Flexible Protection Functions
The flexible protection function is applicable for a variety of protection principles. The user can create up to 20
flexible protection functions and configure them according to their function. Each function can be used either
as an autonomous protection function, as an additional protective element of an existing protection function
or as a universal logic, e.g. for monitoring tasks.
Functional Description
General
The function is a combination of a standard protection logic and a characteristic (measured quantity or derived
quantity) that is adjustable via parameters. The characteristics listed in table 2-20 and the derived protection
functions are available.
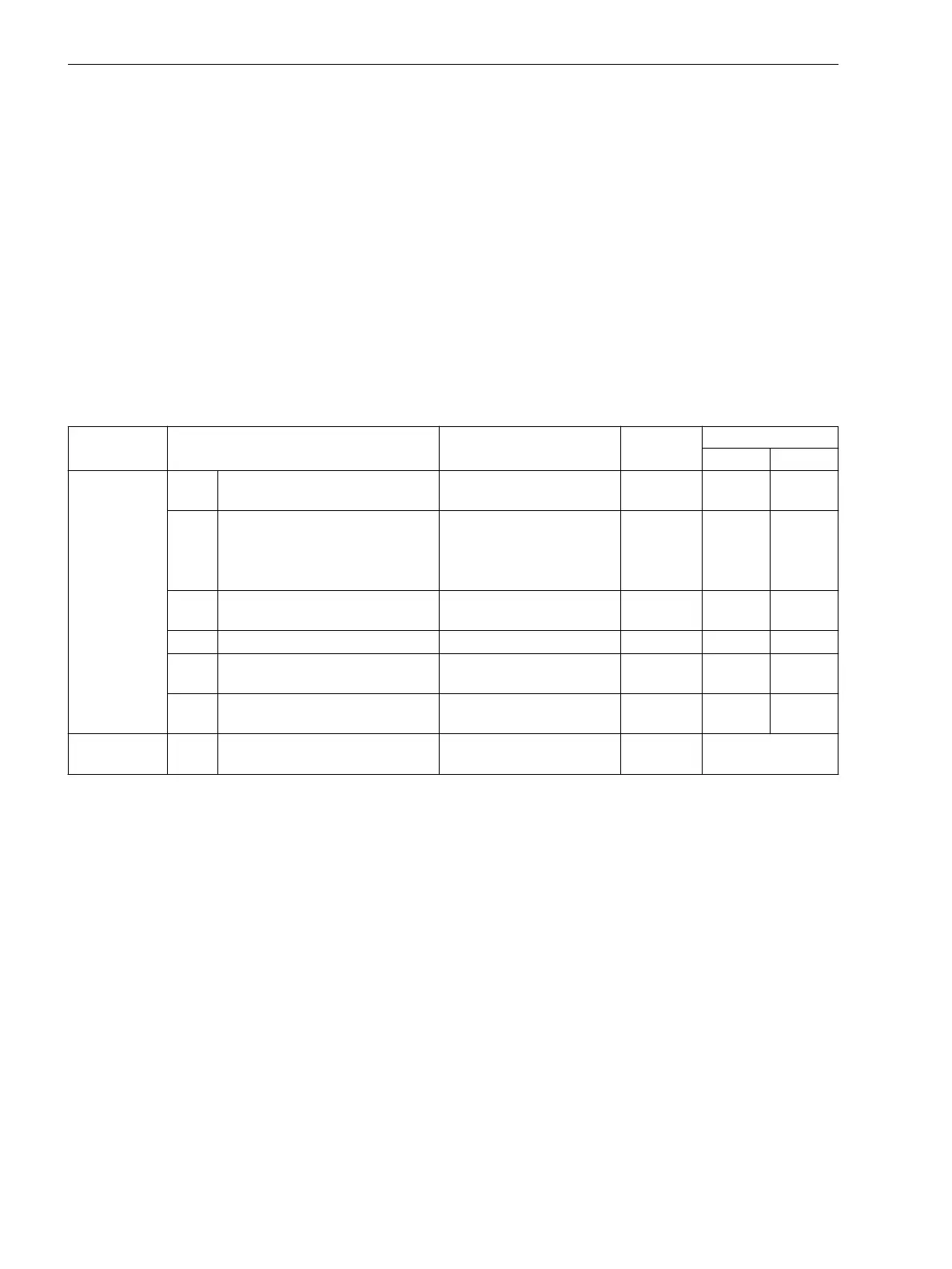
Table 2-11 Possible Protection Functions
Characteristic
Group
Characteristic / Measured Quantity Protective Function ANSI-No. Mode of Operation
3–phase 1–phase
Current
Ι
RMS value of fundamental
component
Time overcurrent protec-
tion
50, 50G X X
Ι
rms
True RMS (r.m.s. value) Time overcurrent protec-
tion
Thermal overload protec-
tion
50, 50G X X
3Ι
0
Zero sequence system Time overcurrent protec-
tion, ground
50N X
Ι1
Positive-sequence component X
Ι2
Negative-sequence component Negative sequence protec-
tion
46 X
Ι2/Ι1
Positive/negative sequence
component ratio
- X
Binary input – Binary input Direct coupling without phase
reference
The maximum 20 configurable protection functions operate independently of each other. The following
description concerns one function; it can be applied accordingly to all other flexible functions. The logic
diagram Figure 2-70 illustrates the description.
Functional Logic
The function can be switched ON and OFF or, it can be set to Alarm Only. In this status, a pickup condition
will neither initiate fault recording nor start the trip time delay. Tripping is thus not possible.
Changing the Power System Data 1 after flexible functions have been configured may cause these functions to
be set incorrectly. Message (FNo.235.2128
$00 inval.set
) reports this condition. The function is inactive
in this case and function's setting has to be modified.
Blocking Functions
The function can be blocked via binary input (FNo. 235.2110
>BLOCK $00
) or via local operating terminal
(“Control”->“Tagging”->“Set”). Blocking will reset the function's entire measurement logic as well as all running
times and indications. Blocking via the local operating terminal may be useful if the function is in a status of
permanent pickup which does not allow the function to be reset.
Parameter BLK f out of r allows you to specify whether the protection function is blocked if the meas-
ured power frequency is outside the operating range of the function (25 Hz to 70 Hz).
2.13
2.13.1
Functions
2.13 Flexible Protection Functions
174 SIPROTEC 4, 7SJ61, Manual
C53000-G1140-C210-6, Edition 05.2016

 Loading...
Loading...











