Communication
11.3 Communication via PROFINET IO
Drive functions
818 Function Manual, 11/2017, 6SL3097-4AB00-0BP5
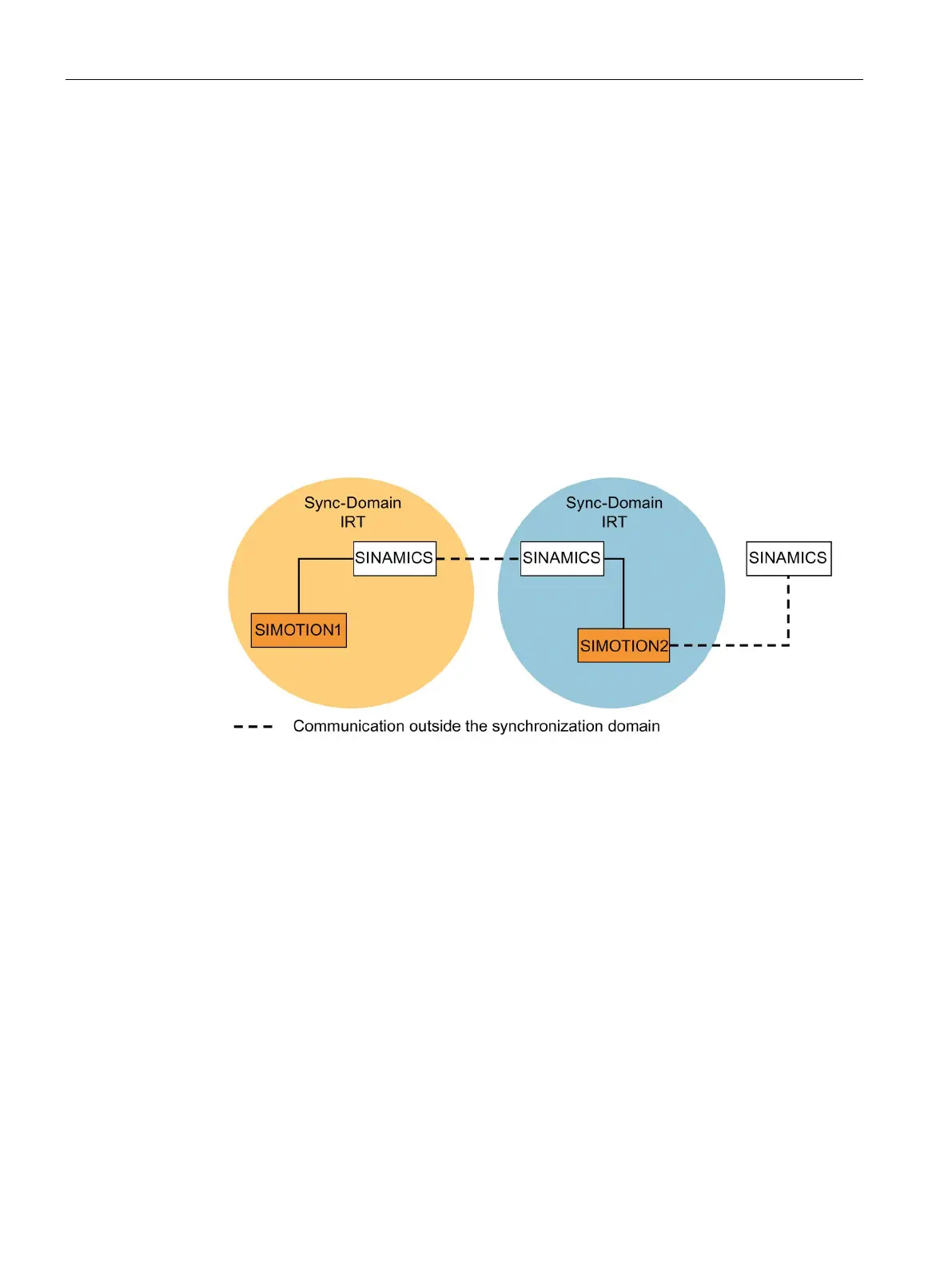
The sum of all devices to be synchronized form a synchronization domain. The whole
domain must be set to a single, specific RT class (real-time class) for synchronization.
Different synchronization domains can communicate with one another via RT.
For IRT, all IO devices and IO controllers must be synchronized with a common
synchronization master.
RT allows an IO controller to communicate with a drive unit outside a synchronization
domain or "through" another synchronization domain. As of version 5.4 SP1, STEP 7
supports multiple synchronization domains on a single Ethernet subnet.
Example:
● Synchronization domain IRT: SIMOTION2 with SINAMICS
● SINAMICS drive that is assigned to the I/O system of SIMOTION1. This is arranged in the
topology in such a way that its RT communication must be established through the IRT
synchronization domain.
Figure 11-30 RT communication across the limits of synchronization domains
Update cycles and send cycles for RT classes
Definition of the update time / send cycle:
If we take a single IO device in the PROFINET IO system as an example, this device has
been supplied with new data (outputs) by the IO controller and has transferred new data
(inputs) to the IO controller within the update time. The send cycle is the shortest possible
update cycle.
All cyclic data is transferred within the send cycle. The actual send cycle that can be set
depends on various factors:
● Bus load
● Type of devices used
● Computing capacity available in the IO controller
● Supported send clocks in the participating PROFINET devices of a synchronization
domain. A typical send cycle is 1 ms.

 Loading...
Loading...























