Do you have a question about the Moxa Technologies NPort W2150Plus Series and is the answer not in the manual?
Introduces the basic features and specifications of the NPort W2150/2250 Plus Series.
Lists standard and optional accessories included with the NPort W2150/2250 Plus Series.
Highlights key capabilities like instant serial device connection, web-based configuration, and security features.
Details technical specifications for WLAN and LAN interfaces, including compliance, rates, and security.
Details the number of ports, interface type, port connector, and buffering for serial communication.
Specifies settings for parity, data bits, stop bits, flow control, and transmission speed.
Lists supported protocols, utilities, and configuration methods for the NPort.
Details the NPort's power input voltage, consumption, and connector type.
Describes material, dimensions, and antenna length of the NPort device.
Specifies operating and storage temperature ranges, and humidity limits.
Lists EMC and Safety certifications, including FCC, CE, UL, and TUV standards.
Illustrates pin configurations for RS-232, RS-485 (4W), and RS-485 (2W) interfaces.
Explains how to connect the hardware features of the NPort W2150/W2250 Plus Series.
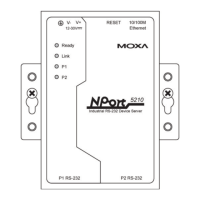
Illustrates the physical layout of the NPort W2250/2150 Plus models, showing ports and indicators.
Describes the meaning of top and end panel LED indicators for status monitoring.
Details jumper settings for pull high/low resistors on RS-422/485 serial ports.
Describes how to place the NPort on a desktop, DIN-rail, or wall.
Provides important safety precautions before connecting the NPort hardware.
Guides on connecting the NPort to an Ethernet network using an Ethernet cable.
Explains how to connect the VDC power line to the NPort and the expected LED behavior.
Details how to connect a serial device to a serial port on the NPort.
Explains methods to assign the NPort's IP address for the first time, recommending web console.
Details the default LAN and WLAN IP addresses and netmasks for the NPort.
Describes using the ARP command to associate the NPort's MAC address with a new IP address.
Provides step-by-step instructions for assigning an IP address via the Telnet console.
Explains how to assign an IP address using a serial console connection and terminal emulator.
Introduces various serial port operation modes and how they interact with network devices.
Allows legacy serial-based software to access NPort serial ports as local COM ports.
Maps a virtual COM port to an NPort serial port using Telnet protocol for general COM port control.
NPort waits for host connections to attached serial devices, supporting multiple simultaneous connections.
NPort actively establishes TCP connections to network hosts for data from attached serial devices.
Faster and more efficient than TCP, suitable for applications where data integrity is less critical.
Connects two NPort device servers over a network for serial-to-serial communication.
Allows legacy OS like MS-DOS to connect to the network via the NPort acting as an Ethernet modem.
Involves connecting terminals to UNIX or Windows servers over a network for serial data transfer.
Connects NPort serial port to a server for terminal sessions, assisting with CR/LF conversion.
Explains how to configure basic settings for the NPort using its web console.
Details the requirement for enabling cookies in web browsers to use the NPort web console.
Guides on accessing and using the NPort web console, including submitting changes and saving.
Allows configuration of server name, location, and time zone for the NPort.
Sets an optional free text field to differentiate NPort device servers.
Sets an optional free text field to identify the physical location of the NPort.
Allows selection of the appropriate time zone for the NPort's real-time clock.
Manages the NPort's built-in real-time clock, allowing modification after setting the time zone.
Specifies an optional time server for automatic time calibration using SNTP.
Explains how to configure all settings under the Network Settings folder in the NPort web console.
Allows modification of DNS server, WINS function, and WINS server settings for network connectivity.
Specifies DNS server IP addresses for translating domain names to IP addresses for host access.
Enables or disables the WINS service for mapping symbolic names to IP addresses via NetBIOS.
Specifies the IP address of the WINS server for name resolution on the network.
