SHAPING THE FUTURE OF SATELLITE COMMUNICATIONS
8 TECHNOLOGY
This chapter describes the DVB-S and DVB-S2 modulation standards and the
processing mode of the EL170/970/470 devices.
8.1 Modulation Standards
8.1.1 DVB-S
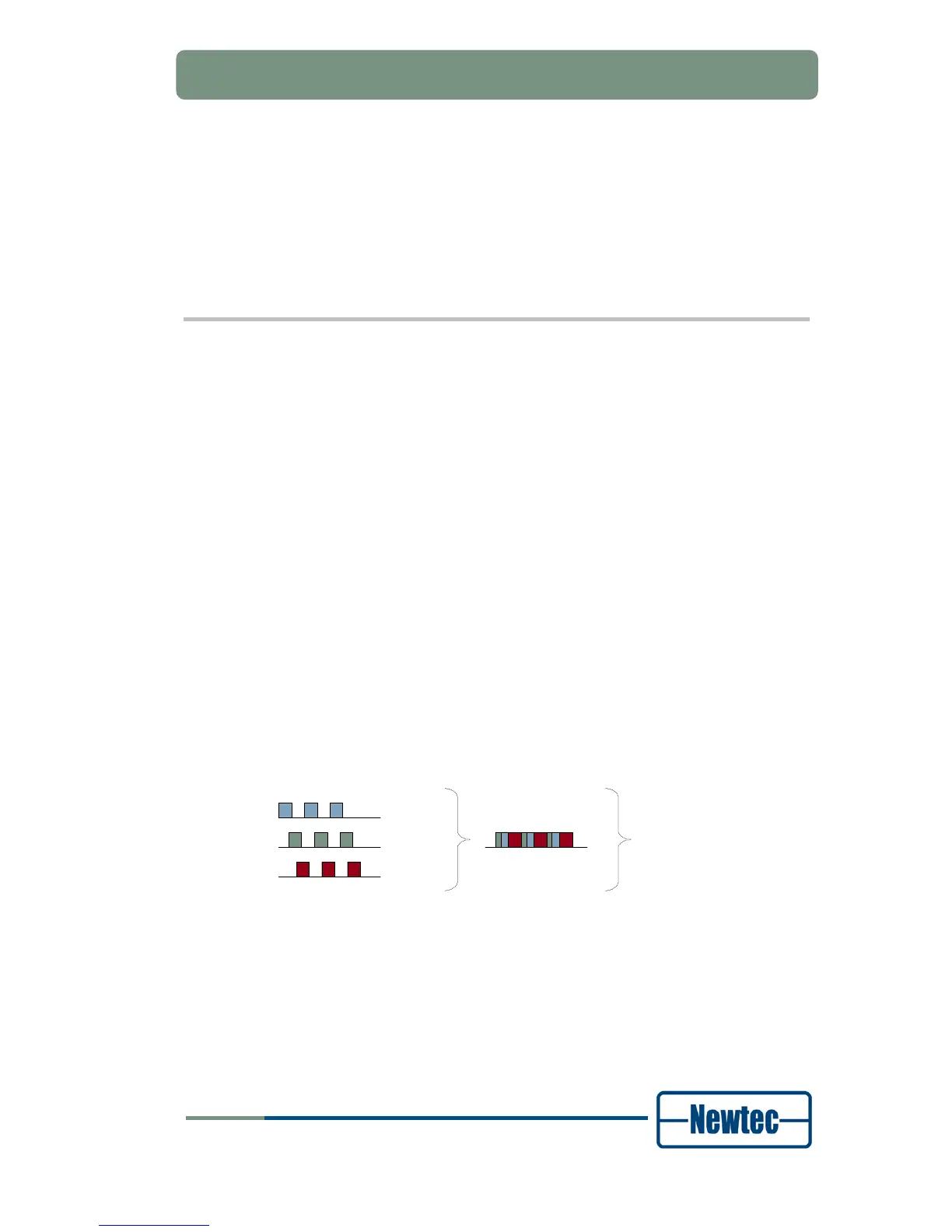
DVB-S is the first generation of a standard for digital broadcasting via satellite.
DVB-S was designed to carry MPEG-2 transport streams over satellite. MPEG-2
transport streams typically carry one or several television or radio services
multiplexed into a synchronous bit stream. All service components are divided in
short packets of 188 bytes, each identified by a Program Identification (PID) tag in
the header of the packet.
Generic data can also be carried in MPEG transport streams, provided that it is first
encapsulated in the transport stream packets. The most common way to
encapsulate IP data into MPEG streams is called Multi Protocol Encapsulation
(MPE) and is also specified by a DVB standard.
The total bit rate of the transport stream is constant but can typically be adjusted to
match the needs of the satellite link. If the desired transport stream rate is greater
than the sum of the carried components, null packets are added to the stream by
the multiplexer or the modulator. This operation is called rate adaptation.
DVB-S uses QPSK modulation and concatenated error protection based on a
convolutional Viterbi code and a shortened RS code.
Figure 58- DVB-S used to Carry Video, Audio and Data in an MPEG Transport Stream
 Loading...
Loading...