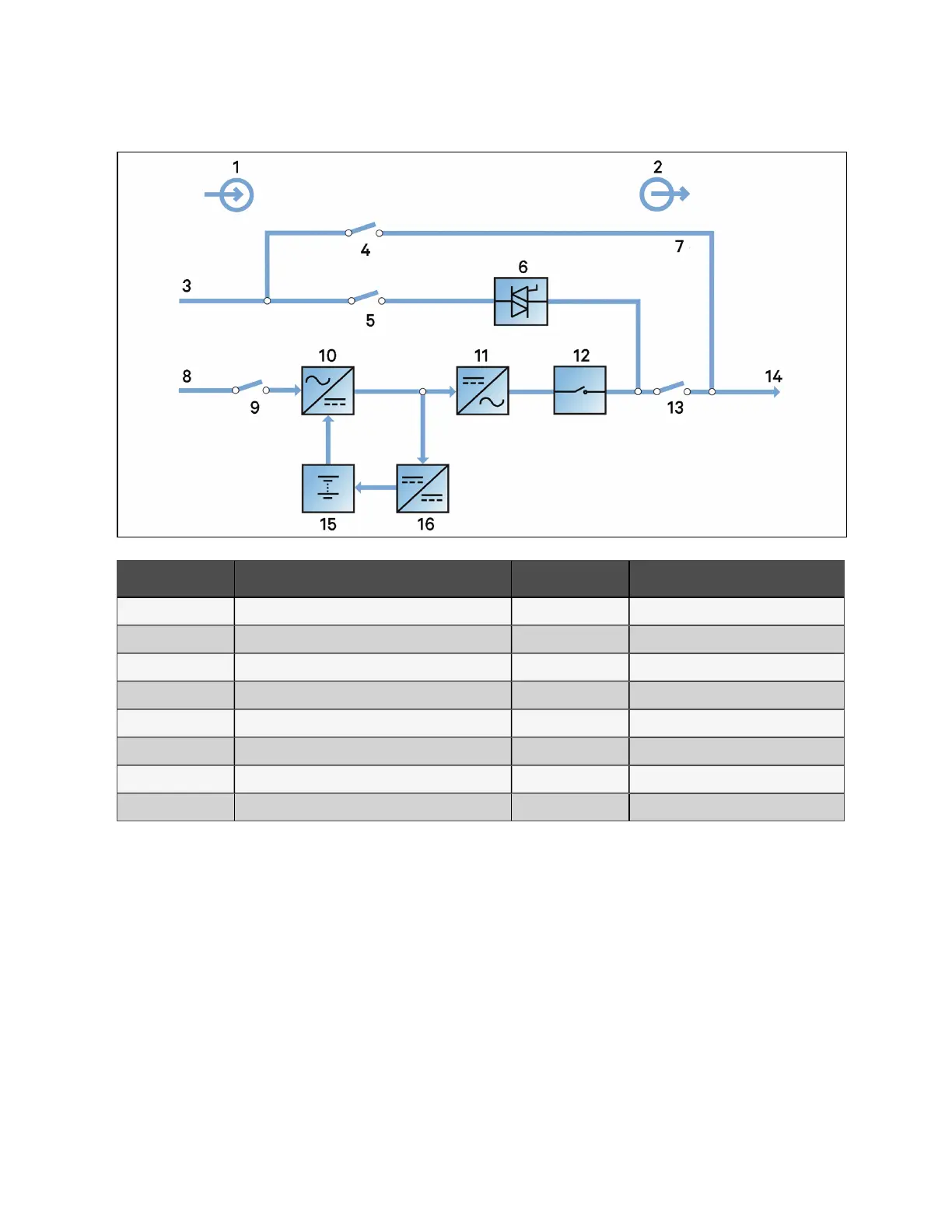
Figure 2.1 Block diagram for w orking principle of UP S sin gle m od ule
N o. Descriptio n N o. Descriptio n
1 Input 9 Rectifier input switch
2 Output 10 Rectifier
3 Bypass input 11 Inverter
4 Maintenance bypass switch 12 Inverter switch
5 Bypass input switch 13 Output switch
6 Static switch 14 UPS output
7 Maintenance bypass 15 Battery
8 Mains input 16 Battery charger
The UPS has its own battery charger and adopts advanced temperature compensation technology to effectively prolong the
battery service life. The inverter adopts three level T-type IGBT topology and uses advanced SVPWM control technology to
derive the stable AC voltage from the DC bus voltage.
When the mains is normal, the rectifier and inverter work together to supply the loads and charge the battery.
When the mains is abnormal, the rectifier stops working, and the battery supplies power to the loads through the inverter. If
the battery voltage falls to end of discharge (EOD) voltage and the mains still has not been recovered, the UPS will shut down
(if the system uses split bypass configuration and the bypass is normal, the system will transfer to bypass). The battery EOD
voltage is preset. When the mains is abnormal, the battery maintains the UPS operation till the battery voltage is reduced to
EOD voltage and the UPS shuts down, this time is called 'Backup Time'. The length of backup time depends on the battery
capacity and the loads.
2 Overview
3
Vertiv™ Liebert® APM Plus User Manual
 Loading...
Loading...











