Beta Draft Confidential
About SVCs
Address Formats
ATM Services Configuration Guide for CBX 3500, CBX 500, GX 550, and B-STDX 9000 1/19/0516-3
E.164 — For E.164 AESA addresses, the IDI field contains an eight-byte E.164
address. This E.164 address uses the international format and consists of up to fifteen
decimal digits. E.164 Anycast AESA provides a group address function for this
address type.
Embedded E.164 AESA format — An embedded E.164 is a specific type of AESA
format that requires a specific encoding in the IDI section. As shown in the
example below, a Native E.164 address is converted to BCD format. Leading
zeros are added to obtain the maximum length of 15 octets and a trailing
semi-octet 0xF is added to pad the final semi-octet. The high-order domain
specific part (HO-DSP) and the end system identifier (ESI) must be all zeros. For
specific information, see Section 5.1.3.1.1.3 of the ATM User-Network Interface
(UNI) Specification 3.1.
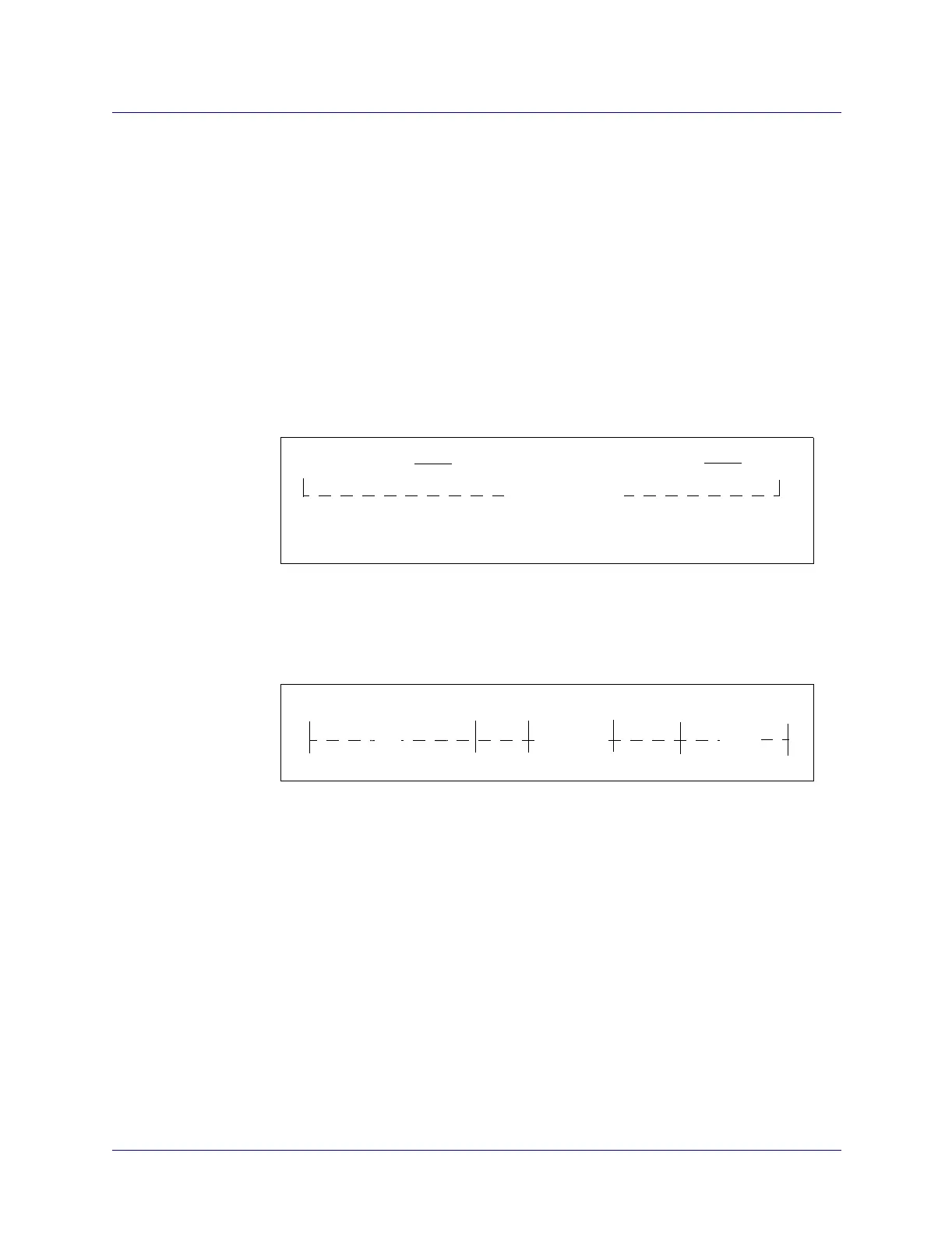
Figure 16-1. Native E.164 Address Converted to BCD Format
An example of an embedded E.164 AESA format is shown below using the Native
E.164 address 1508555.
Figure 16-2. Embedded E.164 AESA Format
Leading Zeros Native E.164 address in BCD format
0xF
The HO-DSP and ESI must be all zeros
8 octets in length
45-000000001508555F
00000000 000000000000
IDI
ESI
HO-DSP

 Loading...
Loading...