED64 b
7
to b
0
b
15
to b
8
b
23
to b
16
b
31
to b
24
Octet number 5. 6. 7. 8.
UNSIGNED8
UNSIGNED16
UNSIGNED24
UNSIGNED32
UNSIGNED40 b
39
to b
32
UNSIGNED48 b
39
to b
32
b
47
to b
40
UNSIGNED56 b
39
to b
32
b
47
to b
40
b
55
to b
48
UNSIGNED64 b
39
to b
32
b
47
to b
40
b
55
to b
48
b
63
to b
56
AKD CANopen | 6 CANopen Communication Profile
Kollmorgen™ | November 2012 29

 Loading...
Loading...