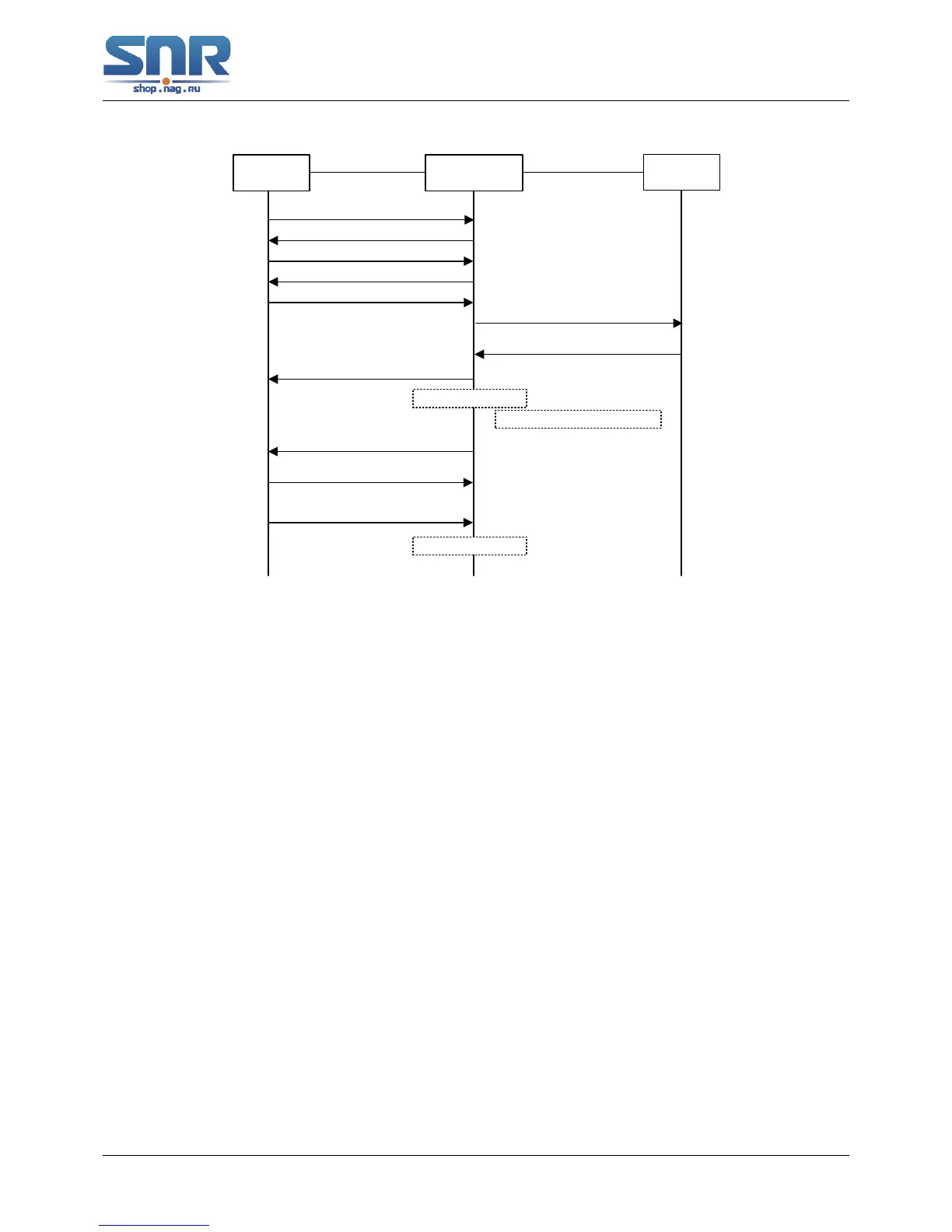
Supplicant
PAE
Authenticator
System PAE
RADIUS
server
EAPOL-Start
EAP-Request/Identity
EAP-Response/Identity
EAP-Request/MD5 Challenge
EAP-Response/MD5 Challenge
RADIUS Access-Request
(CHAP-Response/MD5 Challenge)
EAP-Success
RADIUS Access-Accept
(CHAP-Success)
EAPOL RADIUS
Handshake request packet
[EAP-Request/Identity]
Handshake response packet
{EAP-Response/Identity]
EAPOL-Logoff
...
Port authorized
Port unauthorized
Expiry of the handshake timer
Figure 45.12: the Authentication Flow of 802.1x EAP Termination Mode
• Tunnel-Medium-Type = 802 (6)
• Tunnel-Private-Group-ID = VLANID
The VLANID here means the VID of VLAN, ranging from 1 to 4094. For example, Tunnel-
Private-Group-ID = 30 means VLAN 30.
When the switch receives the assigned Auto VLAN information, the current Access port will
leave the VLAN set by the user and join Auto VLAN.
Auto VLAN won't change or affect the port's configuration. But the priority of Auto VLAN is
higher than that of the user-set VLAN, that is Auto VLAN is the one takes effect when the authen-
tication is finished, while the user-set VLAN do not work until the user become offline.
Notes: At present, Auto VLAN can only be used in the port-based access control mode, and
on the ports whose link type is Access.
2. Guest VLAN
Guest VLAN feature is used to allow the unauthenticated user to access some specified re-
sources.
The user authentication port belongs to a default VLAN (Guest VLAN) before passing the
802.1x authentication, with the right to access the resources within this VLAN without authenti-
cation. But the resources in other networks are beyond reach. Once authenticated, the port will
leave Guest VLAN, and the user can access the resources of other networks.
In Guest VLAN, users can get 802.1x supplicant system software, update supplicant system
or update some other applications (such as anti-virus software, the patches of operating system).
315

 Loading...
Loading...