96
The router supports the following two encryption algorithms:
DES: Data Encryption Standard. It uses a 56-bits key to encrypt 64 bits data with the
last 8 bits reserved for parity checking.3DES, or triple DES, uses three 56-bit keys to
encrypt.
AES: Advanced Encryption Standard. AES128/192/256 indicates that it uses
128/192/256-bit keys to encrypt.
Integrity
Verification
Algorithm
It specifies the verification algorithm applied to IKE conversation.
The router supports the following two verification algorithms:
MD5: The message digest algorithm generates a 128 bit digest to prevent data
tampering.
SHA1: The secure hash algorithm generates a 160 bit digest, which is more difficult to
crack than MD5.
It specifies the group information for Diffie-Hellman algorithm. It is used to generate the
key to encrypt an IKE tunnel.
It specifies the lifetime of IPSec SA.
Keys made with Perfect Froward Secrecy (PFS) in IKE period 2 have nothing to do with
the previous keys generated in period 1. Therefore, keys in period 2 remains secure even
if keys in period 1 have been compromised.
If the PFS is disabled, new session keys are made from the previous keys. Once the
previous keys are compromised, new session keys are insecure too, threatening the
communication security.
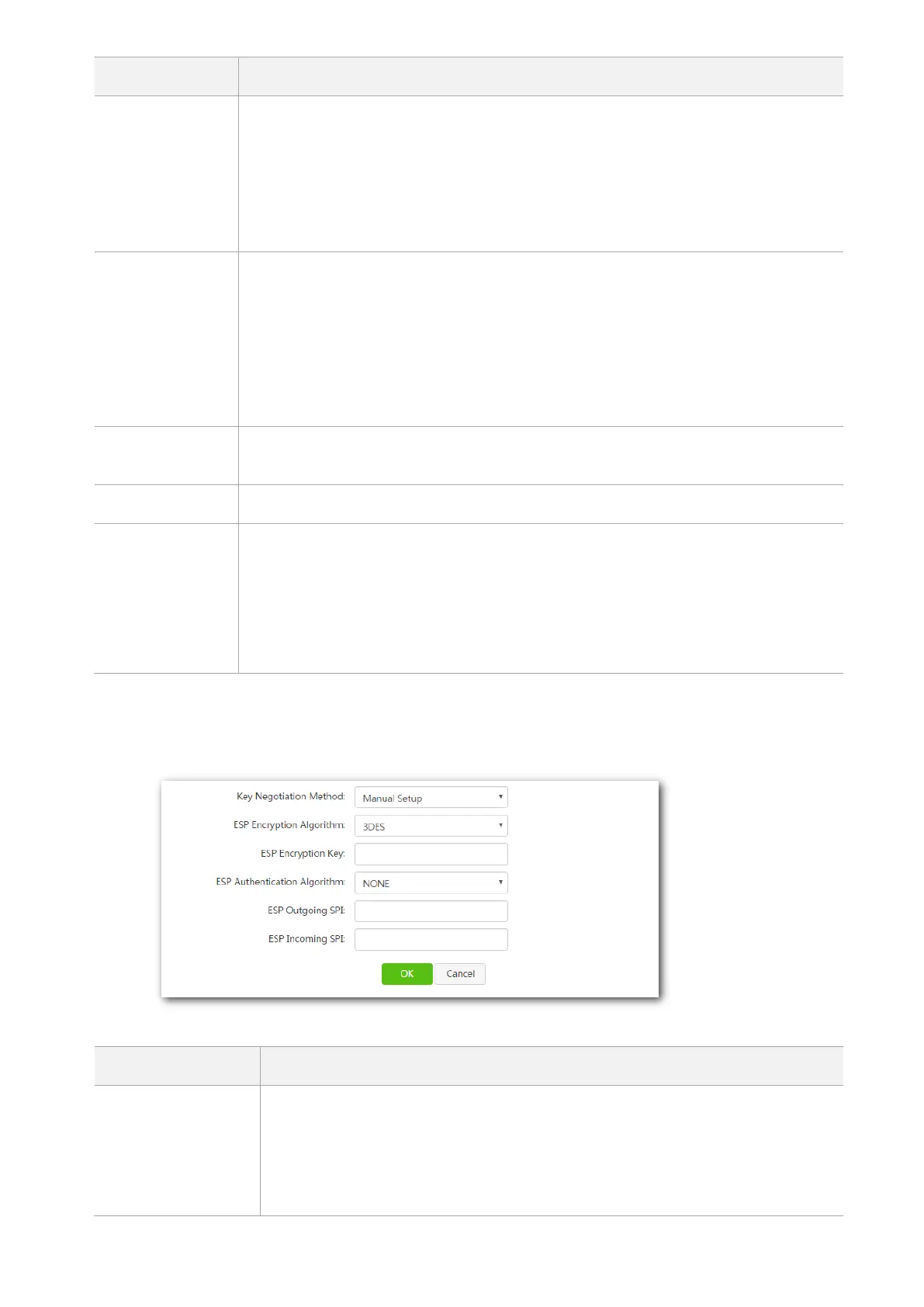
Key Negotiation Method – Manual Negotiation
To access the page, select Manual Negotiation from the drop-down list box of Key Negotiation Method.
Parameter description
The ESP encryption algorithm is configurable when ESP is selected as the Tunnel
Protocol.
The router supports the following two encryption algorithms:
DES: Data Encryption Standard. It uses a 56-bit key to encrypt a 64-bit data with
the last 8 bits reserved for parity checking. While the triple DES uses three 56-bit
 Loading...
Loading...