APPENDIX B APPLICATION NOTES
B-1
2φ
φφ
φ CT Configuration
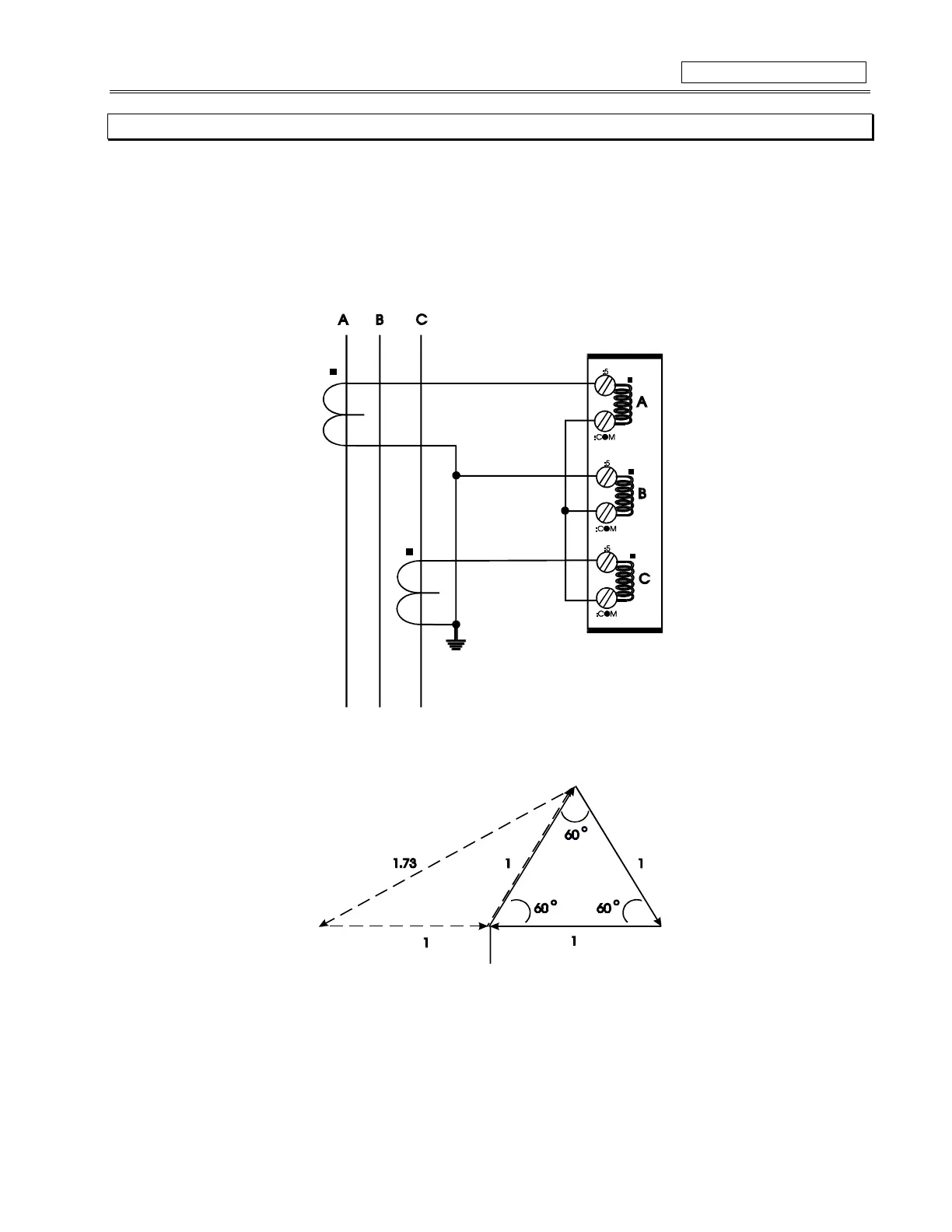
The purpose of this Appendix is to illustrate how two CT’s may be used to sense three phase currents.
The proper configuration for the use of two CTs rather than three to detect phase current is shown. Each of the two CTs acts as a cur-
rent source. The current that comes out of the CT on phase ‘A’ flows into the interposing CT on the relay marked ‘A’. From there, the
current sums with the current that is flowing from the CT on phase ‘C’ which has just passed through the interposing CT on the relay
marked ‘C’. This ‘summed’ current flows through the interposing CT marked ‘B’ and from there, the current splits up to return to its re-
spective source (CT).
Polarity is very important since the value of phase ‘B’ must be the negative equivalent of 'A' + 'C' in order
for the sum of all the vectors to equate to zero.
Note, there is only one ground connection as shown. If two ground connections are
made, a parallel path for current has been created.
In the two CT configuration, the currents will sum vectorially at the common point of the two CTs. The diagram illustrates the two possi-
ble configurations. If one phase is reading high by a factor of 1.73 on a system that is known to be balanced, simply reverse the polarity
of the leads at one of the two phase CTs (taking care that the CTs are still tied to ground at some point).
Polarity is important.
To illustrate the point further, the diagram here shows how the current in phases 'A' and 'C' sum up to create phase 'B'.
 Loading...
Loading...