MPLS and RSVP
7210 SAS M, T, X, R6, Mxp MPLS Configuration Guide Page 35
space that may be separate from the IP addressing plan of the underlying network. If no
node ID is configured, then the node ID is taken to be the system interface IPv4 address of
the node. When configuring a tunnel at an LER, either an IPv4 or an unsigned integer
Node ID can be configured as the source and destination identifiers, but both ends must be
of the same type.
Statically configured LSPs are identified using GMPLS-compatible identifiers with the addition of
a Tunnel_Num and LSP_Num. As in RSVP-TE, tunnels represent, for example, a set of working
and protect LSPs. These are GMPLS-compatible because GMPLS chosen by the IETF as the
control plane for MPLS-TP LSPs, although this is not supported in 7210 SAS 6.1R1 release. PWs
are identified using a PW Path ID which has the same structure as FEC129 AII Type 2.
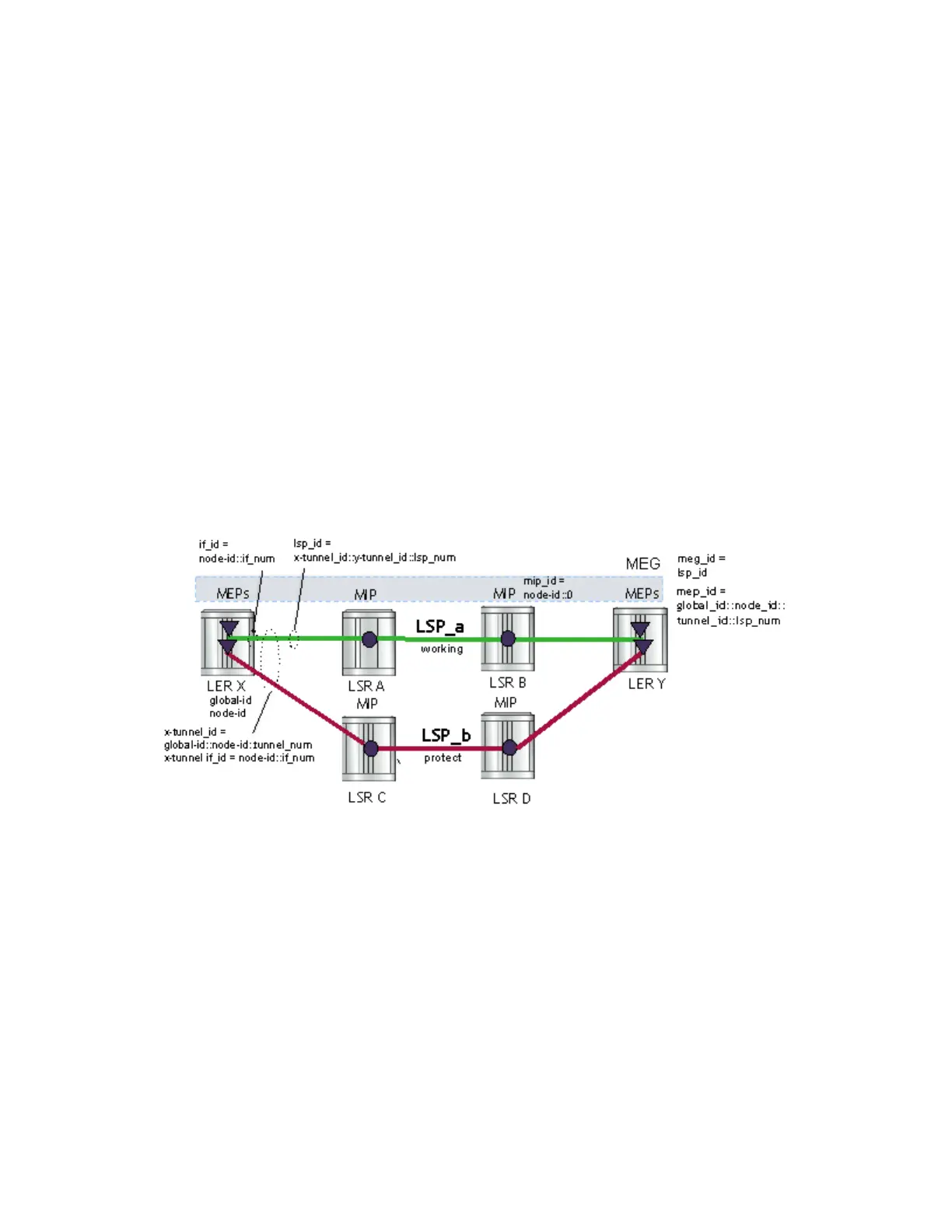
The 7210 SAS derives the identifiers for MEPs and MIPs on LSPs and PWs based on the
configured identifiers for the MPLS-TP Tunnel, LSP or PW Path ID, for use in MPLS-TP OAM
and protection switching, as per RFC6370.
The information models for LSPs and PWs supported in 7210 SAS are illustrated in Figure 10 and
Figure 11. The figures use the terminology defined in RFC6370.
Figure 10: MPLS-TP LSP and Tunnel Information Model

 Loading...
Loading...















