SHAPING THE FUTURE OF SATELLITE COMMUNICATIONS
2.1.2 IP Bridging in the Satellite Subnet
2.1.2.1 Introduction
IP bridging is more efficient than Ethernet bridging.
IP bridging has the following advantages:
• It reduces the overhead on the satellite link:
the Ethernet link is terminated in the same way as a router does.
The Ethernet header and optional VLAN header are not transmitted on the
satellite link;
• Ethernet broadcast traffic, ARP traffic and other L2 control packets (pause
frames, 802.1x, LACP, ...) are not sent over the satellite link when IP bridging is
selected.
For IP bridging further partition of the satellite subnet into distinct IP ranges is
needed. A part of the IP addresses is at the local side of the satellite, part of the
IP addresses is at the remote end of the satellite link (there can be multiple
remote sites).
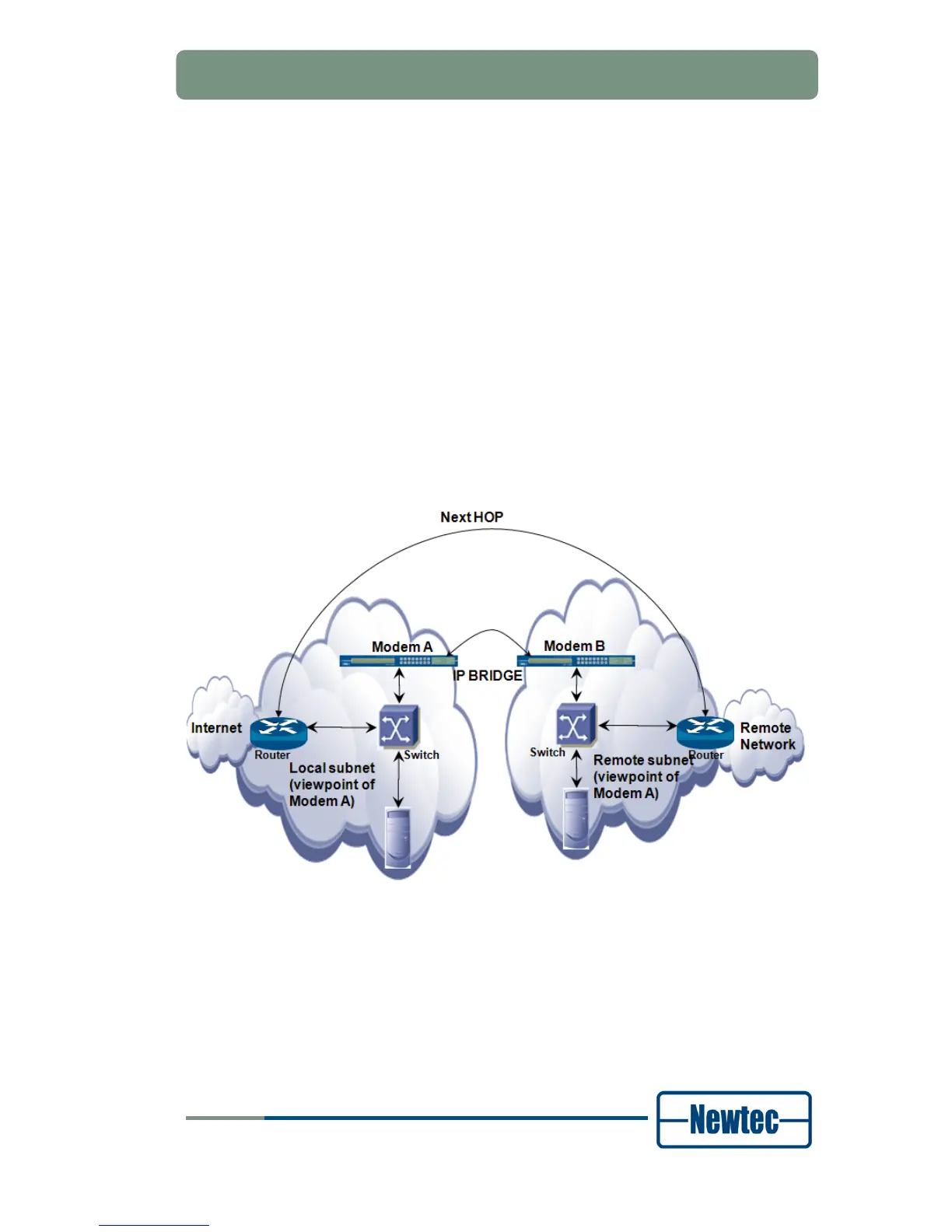
Figure 3 - IP Bridge
The routers and the IP hosts in the satellite subnet think that the local and remote
parts of the subnet are 1 big subnet (e.g. a /24 subnet with 256-2 = 254 host IP
addresses). Only the modems/modulators/demodulators must know which IP
range exists locally, and which IP range is located in a remote site.
 Loading...
Loading...