MPLS Transport Profile (MPLS-TP)
Page 40 7210 SAS M, T, X, R6, Mxp MPLS Configura-
tion Guide
RFC6426 adds address type 5 for use with Non IP interfaces, including MPLS-TP interfaces. In
addition, this RFC specifies that type 5 must be used when non-IP ACH encapsulation is used for
LSP Trace.
It is possible to send and respond to a DSMAP/DDMAP TLV in the LSP Trace packet for
numbered IP interfaces as per RFC4379. In this case, the echo request message contains a
downstream mapping TLV with address type 1 (IPv4 address) and the IPv4 address in the
DDMAP/DSMAP TLV is taken to be the IP address of the IP interface that the LSP uses. The LSP
trace packet therefore contains a DSMAP TLV in addition to the MPLS-TP static LSP TLV in the
target FEC stack.
DSMAP/DDMAP is not supported for pseudowires.
Proactive CC, CV and RDI
Proactive Continuity Check (CC) is used to detect a loss of continuity defect (LOC) between two
MEPs in a MEG. Proactive Connectivity Verification (CV) is used to detect an unexpected
connectivity defect between two MEPs (For example: mis-merging or disconnection), as well as
unexpected connectivity within the MEG with an unexpected MEP. This feature implements both
functions using proactive generation of OAM packets by the source MEP that are processed by the
peer sink MEP. CC and CV packets are always sent in-band such that they fate share with user
traffic, either on an LSP, PW or section and are used to trigger protection switching mechanisms.
Proactive CC/CV based on bidirectional forwarding detection (BFD) for MPLS-TP is described in
RFC6428. BFD packets are sent using operator configurable timers and encapsulated without
UDP/IP headers on a standardized G-ACh channel on an LSP or PW. CC packets simply consist of
a BFD control packet, while CV packets also include an identifier for the source MEP in order that
the sink MEP can detect if it is receiving packets from an incorrect peer MEP, thus indicating a
mis-connectivity defect. Other defect types (including period mis-configuration defect) should be
supported. When a supported defect is detected, an appropriate alarm is generated (for example:
log, SNMP trap) at the receiving MEP and all traffic on the associated transport path (LSP or PW)
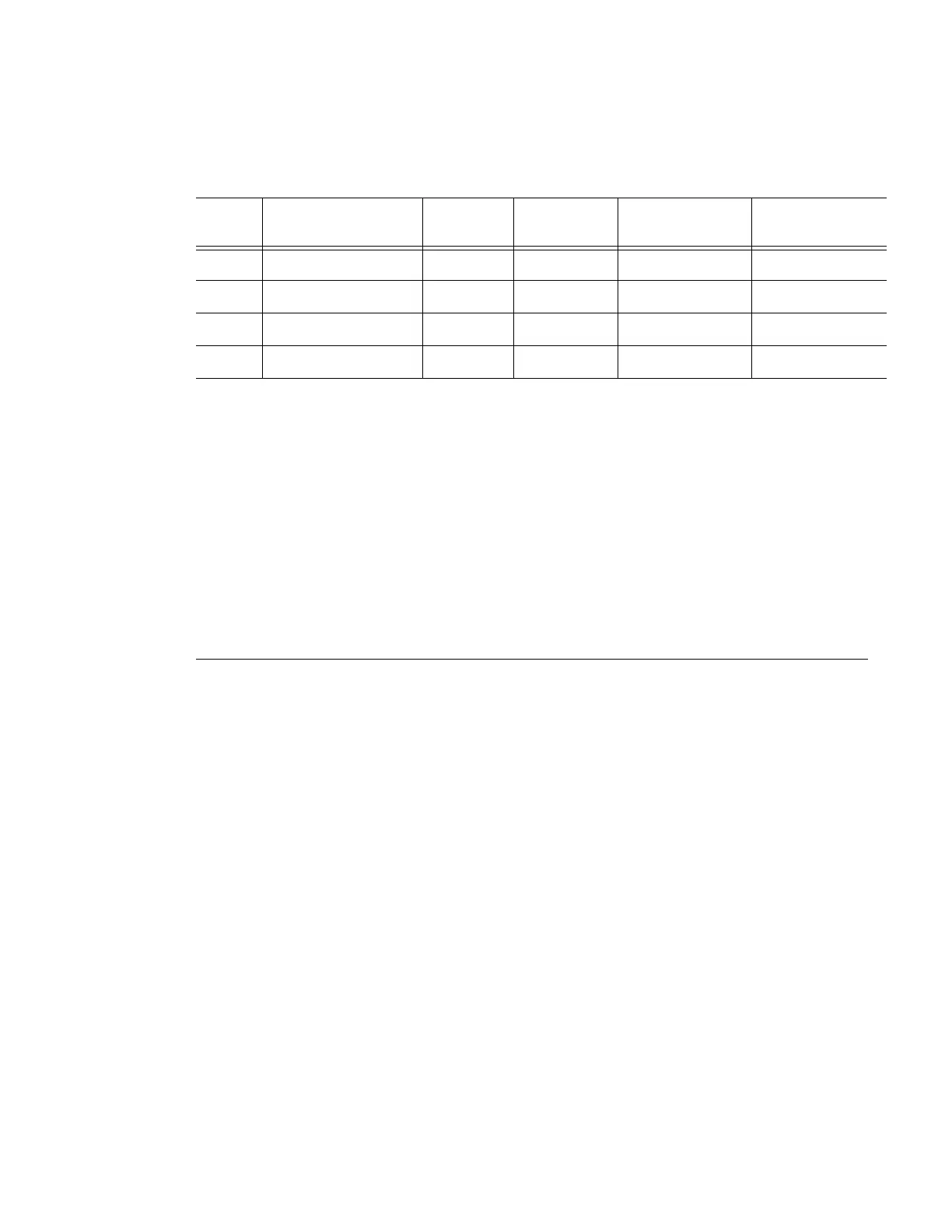
Table 4: Address types for the downstream mapping TLV
Type # Address Type K Octets Reference
7210 SAS-R6
support
7210 SAS-T
support
1 IPv4 Numbered 16 RFC 4379 Yes Yes
2 IPv4 Unnumbered 16 RFC 4379 Yes Yes
3 IPv6 Numbered 40 RFC 4379 No No
4 IPv6 Unnumbered 28 RFC 4379 No No
 Loading...
Loading...















