PPPoE user account and PPPoE password: For dynamic broadband networks such as xDSL or cable modem,
users must enter the username and password that they received from their ISP to establish network connection.
If a serial port on the CN2600 will be using PPPoE, enter the account name and password in these fields.
WINS function (default=enable): Enable or disable the WINS (Windows Internet Naming Service) server.
WINS server: If a WINS Server is connected to the network, enter the WINS Server’s IP address in this field.
TCP/IP uses IP addresses to identify hosts, but users often use symbolic names, such as computer names. The
WINS Server, which uses NetBIOS over TCP/IP, contains a dynamic database to map computer names to IP
addresses.
LAN speed (default=Auto): You may configure the network speed for the built-in Ethernet connection on the
CN2600. IEEE802.3 Ethernet supports auto negotiation of transfer speed. However, some switches/hubs
require that the communication speed be fixed at 100Mbps or 10Mbps.
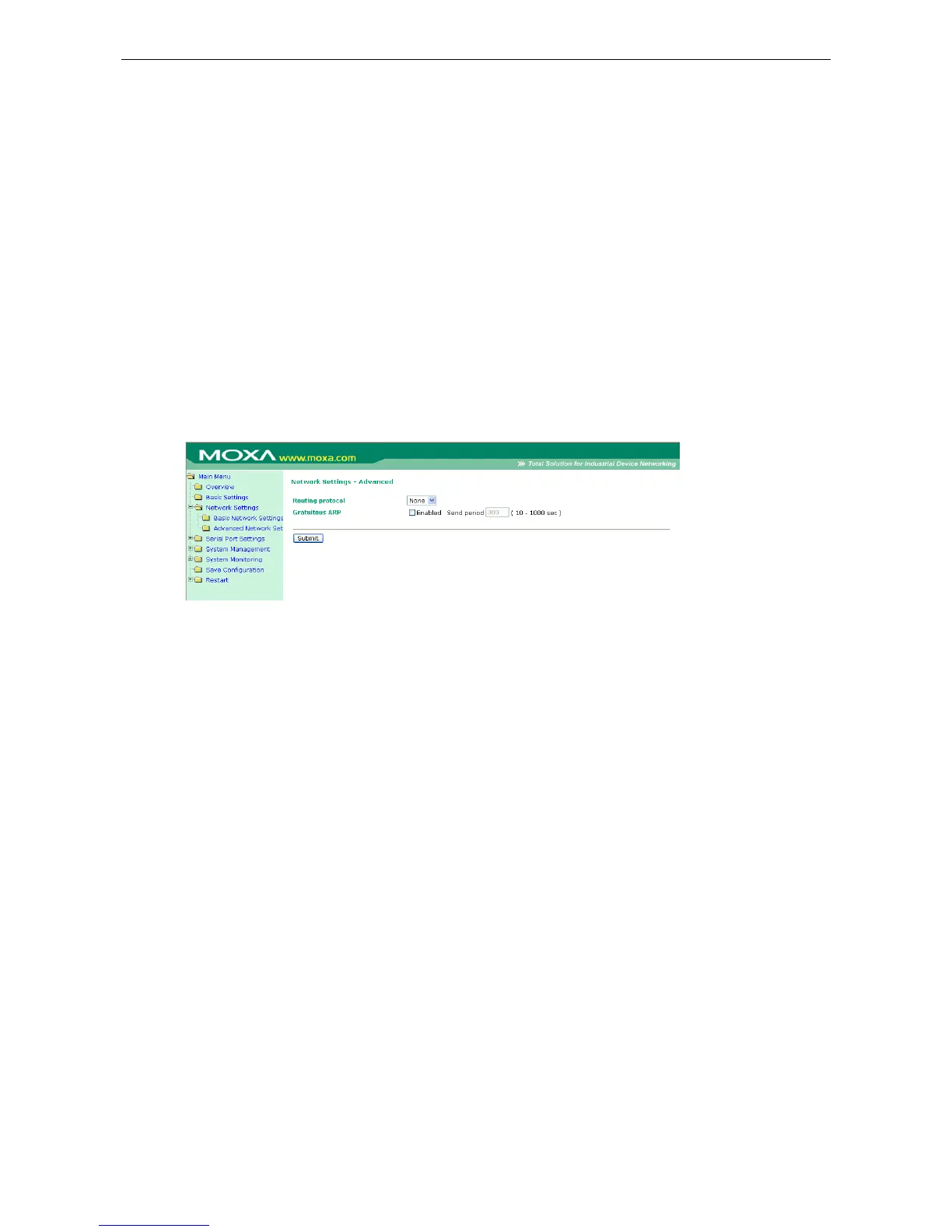
Advanced Network Settings
You can access Advanced Network Settings by expanding the Network Settings item in the navigation panel.
Advanced Network Settings is where the routing protocol and gratuitous ARP are configured.
What is RIP?
RIP (Routing Information Protocol) is a protocol used to manage routing information within a self-contained
network, such as a corporate LAN (Local Area Network) or an interconnected group of such LANs.
By using RIP, a gateway host with a router can send its entire routing table, which lists all the other hosts it
knows about, to its closest neighbor host every 30 seconds. The neighbor host in turn will pass this information
on to its closest neighbor, and so on, until all hosts within the network have the same routing path information.
This state is known as network convergence. RIP uses a hop count as a way of determining network distance.
(Other protocols use more sophisticated algorithms that also include timing.) After receiving a packet headed
for a specific destination, a network host with a router uses the routing table information to determine the next
host to route the packet to.
RIP is considered an effective solution for small homogeneous networks. For larger, more complicated
networks, transmitting the entire routing table every 30 seconds can bog down the network with a lot of extra
traffic.
RIP 2 is an extension of RIP. Its purpose is to expand the amount of useful information contained in RIP packets,
and to add security elements. RIP 2 has become the standard version of RIP, and the original RIP is no longer
used.
Routing Protocol: You may select which routing protocol, if any, your network will employ.
Gratuitous ARP: In some applications, you may need the CN2600 to send broadcast packets to update the
ARP table on the server. If you enable this function and set the send period, the CN2600 will send periodically
send broadcast packets at the specified time interval.

 Loading...
Loading...











