EXAMPLE 4 - DUAL POINT DIFFERENTIAL
This mode of operation is commonly used for water and waste water processing to monitor the level on either
side of a screen or filter to identify a "blocked" screen condition. Similar operation is also commonly used to
operate waterway control gates to maintain rivers and lakes at predetermined levels.
For this example we’ll assume the following:
» the river level is typically 280 m ± 0.5 m above sea level.
» when the river level is 280 m, the river side of the infeed channel is 125 cm.
» a control room alarm is required if the river levels exceeds 281 meters or falls below 279 m.
» the plant infeed channel includes a series of screens to prevent large solids from entering.
» under normal conditions the difference between river and plant sides of the screens is 6 cm.
» a control room alarm is required if the river/plant side differential level reaches 12 cm.
» the river level rate of change is very slow (several days for a 6 cm change).
» the plant side level decreases slow but increases fast (after screen cleaning).
» a mA output proportional to the river side level is desired (4 mA = low, 20 mA = high).
» a mA output proportional to the difference (4 mA = 0 cm, 20 mA = 12 cm) is also required.
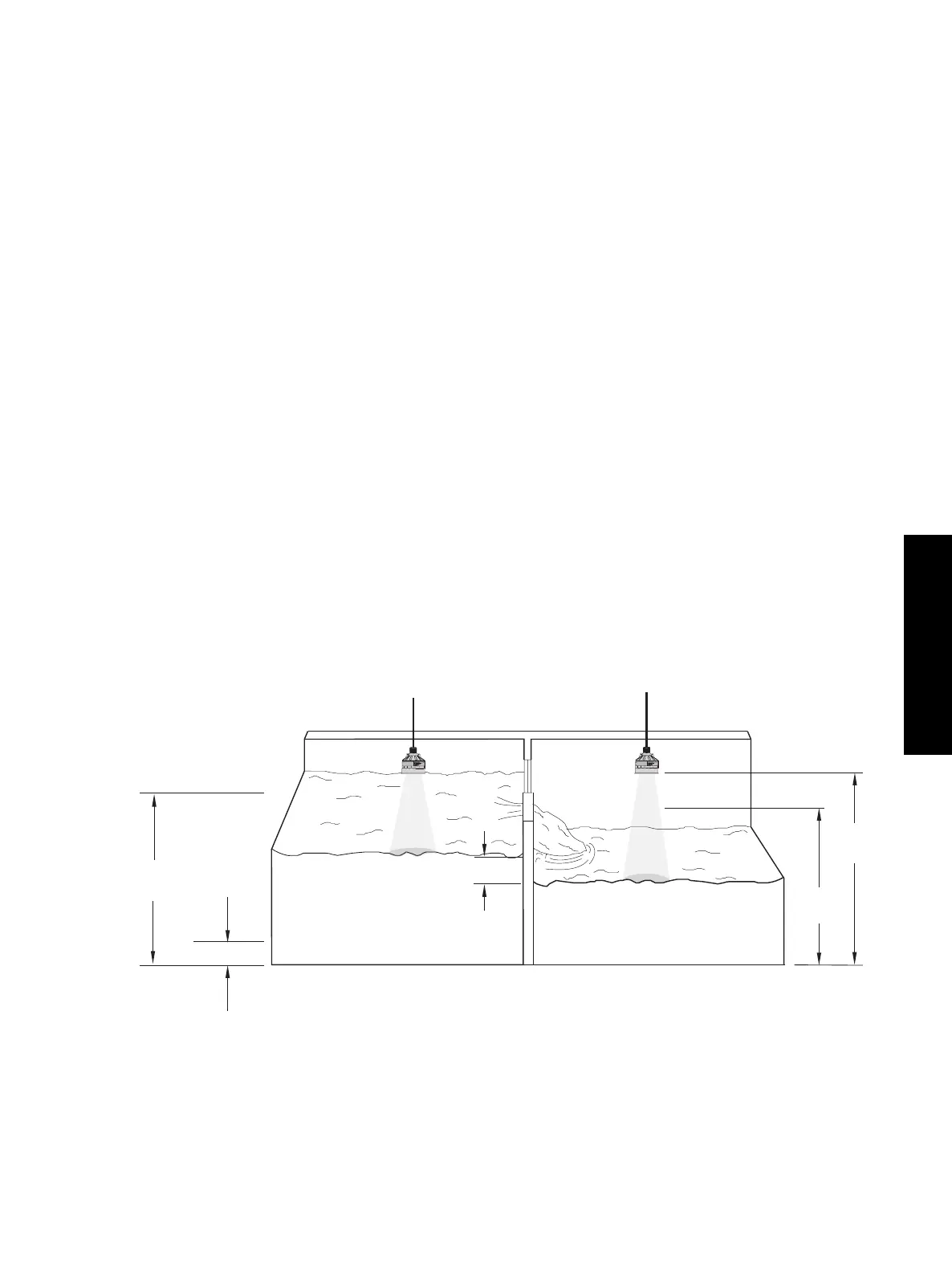
» Transducer 1 (an XPS-10) is mounted on the river side of the filter, 275 cm above the channel.
» Transducer 2 (an XPS-10) is mounted on the plant side of the filter, 275 cm above the channel.
APPROVED
FM
APPROVED
FM
242.0 cm
(P007)
275.0 cm
(P006)
Plant Side
Transducer 2
Transducer 1
225 cm
(P101)
River Side
12 cm
(P112)
25 cm
(P102)
TECHNICAL REFERENCE
PL-508 87
 Loading...
Loading...