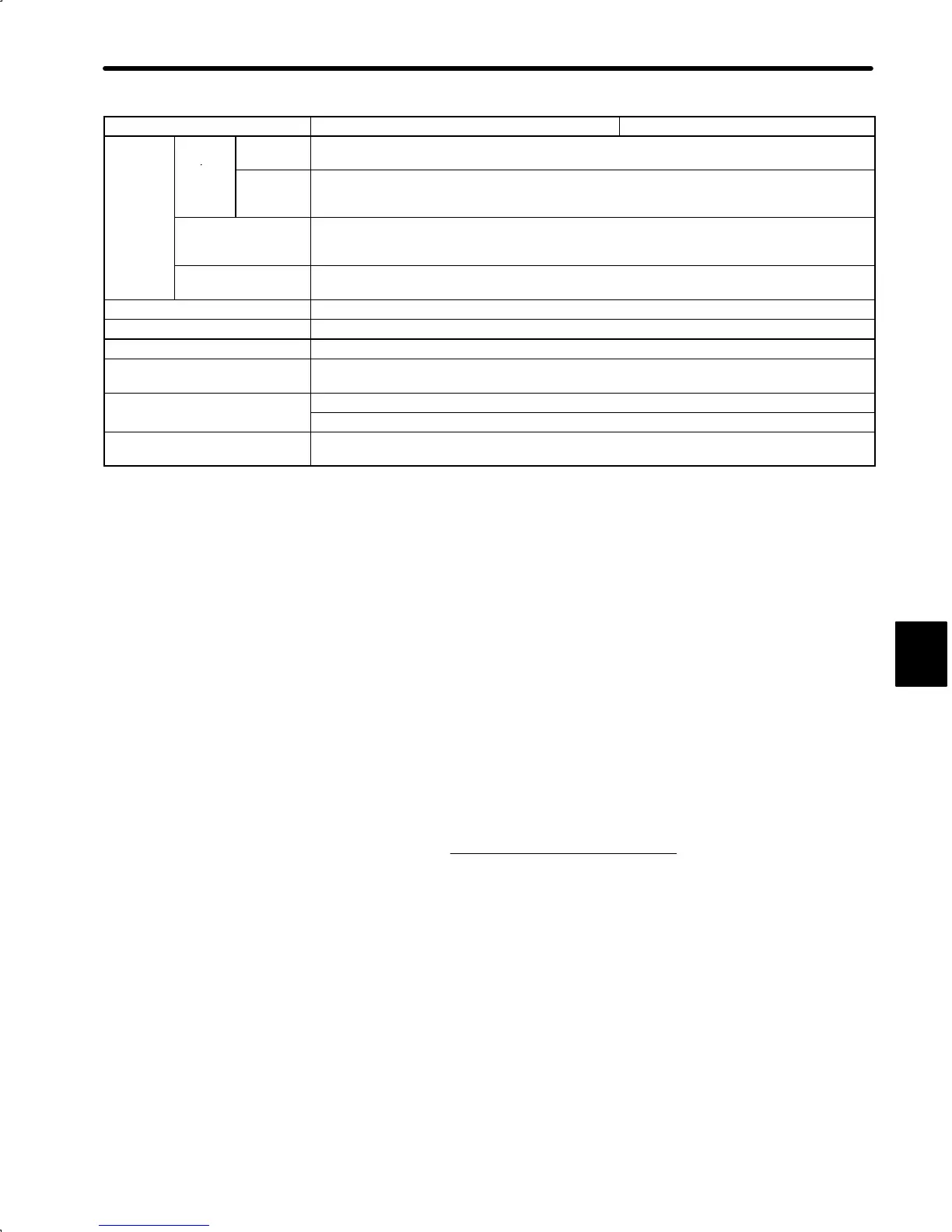
5.3 Servopack Rating and Specifications
237
Voltage 100 VAC200 VAC
I/O
Position
Output
Output
Form
A-, B-, C-phase line driver
Frequency
Dividing
Ratio
(16 to N) /N N=2048, 1024*
6
Sequence Input Servo ON, P drive (or motor forward/reverse by torque control, zero-clamp drive reference, or
internal setting speed), forward run stop (P-OT), reverse run stop (N-OT), current limit + selection (or
internal speed selection), current limit − selection (or internal speed selection), alarm reset
Sequence Output Current limit detection (or TGON), speed coincidence, external brake interlock, servo alarm, 3-bit
alarm codes
Dynamic Brake Operated at main power OFF, servo alarm or overtravel.
External Regenerative Unit Required when exceeding the allowable load inertia*
1
Overtravel Dynamic brake stop at P-OT or N-OT or deceleration stop
Protective Functions Overcurrent, grounding, overload, overvoltage, overspeed, reference input read error, overrun
prevention, origin error, CPU error, encoder error
Indicators
Alarm and power LEDs
Programming panel is available as an option
Others Torque control, zero clamp operation (position loop stop}, soft start/stop, speed coincidence, brake
interlock signal output, reverse run connection, JOG run, auto-tuning
*
1
Allowable load inertia ranges require no optional external regenerative unit. Values
are 30 times the moment of inertia for 30 W (0.04 HP) to 200 W (0.27 HP) Servomo-
tors, and 20 times for 400 W (0.53 HP) and 750 W (1.01 HP) Servomotors. If load iner-
tias exceed these ranges, restrict the operation or use a regenerative unit.
*
2
Supply voltage should not exceed 230 V + 10% (253 V) or 115 V + 10% (127 V). A
step-down transformer is required if the voltage should exceed these values.
*
3
Use within the ambient temperature range. When enclosed in a box, the internal tem-
peratures must not exceed the ambient temperature range.
*
4
The lowest speed of the speed control range is the speed at which the motor does not
stop under 100% load.
*
5
Speed regulation is defined as follows:
Speed regulation =
No-load-speed – Full-load-speed
Rated speed
× 100%
The motor speed may change due to voltage variations or amplifier drift and changes
in processing resistance due to temperature variation.
These ratios of the speed changes to the rated speed represent the speed regulation
due to voltage and temperature variations.
*
6
N is the number of encoder pulses.
5

 Loading...
Loading...











