Program instructions
7.6 Counters
S7-200 SMART
System Manual, V2.3, 07/2017, A5E03822230-AF
257
High-speed counter instructions
High-speed counters can count high-speed events that cannot be controlled by standard
counters. Standard counters operate at a slower rate that is limited by the PLC scan time.
You can use the HDEF and HSC instructions and create your own HSC routines, or you can
simplify the programming tasks by using the High Speed Counter wizard.
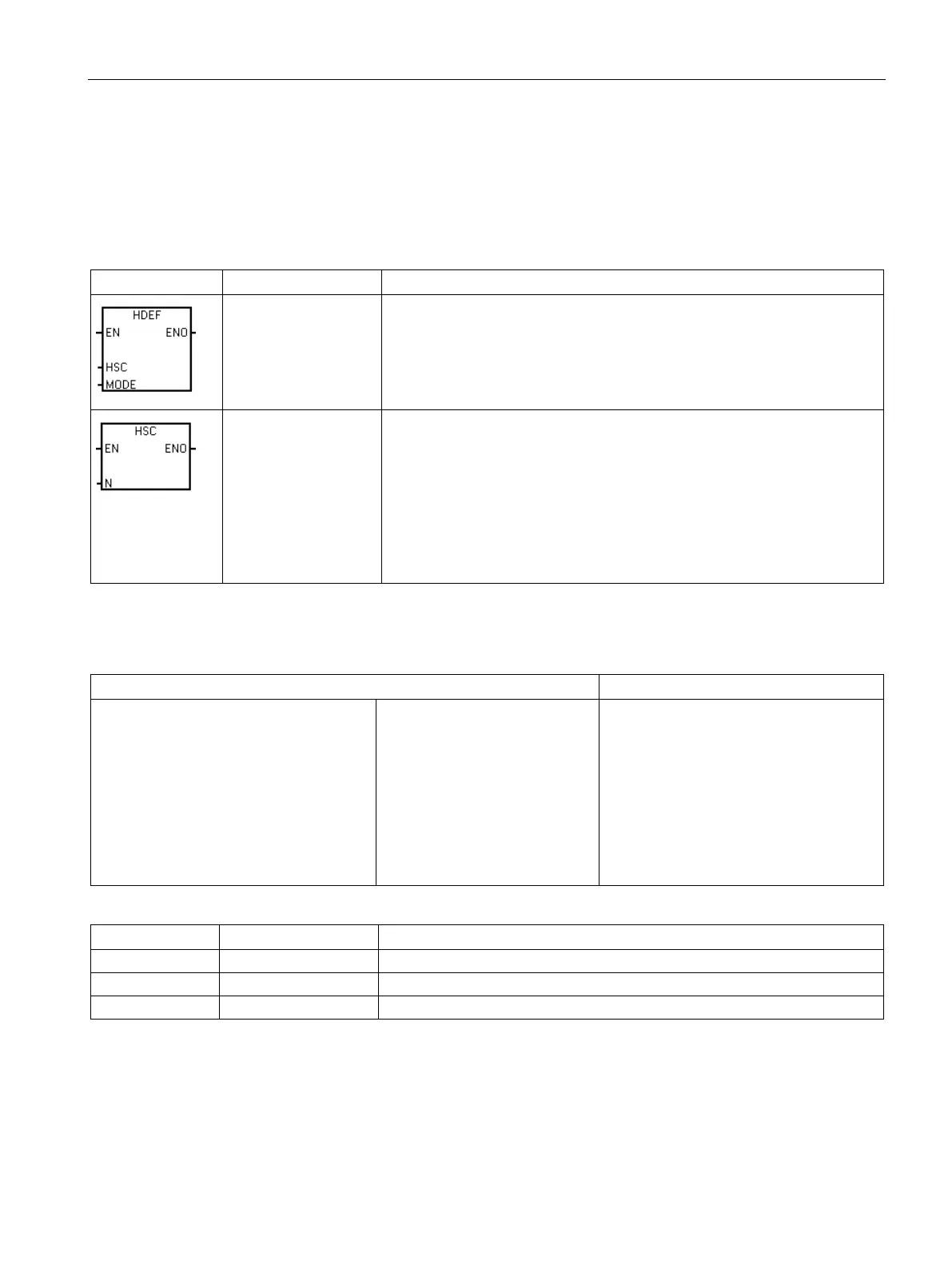
The High-Speed Counter Definition instruction (HDEF) selects the operating
mode of a specific high-speed counter (HSC0-5). The mode selection de-
fines the clock, direction, and reset functions of the high-speed counter.
You must use one High-Speed Counter Definition instruction for each of up
to six active high-speed counters. The S model CPUs
1
have six HSCs. The
2
The High-Speed Counter (HSC) instruction configures and controls the high-
speed counter, based on the state of the HSC special memory bits. The
parameter N specifies the high-speed counter number.
The high-
speed counters can be configured for up to eight different modes of
operation.
Each counter has dedicated inputs for clocks, direction control, and reset
where these functions are supported. In AB quadrature phase, you can se-
lect one times (1x) or four times (4x) the maximum counting rate. All coun-
ters run at maximum rates without interfering with one another.
S model CPUs: SR20, ST20, SR30, ST30, SR40, ST40, SR60, and ST60
2
C model CPUs: CR20s, CR30s, CR40s, and CR60s
Error conditions with ENO = 0
HDEF:
• 0003H Input point conflict
• 0004H Illegal instruction in interrupt
• 000AH HSC redefinition
• 0016H Attempted to use HSC or Edge
Interrupt on Input that is allocated for
use by Motion Functionality
• 0090H Invalid HSC number
HSC:
• 0001H HSC before HDEF
• 0005H Simultaneous
HSC/PLS
• 0090H Invalid HSC number
None
HSC number constant (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5)
Mode number constant: Eight possible modes (0, 1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, or 10)
HSC number constant (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5)

 Loading...
Loading...


















