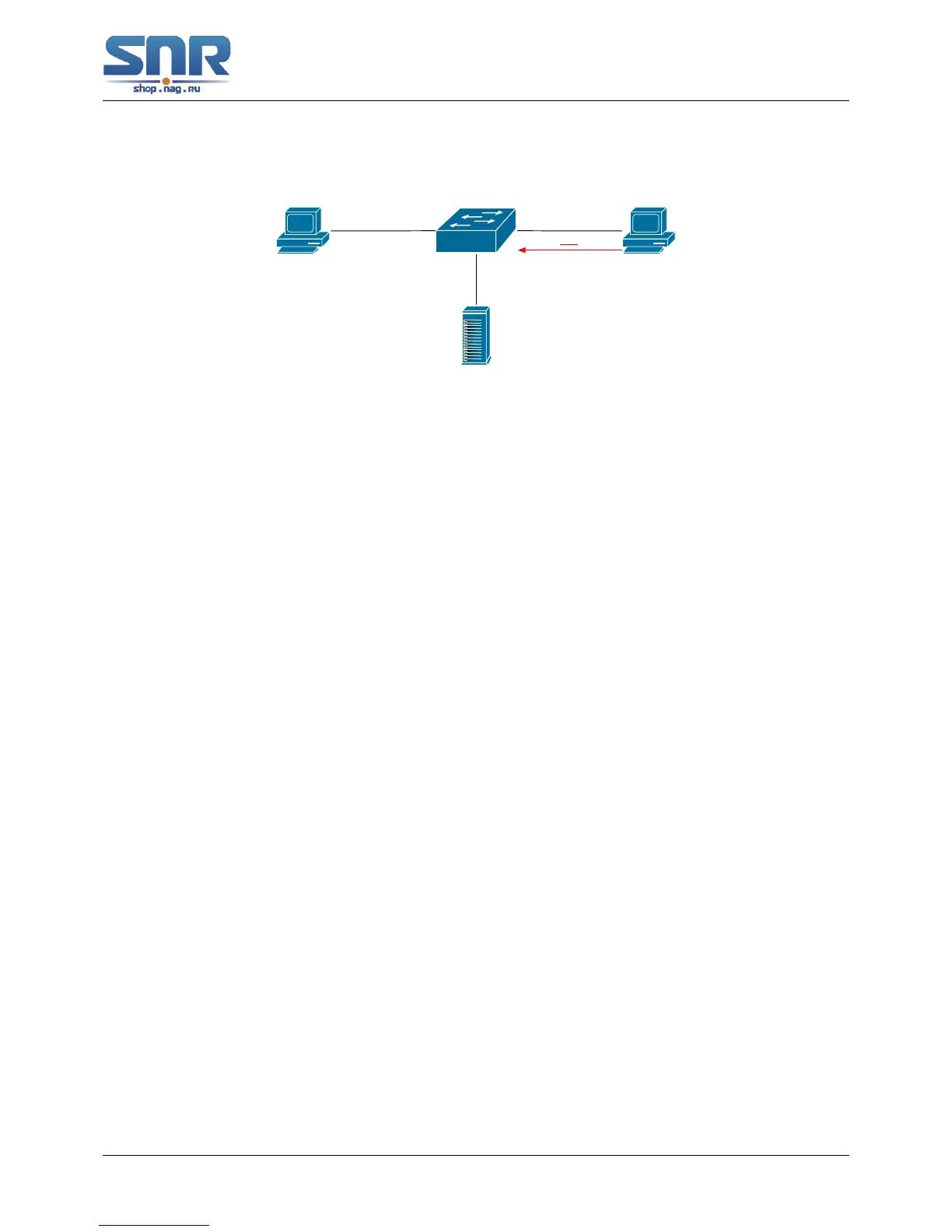
Figure 39.1: Sketch Map of TRUNK
As showed in the above chart, Mac-AA device is the normal user, connected to the non-trusted
port 1/0/1 of the switch. It operates via DHCP Client, IP 1.1.1.5; DHCP Server and GateWay
are connected to the trusted ports 1/0/11 and 1/0/12 of the switch; the malicious user Mac-BB is
connected to the non-trusted port 1/0/10, trying to fake a DHCP Server (by sending DHCPACK).
Setting DHCP Snooping on the switch will effectively detect and block this kind of network attack.
Configuration sequence is:
switch(config)#ip dhcp snooping enable
switch(config)#interface ethernet 1/0/11
switch(Config-Ethernet1/0/11)#ip dhcp snooping trust
switch(Config-Ethernet1/0/11)#exit
switch(config)#interface ethernet 1/0/12
switch(Config-Ethernet1/0/12)#ip dhcp snooping trust
switch(Config-Ethernet1/0/12)#exit
switch(config)#interface ethernet 1/0/1-10
switch(Config-Port-Range)#ip dhcp snooping action shutdown
39.4 DHCP Snooping Troubleshooting Help
39.4.1 Monitor and Debug Information
The 'debug ip dhcp snooping' command can be used to monitor the debug information.
39.4.2 DHCP Snooping Troubleshooting Help
If there is any problem happens when using DHCP Snooping function, please check if the problem
is caused by the following reasons:
• Check that whether the global DHCP Snooping is enabled;
• If the port does not react to invalid DHCP Server packets, please check that whether the port
is set as a non-trusted port of DHCP Snooping.
256

 Loading...
Loading...