Allows configuration of IP settings, netmask, gateway, and speed for the Ethernet interface.
Determines how the NPort's IP address is assigned (Static, DHCP, BOOTP).
Assigns a unique IP address to the NPort device server for network identification.
Defines the subnet mask for the local network segment to facilitate network communication.
Specifies the IP address of the gateway computer for communication with external networks.
Sets the network speed for the built-in Ethernet connection, supporting auto-negotiation.
Configures IP settings (IP, Netmask, Gateway) for the NPort's wireless WLAN interface.
Configures the NPort for Ad-hoc or Infrastructure wireless operation, adjusting settings per profile.
Specifies whether the NPort operates in Ad-hoc or Infrastructure mode for wireless communication.
Sets priorities for multiple available WLAN profiles in Infrastructure Mode for roaming behavior.
Defines the NPort's roaming behavior, specifying how it connects to different Access Points.
Sets a signal strength threshold for disconnecting from an AP and reconnecting to another.
Configures general properties for a WLAN profile, including network type and profile name.
Determines the wireless standard (802.11a/b/g) used by the NPort for communication.
Specifies the SSID (name) of the wireless network for NPort to connect to.
Configures security parameters like authentication and encryption for the WLAN profile.
Specifies how wireless devices are authenticated (Open System, Shared Key, WPA, WPA2).
Selects the type of encryption (WEP, TKIP, AES-CCMP) for wireless communication security.
Sets a pre-shared key for WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK authentication, matching the AP's passphrase.
Configures WEP key length, index, and source for wireless data encryption.
Explains how to configure all settings under the Serial Port Settings folder in the NPort web console.
Configures the operation mode and related settings for serial ports 1 and 2 on the NPort.
Specifies the type of application for the serial port, determining available operation modes.
Selects the serial port's operation mode (RealCOM, TCP Server, etc.) based on the application type.
Configures RealCOM mode settings like TCP alive check time, max connections, and IP handling.
Configures TCP Server mode settings like TCP alive check time, inactivity time, and max connections.
Configures TCP Client mode settings like TCP alive check time, inactivity time, and IP handling.
Configures UDP mode settings like destination address, listen port, and packet length.
Configures Pair Connection Master/Slave settings, extending RS-232 transmission.
Configures Ethernet Modem mode, including TCP alive check time.
Configures Terminal ASCII mode settings like TCP alive check time, inactivity time, and auto-link protocol.
Configures Terminal Binary mode for file transfers (XMODEM/ZMODEM), allowing one session.
Configures Reverse Terminal mode settings like TCP alive check time, inactivity time, and TCP port.
Configures serial communication settings such as Baud rate, Data bits, Stop bits, Parity, Flow Control, FIFO, and Interface.
Enables or disables port buffering and serial data logging for each serial port.
Allows enabling and entering a welcome message to greet terminal users.
Explains how to configure all settings under the System Management folder in the NPort web console.
Restricts NPort access by IP address, allowing only specified addresses or ranges.
Configures the NPort's SNMP agent, including enabling/disabling and community strings.
Specifies the read community string for SNMP Agent queries, used for weak authentication.
Specifies the write community string for SNMP Agent changes, used for weak authentication.
Assigns host names to IP addresses for use in the web console, allowing hostname usage instead of IPs.
Manages local user authentication for terminal access, supporting up to 64 entries.
Specifies settings for an external RADIUS server for authentication.
Selects the types of events to be logged by the NPort for system monitoring.
Specifies how the NPort notifies users of system and configuration events via Mail or Trap.
Specifies how the NPort notifies users of DCD and DSR signal changes for each serial port.
Configures how and where emails are sent for automatic notification of system and serial port events.
Specifies SNMP trap settings for automatic notification of system and serial port events.
Enables or disables access to HTTP, HTTPS, Telnet, and SSH consoles.
Tests Ethernet connections or verifies IP addresses by performing a ping test.
Updates the NPort firmware by selecting and uploading a firmware file.
