Tool offsets
7.3 Special handling of tool offsets
Job planning
Programming Manual, 07/2010, 6FC5398-2BP40-0BA0
401
Further information
Distinguishing features
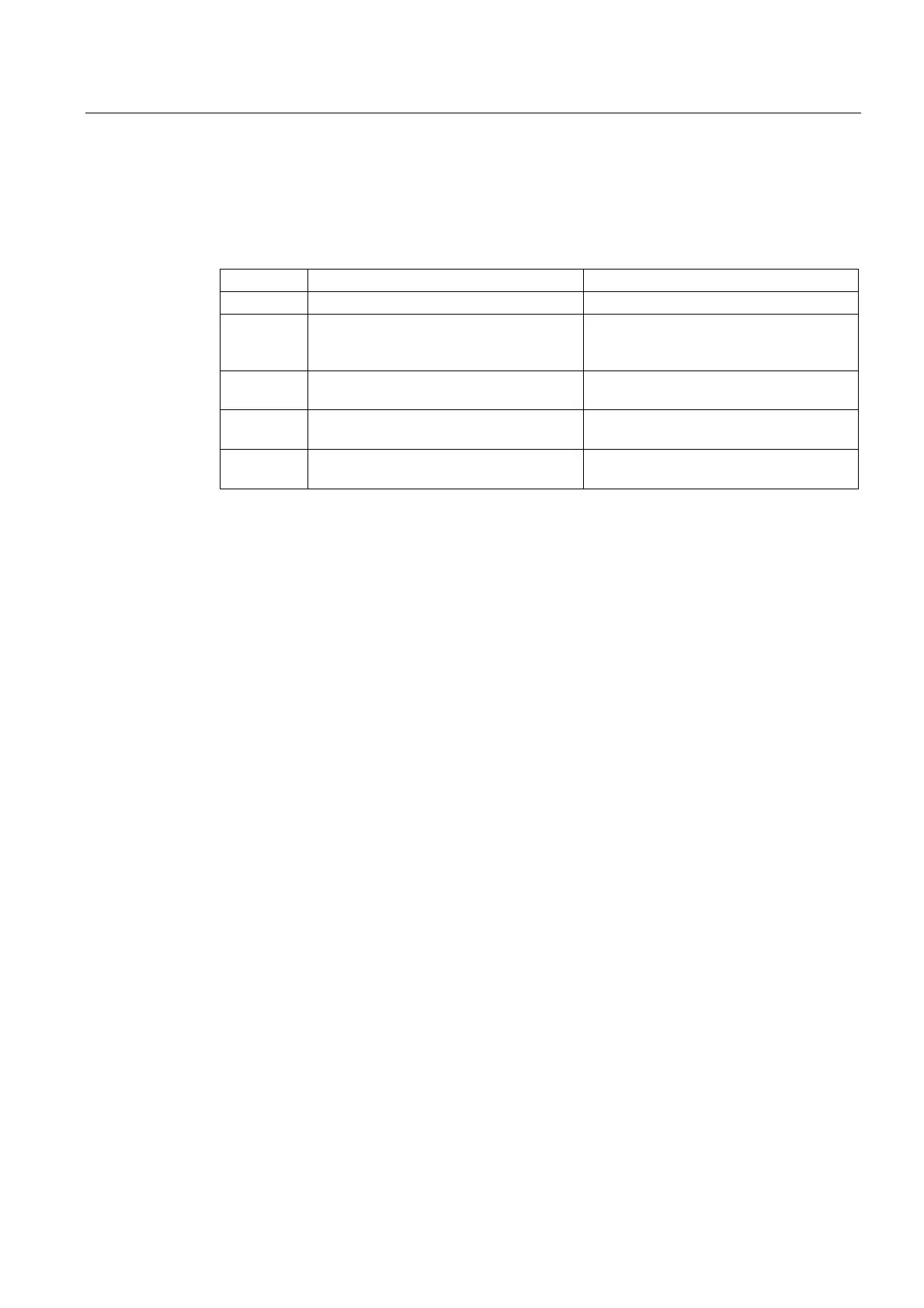
The most important distinguishing features are shown in the following table:
G code Wear value Active orientable toolholder
TOWSTD
Initial value, tool length Wear values are subject to rotation.
TOWMCS
Wear value in MCS.
TOWMCS is identical to
TOWSTD if a tool holder that can be
orientated is not active.
It only rotates the vector of the resultant
tool length without taking into account the
wear.
TOWWCS
The wear value is converted to the MCS in
the WCS.
The tool vector is calculated as for
TOWMCS
without taking into account the wear.
TOWBCS
The wear value is converted to the MCS in
the BCS.
The tool vector is calculated as for
TOWMCS
without taking into account the wear.
TOWTCS
The wear value is converted to the MCS in
the workpiece coordinate system.
The tool vector is calculated as for
TOWMCS
without taking into account the wear.
TOWWCS , TOWBCS, TOWTCS: The wear vector is added to the tool vector.
Linear transformation
The tool length can be defined meaningfully in the MCS only if the MCS is generated by
linear transformation from the BCS.
Non-linear transformation
For example, if with TRANSMIT a non-linear transformation is active, then when specifying
the MCS as requested coordinate system, BCS is automatically used.
No kinematic transformation and no orientable toolholder
If neither a kinematic transformation nor an orientable toolholder is active, then all the other
four coordinate systems (except for the WCS) are combined. It is then only the WCS, which
is different to the other systems. Since only tool lengths need to be evaluated, translations
between the coordinate systems are irrelevant.
References:
For more information on tool compensation, see:
Function Manual Basic Functions; Tool Offset (W1)

 Loading...
Loading...


















