MPLS and RSVP
7210 SAS M, T, X, R6, Mxp MPLS Configuration Guide Page 31
Note that in 7210 SAS, all MPLS-TP LSPs are bidirectional co-routed, as detailed in RFC5654.
That is, the forward and backward directions follow the same route (in terms of links and nodes)
across the network. Both directions are setup, monitored and protected as a single entity.
Therefore, both ingress and egress directions of the same LSP segment are associated at the LER
and LSR and use the same interface (although this is not enforced by the system).
In the above model, an SDP can use one MPLS-TP LSP. This abstracts the underlying paths
towards the overlying services, which are transported on pseudowires. Pseudowires are modelled
as spoke SDPs and can also use MPLS-TP OAM. PWs with static labels may use SDPs that in-
turn use either signaled RSVP-TE LSPs, or one static MPLS-TP LSP.
MPLS-TP Provider Edge and Gateway
This section describes some example roles for the 7210 SAS in an MPLS-TP network.
VLL Services
The 7210 SAS may use MPLS TP LSPs, and PWs, to transport point to point virtual leased line
services. The node plays the role of a terminating PE or switching PE for VLLs. Only T-PE
functionality is supported on 7210 SAS-T (network mode). Both T-PE and S-PE (static only)
functionality is supported on 7210 SAS-R6. Epipe is supported.
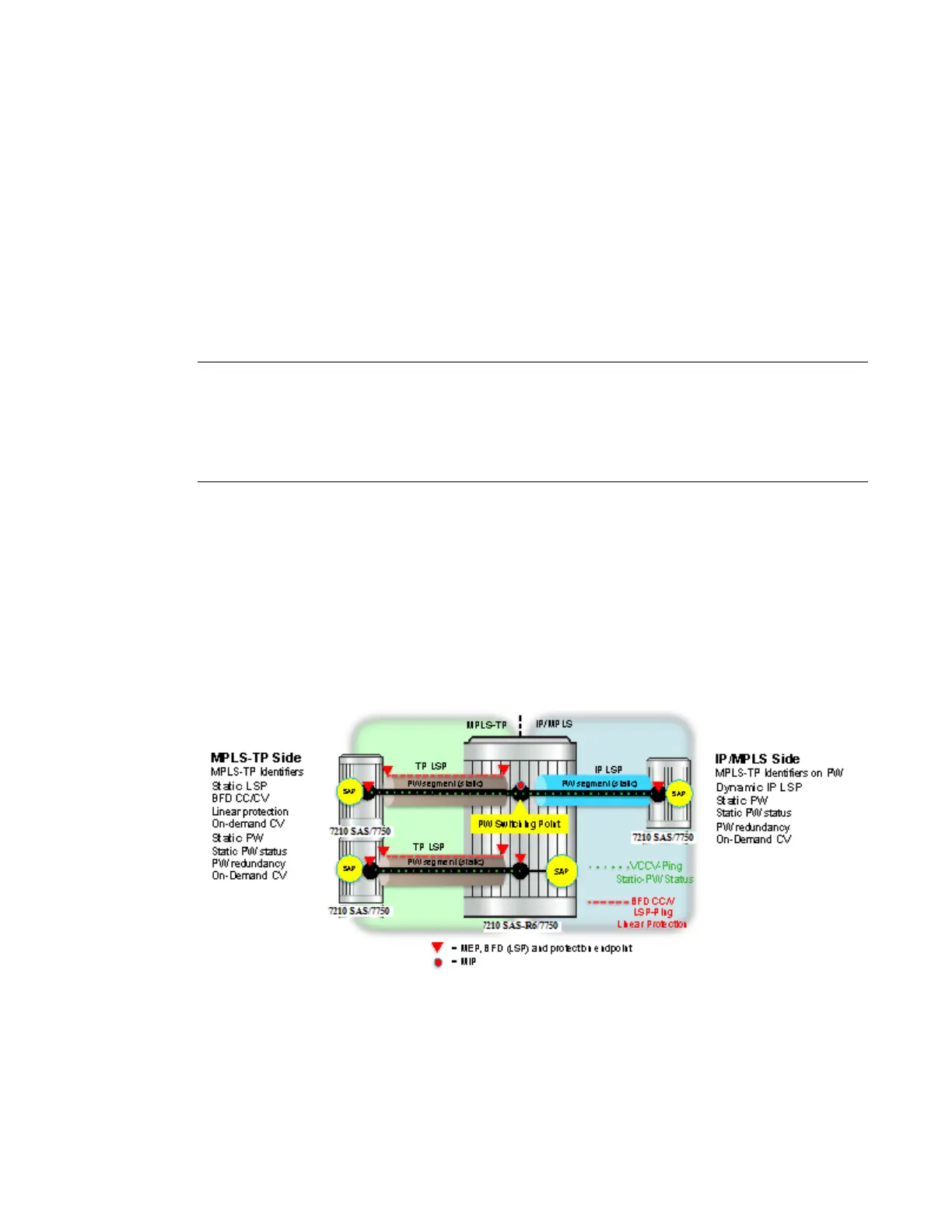
Figure 6 illustrates the use of the 7210 SAS as a T-PE/S-PE for services in an MPLS-TP domain.
Figure 6: MPLS-TP Provider Edge and Gateway, VLL Services

 Loading...
Loading...















