January 2016 Page 3–3
Chapter 3. Applications
3
gle-phase voltage output proportional to the posi-
tive, negative, and zero sequence current input.
Sensitivity to different types of faults depends on
the weighting factors or constants designed into
the sequence current network. Adjustments to the
network are provided.
A squaring amplifier in the controlling relay con-
verts the single-phase voltage output to a square
wave. The positive voltage portion corresponds to
the positive half-cycle of the filter voltage wave
and the zero portion corresponds to the negative
half-cycle. The square wave is used to key the
UPLC-II™, transmitting to the remote terminal.
The square wave from the remote terminal is com-
pared to the local square wave, which has been
delayed by an amount equal to the absolute chan-
nel delay time. This comparison of the local and
remote square waves at each terminal determines
whether a fault is internal or external.
Fault detectors are used to determine whether a
fault has occurred and to supervise tripping. The
fault detectors must be overreaching, i.e., set sen-
sitively enough to operate for all internal phase
and ground faults.
Because overcurrent fault detectors are normally
used, voltage transformers are not required. Such
a scheme is current only. Fault detectors should be
set above maximum load, yet operate for all inter-
nal faults. Distance fault detectors, which require
voltage transformers, are used on heavy-loaded or
long lines when distance supervision is required.
3.1.2.1 Single Phase-Comparison
Blocking, Current Only
In the current only system, the UPLC-II™ is used
with two overcurrent fault detectors (FD
l and
FD2). FD1, the carrier start unit, is set more sensi-
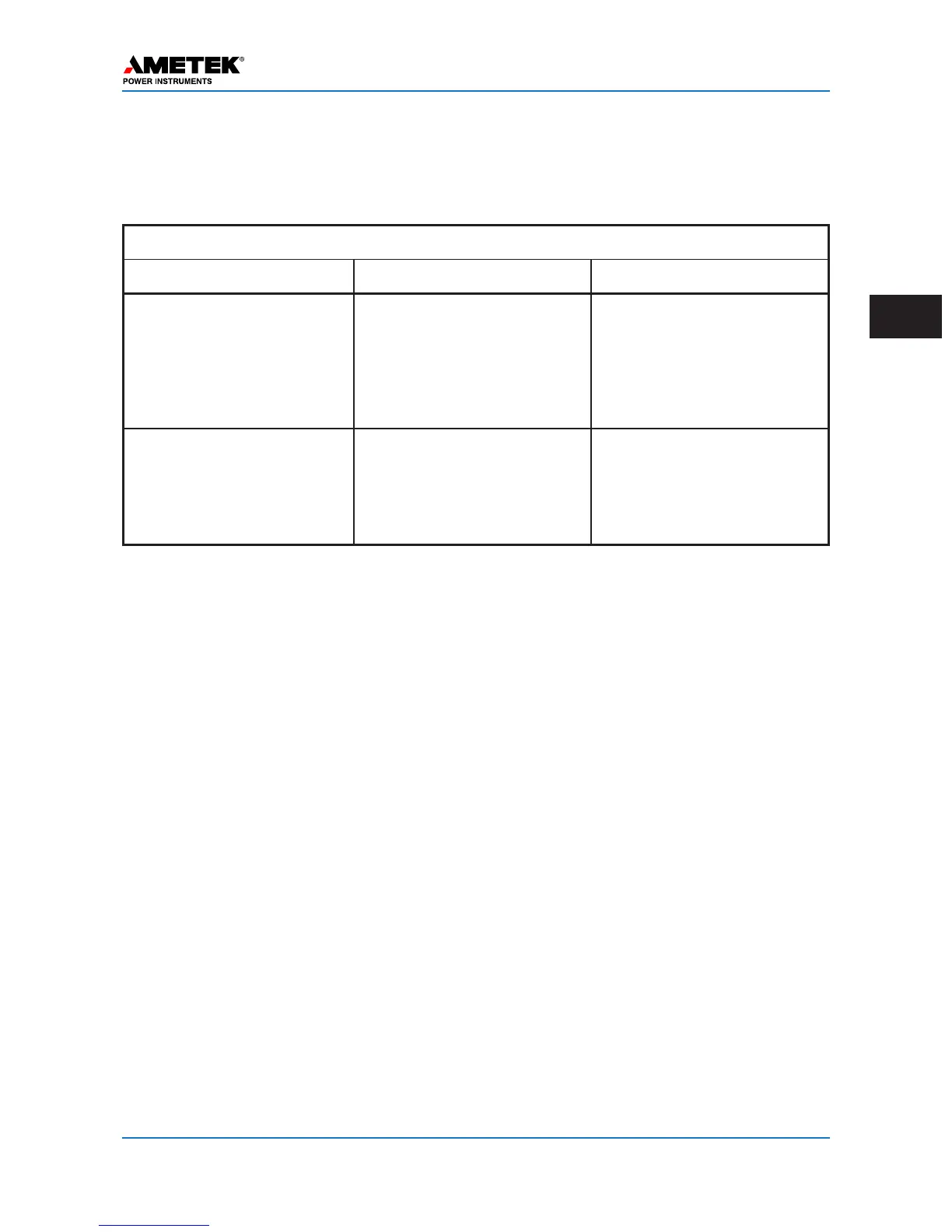
Table 3–1. Directional Comparison Blocking Operations for External and Internal Faults
* For external faults, the CS unit or timer x/o assure that a blocking signal is established.
OPERATION FOR EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL FAULTS
Type of Fault Events at Station G Events at Station H
External (F
E
)
For external faults, the
CS unit or timer x/o
assure that a blocking
signal is established.
P
1
operates; S
1
does not see
fault. Blocking signal received
from station H. RR back con-
tacts open (or 1 signal negates
AND).
No trip.
S
2
operates to key transmitter.
Blocking signal sent to station
G. P
2
does not see fault.
No trip.
Internal (F
I
) P
1
operates; S
1
may or may
not operate, but P
1
operation
prevents transmission of a
blocking signal.
Breaker 1 tripped.
P
2
operates, S
2
may or may
not operate but P
2
operation
prevents transmission of a
blocking signal.
Breaker 2 tripped.
 Loading...
Loading...