FX Series Programmable Controllers Points Of Technique 10
10-22
FX2N (V2.00 or above) Communications
In the FX2N V2.00 or above and FX2NC, full duplex communication is performed.
1) No Hardware Handshaking D8120 (B12, b11, b10) = (0,0,0)
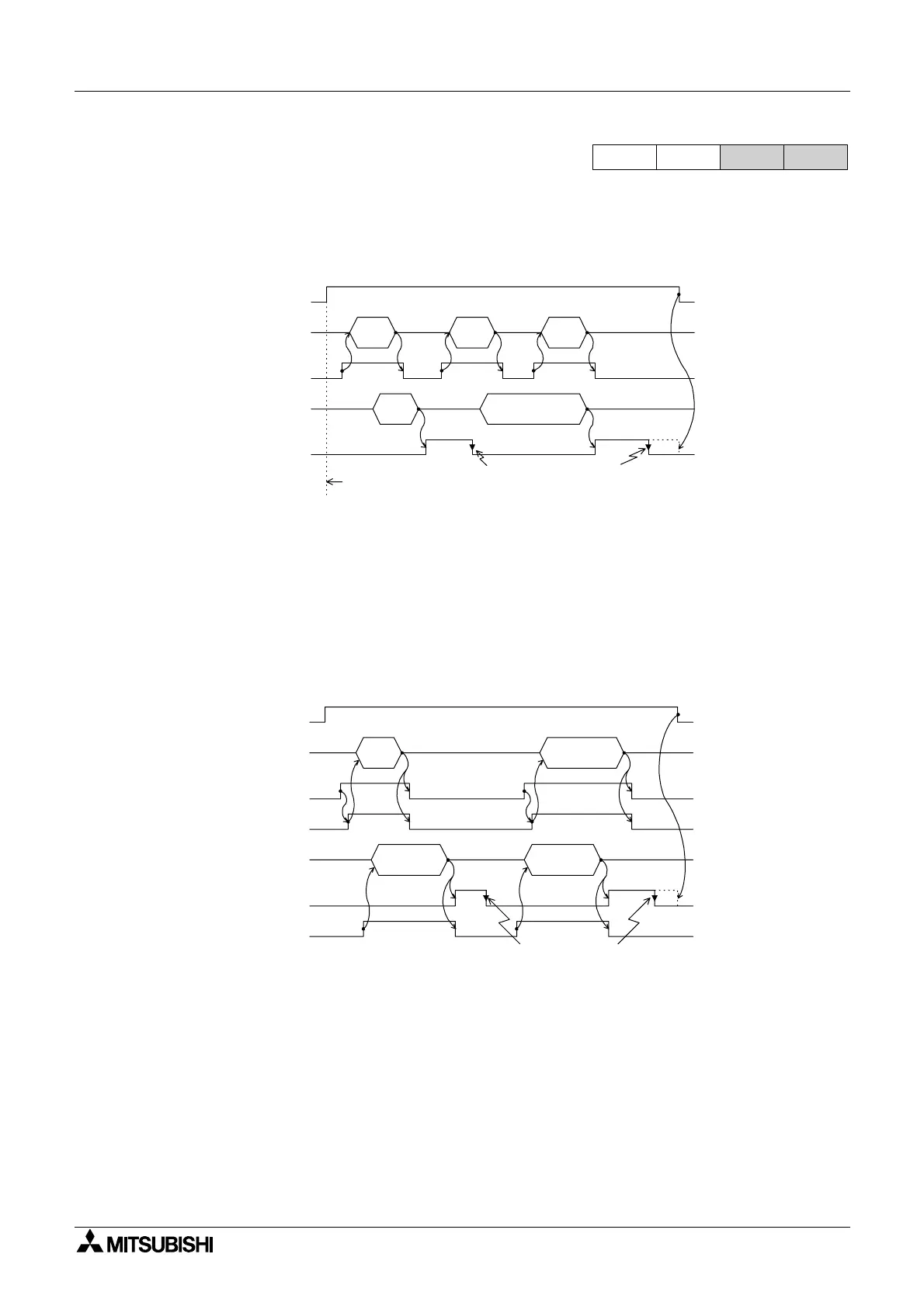
2) Terminal Mode
The control line and transmission sequence are identical to those in the FX, on page
3) Normal Mode 1 D8120 (b12, b11, b10) = (0, 1, 1)
FX
1S
FX
1N
FX
2N
FX2NC
Resetitusingaprogram.
When it is not turned off, the
next data cannot be received.
Data 1
RS
instruction
Send data
SD (TXD)
OFF ON
Data 5
OFF
ON
Send request
M8122
Receive
completion
M8123
Data 3
Data 2
Data 4
OFF
ON
ON
The receive wait
status is started
Receive data
RD (RXD)
Reset using a program.
When it is not turned off, the
next data cannot be received.
Data 1
OFF
OFF ON
ON
Data 4
OFF ON
RS
instruction
Send data
SD (TXD)
ER(DTR)
ON
Receive
completion
M8123
OFF ON
Data 2 Data 3
Receive data
RD (RXD)
OFF ON
Send request
M8122
DR(DSR)

 Loading...
Loading...