Loads previously saved or exported NPort configurations, including IP settings.
Saves the NPort's current configuration to a file on the local host.
Resets all NPort settings to factory defaults, with an option to preserve IP settings.
Allows changing the NPort's console password or removing password protection.
Loads the Ethernet SSL certificate file into the NPort.
Imports a WLAN SSL certificate, which is often auto-generated by default.
Loads the WPA server certificate for authenticating the RADIUS server in WLAN Security.
Loads the WPA user certificate for NPort authentication when using WPA/WPA2/TLS.
Loads the WPA user private key for NPort authentication with WPA/WPA2/TLS.
Deletes installed certificates or WPA keys from the NPort.
Explains how to use System Monitoring functions to monitor various aspects of NPort operation.
Monitors current operation mode and host connection status for each serial port.
Monitors signal and data transmission status, including packet counts, for each serial port.
Displays current frame, parity, overrun, and break errors for each serial port.
Displays the current communication settings for each serial port.
Displays the current status of any network connection to the NPort.
Provides current network transmission statistics for Ethernet and WLAN interfaces.
Allows viewing and downloading serial port data logs in ASCII or HEX format.
Displays and manages the log of NPort system events.
Displays the current WLAN settings and status of the NPort.
Views live wireless signal strength and characteristics for site survey purposes.
Explains how to save configuration changes and restart the NPort for settings to take effect.
Saves all configuration changes to the NPort, making them effective upon restart.
Restarts the NPort system, applying saved configuration changes.
Restarts selected serial ports on the NPort, applying any saved configuration changes.
Describes installation of NPort Windows Driver Manager, Search Utility, and Linux/UNIX drivers.
Installs and manages NPort COM drivers for COM mapping, treating remote ports as local COM ports.
Step-by-step guide for installing the NPort Windows Driver Manager utility.
Adds COM ports to the PC mapped to NPort serial ports in Real COM mode.
Modifies settings of mapped serial ports, assigning COM numbers and configuring advanced options.
Provides network utility for finding, configuring, and upgrading NPort devices.
Step-by-step guide for installing the NPort Search Utility software.
Uses NPort Search Utility to locate NPort device servers on the network by MAC address.
Changes the IP address of NPort device servers found on the network using NPort Search Utility.
Upgrades NPort firmware using NPort Search Utility by selecting a firmware file.
Maps Linux TTY ports to NPort serial ports, allowing serial port access as local TTY ports.
Uses mxaddsvr utility to map NPort serial ports to host TTY ports, either automatically or manually.
Maps UNIX host TTY ports to NPort serial ports for serial port access.
Steps for installing the MOXA TTY driver on UNIX systems.
Modifies moxattyd.cf configuration file and adds entries to /etc/inittab to start the moxattyd daemon.
Lists standard MIB-II groups and variable implementations for the NPort.
Lists ICMP MIB variables supported by the NPort SNMP agent.
Lists UDP MIB variables supported by the NPort SNMP agent.
Lists TCP MIB variables supported by the NPort SNMP agent.
Lists SNMP MIB variables supported by the NPort SNMP agent.
Details RS-232 MIB objects, including generic groups, port tables, and signal tables.
Describes how the NPort handles TCP/IP connection requests from remote Ethernet modems or hosts.
Explains how the NPort accepts ATD commands to initiate TCP connections to remote devices.
Initiates disconnection from data mode by sending '+++' and entering 'ATH' command.
Lists common AT commands supported by the NPort in Ethernet Modem mode, with descriptions and remarks.
Details the purpose and default values of NPort S registers, used for modem control.
| Serial Interface | RS-232/422/485 |
|---|---|
| Wireless Interface | IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n |
| Category | Serial Device Server |
| Ethernet Interface | 10/100 Mbps |
| Power Input | 12 to 48 VDC |
| Security | WEP/WPA/WPA2 |
| Certifications | CE, FCC, UL, cUL |