9410 series Logging
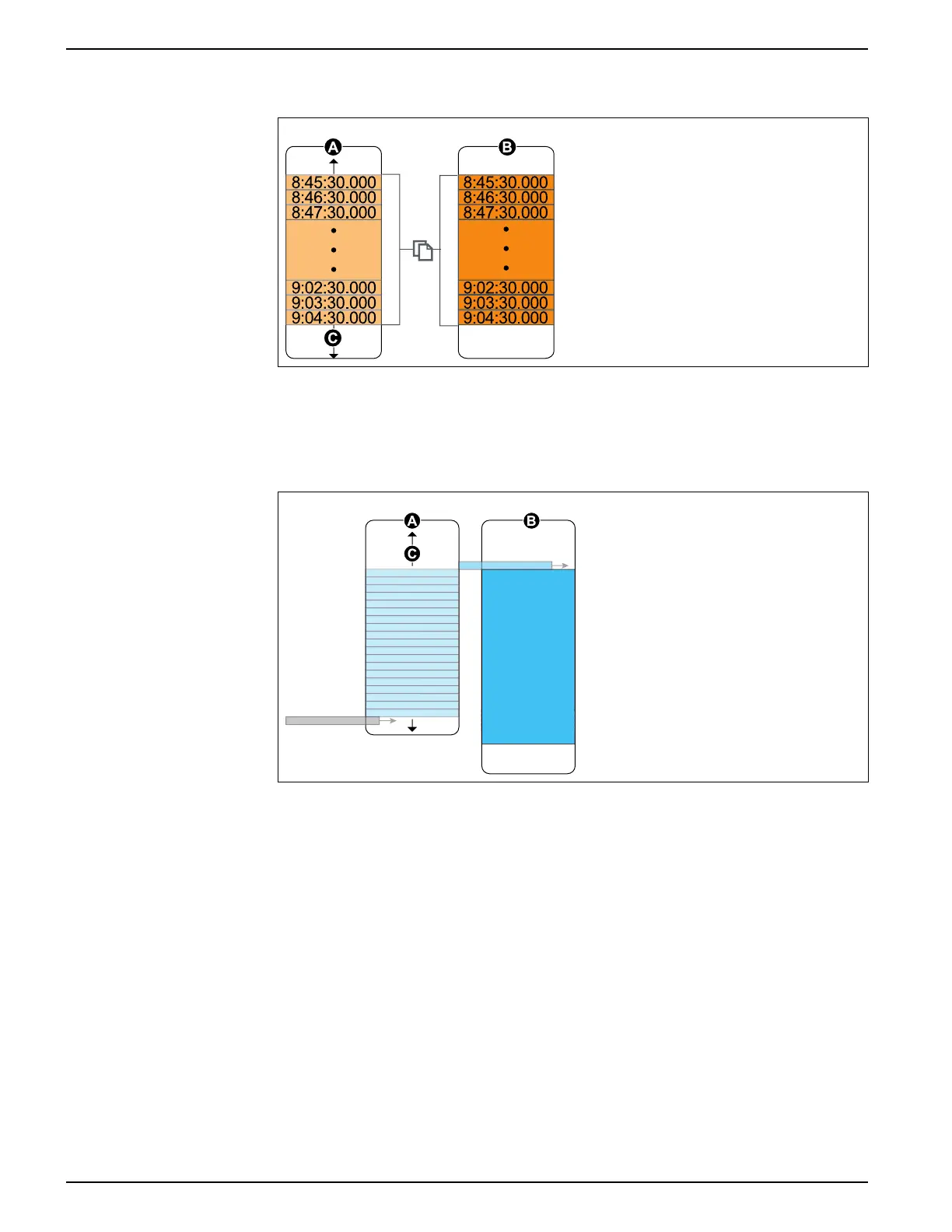
Example: fully buffered log records replicated from short-term to long-term
memory
8:46:30.000
8:47:30.000
9:02:30.000
9:03:30.000
9:04:30.000
8:45:30.000
8:46:30.000
8:47:30.000
9:02:30.000
9:03:30.000
9:04:30.000
8:45:30.000
A. Log buffer
B. Long-term memory
C. Total available space in
the log buffer (for
example, 20 records)
In this example, the log buffer equals the log depth and all the records are replicated in
both the short-term memory and the long-term memory.
Example: Partially buffered log records replicated from short-term memory to
long-term memory
A. Log buffer
B. Long-term memory
C. Total available space in
the log buffer (for
example, 20 records)
In this example, the buffer depth equals 20. The first record has already replicated to
the long-term memory, making room in the log buffer for the new records (including the
newest record, in gray).
Example: Resulting gaps in data when a partially buffered log is full
However, depending on your configuration, there may be instances where the log
buffer fills up faster than it can replicate records to long-term memory. In this case, you
may lose records and see gaps in your data.
132 7EN05-0336-03

 Loading...
Loading...











