Argus Radar - SERIAL INTERFACE SPECIFICATIONS
988-10187-004 2.23
MWD – Wind direction and speed
The direction from which the wind blows across the earth’s surface, with respect to north,
and the speed of the wind.
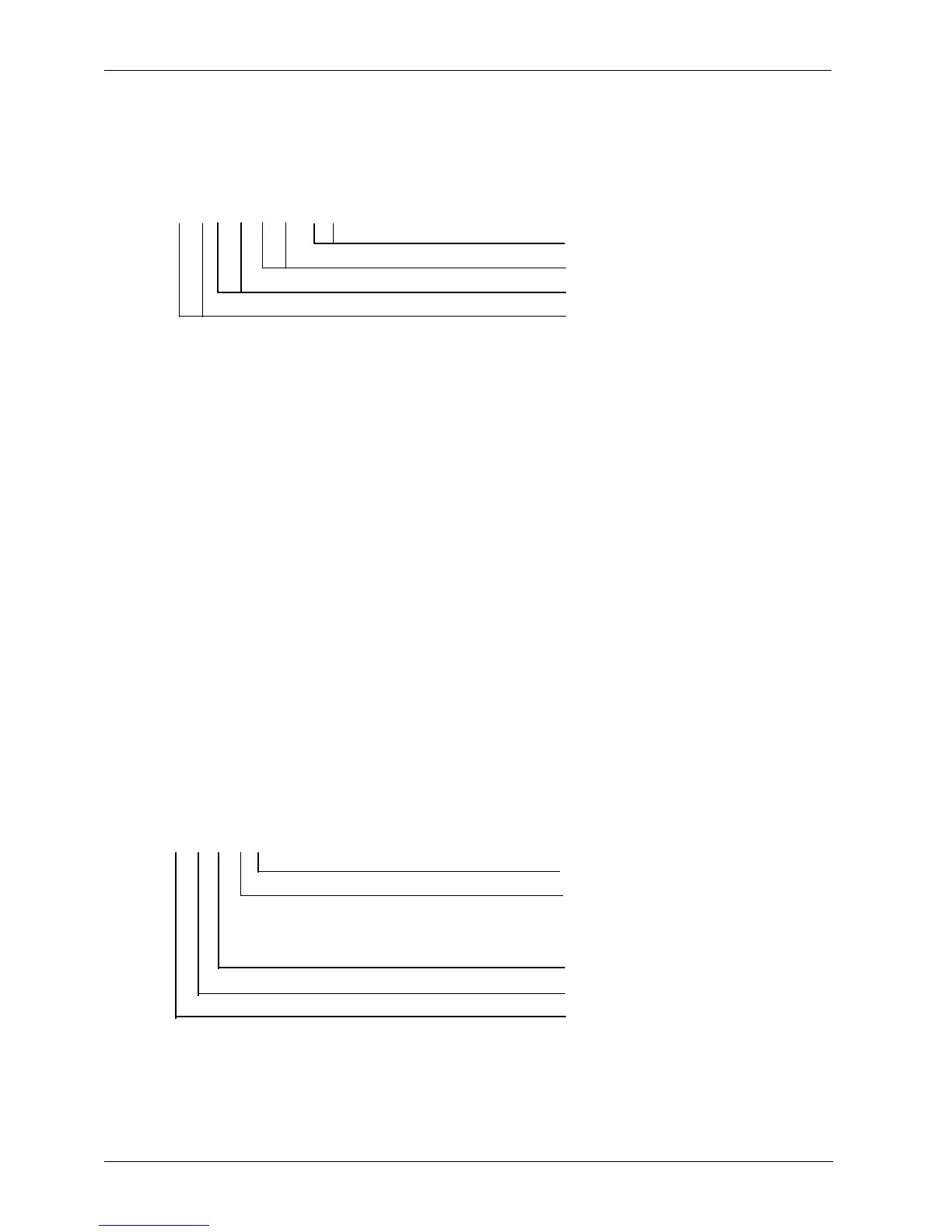
$--MWD, x.x,T,x.x,M,x.x,N,x.x,M*hh<CR><LF>
Wind speed, m/s
Wind speed, knots
Wind direction, 0° to 359° magnetic
Wind direction, 0° to 359° true
MWV – Wind speed and angle
When the reference field is set to R (Relative), data is provided giving the wind angle in
relation to the vessel's bow/centreline and the wind speed, both relative to the (moving)
vessel. Also called apparent wind, this is the wind speed as felt when standing on the
(moving) ship.
When the reference field is set to T (Theoretical/calculated wind), data is provided giving the
wind angle in relation to the vessel's bow/centreline and the wind speed as if the vessel was
stationary. On a moving ship, these data can be calculated by combining the measured
relative wind with the vessel's own speed.
Example 1 If the vessel is heading west at 7 knots and the wind is from the east at 10 knots
the relative wind is 3 knots at 180°. In this same example the theoretical wind is 10 knots at
180° (if the boat suddenly stops the wind will be at the full 10 knots and come from the stern
of the vessel 180° from the bow).
Example 2 If the vessel is heading west at 5 knots and the wind is from the southeast at 7,07
knots the relative wind is 5 knots at 270°. In this same example the theoretical wind is 7,07
knots at 225° (if the boat suddenly stops the wind will be at the full 7,07 knots and come
from the port-quarter of the vessel 225° from the bow).
$--MWV, x.x, a, x.x, a, A *hh<CR><LF>
Status, A = data valid V= data invalid
Wind speed units, K = km/h
M = m/s
N = knots
Wind speed
Reference, R = relative, T = true
Wind angle, 0° to 359°
 Loading...
Loading...