CN2600 Series Configuration with the Web Console
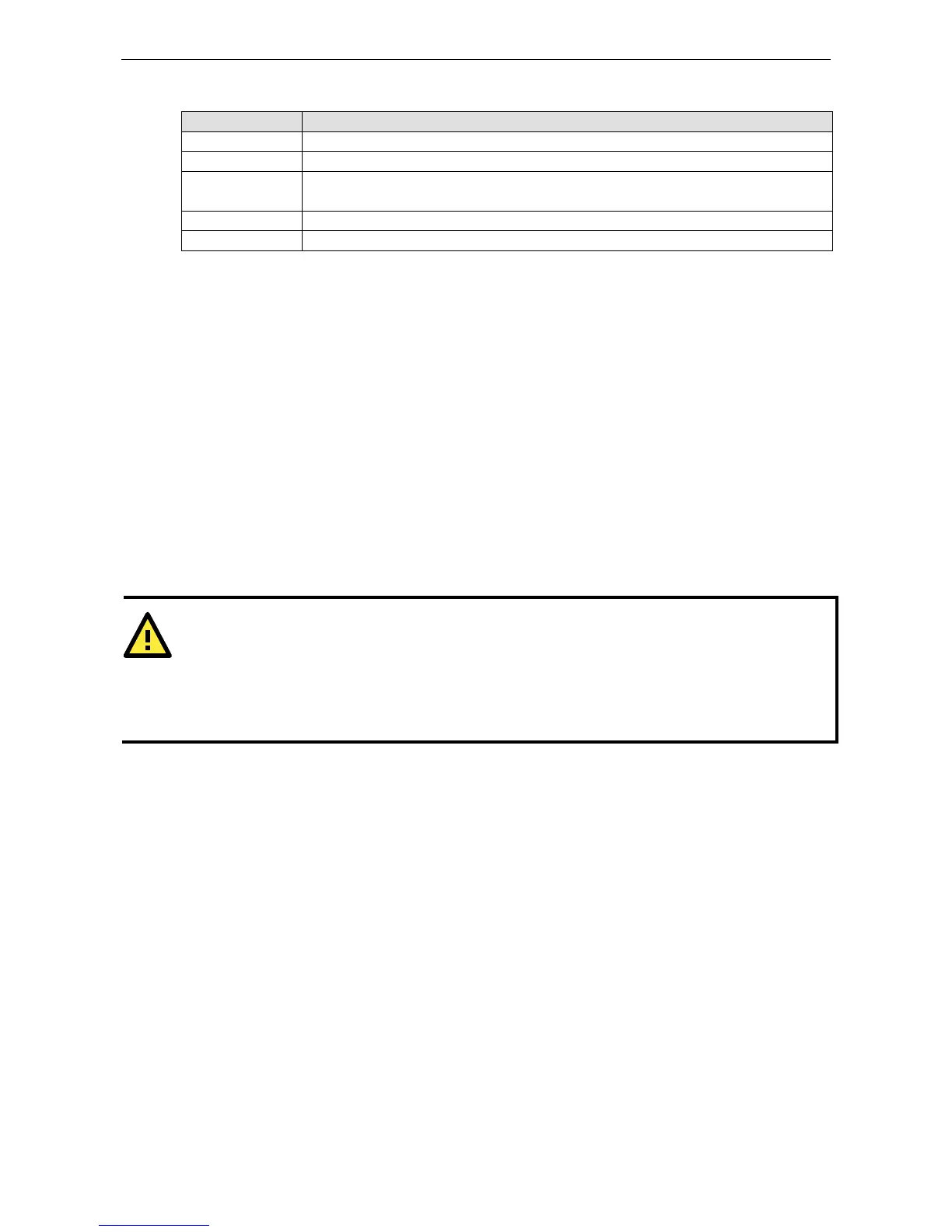
IP configuration (default=Static): You can choose from four possible IP configuration modes.
Option Description
Static User-defined IP address, netmask, gateway.
DHCP DHCP server-assigned IP address, netmask, gateway, DNS, and time server
DHCP/BOOTP DHCP server-assigned IP address, netmask, gateway, DNS, and time server, or BOOTP
server-assigned IP address (if the DHCP server does not respond)
BOOTP BOOTP server-assigned IP address
PPPoE PPP over Ethernet, remote ISP-assigned IP address
IP Address (LAN1 default = 192.168.127.254; LAN2 default = 192.168.126.254): Enter the IP address that
will be assigned to your CN2600. All ports on the CN2600 will share this IP address. An IP address is a number
assigned to a network device (such as a computer) as a permanent address on the network. Computers use the
IP address to identify and talk to each other over the network. Choose a proper IP address that is unique and
valid in your network environment.
Netmask (default=255.255.255.0): Enter the subnet mask. A subnet mask represents all of the network hosts
at one geographic location, in one building, or on the same local area network. When a packet is sent out over
the network, the CN2600 will use the subnet mask to check whether the desired TCP/IP host specified in the
packet is on the local network segment. If the address is on the same network segment as the CN2600, a
connection is established directly from the CN2600. Otherwise, the connection is established through the given
default gateway
Gateway: Enter the IP address of the gateway if applicable. A gateway is a network computer that acts as an
entrance to another network. Usually, the computers that control traffic within the network or at the local
Internet service provider are gateway nodes. The CN2600 needs to know the IP address of the default gateway
computer in order to communicate with the hosts outside the local network environment. For correct gateway
IP address information, consult the network administrator.
ATTENTION
In dynamic IP environments, the firmware will try to get the network settings from the DHCP or BOOTP server
3 times every 30 seconds until network settings are assigned by the DHCP or BOOTP server. The first try times
out after 1 second, the seco
nd after 3 seconds, and the third after 5 seconds.
If the DHCP/BOOTP server is unavailable, the firmware will use the default IP address (192.168.127.254),
netmask, and gateway settings.
DNS server 1: This is an optional field. If your network has access to a DNS server, you may enter the DNS
server’s IP address in this field. This allows the CN2600 to use domain names instead of IP addresses to access
hosts.
Domain Name System (DNS) is the way that Internet domain names are identified and translated into IP
addresses. A domain name is an alphanumeric name, such as www.moxa.com, that it is usually easier to
remember than the numeric IP address. A DNS server is a host that translates this kind of text-based domain
name into the actual IP address used to establish a TCP/IP connection. When the user wants to visit a particular
website, the user’s computer sends the domain name (e.g., www.moxa.com) to a DNS server to request that
website’s numeric IP address. When the IP address is received from the DNS server, the user’s computer uses
that information to connect to the website’s web server.
The CN2600 will play the role of a DNS client, in the sense that it will actively query the DNS server for the IP
address associated with a particular domain name. The following functions on the CN2600 web console support
the use of domain names in place of IP addresses: Time Server, Destination IP Address (in TCP Client mode),
Mail Server, SNMP Trap Server, Destination Address (in Pair Connection mode), Primary/Secondary Host
Address (in Terminal mode), RADIUS Server and SMTP Server.
DNS server 2: This is an optional field. The IP address of another DNS server may be entered in this field for
times when DNS server 1 is unavailable.

 Loading...
Loading...











