Installing the Arduino IDE on Linux
Installation procedures on Linux distributions are still not very homogeneous.
The Arduino IDE works fine on nearly all modern Linux versions, but the
installation process differs from distribution to distribution. Also, you often
have to install additional software (the Java Virtual Machine, for example)
that comes preinstalled with other operating systems.
It’s best to check the official documentation
14
and look up the instructions
for your preferred system.
Now that the drivers and IDE are installed, let’s see what it has to offer.
Meeting the Arduino IDE
Compared to IDEs such as Eclipse, Xcode, or Microsoft Visual Studio, the
Arduino IDE is simple. It mainly consists of an editor, a compiler, a loader,
and a serial monitor. (See Figure 5, The Arduino IDE is well organized, on
page 15 or, even better, start the IDE on your computer.)
It has no advanced features such as a debugger or code completion. You can
change only a few preferences, and as a Java application it does not fully
integrate into the Mac desktop. It’s still usable, though, and even has decent
support for project management.
The image that follows shows the IDE’s toolbar, which gives you instant access
to the functions you’ll need most:
Verify New
Open
Save
Upload
Serial Monitor
• With the Verify button, you can compile the program that’s currently in
the editor. So, in some respects, “Verify” is a misnomer, because clicking
the button doesn’t only verify the program syntactically, it also turns the
program into a representation suitable for the Arduino board. You can
invoke this function using the DR keyboard shortcut on a Mac or Ctrl-R
on all other systems.
14.
http://www.arduino.cc/playground/Learning/Linux
Chapter 1. Welcome to the Arduino • 14
report erratum • discuss
www.it-ebooks.info

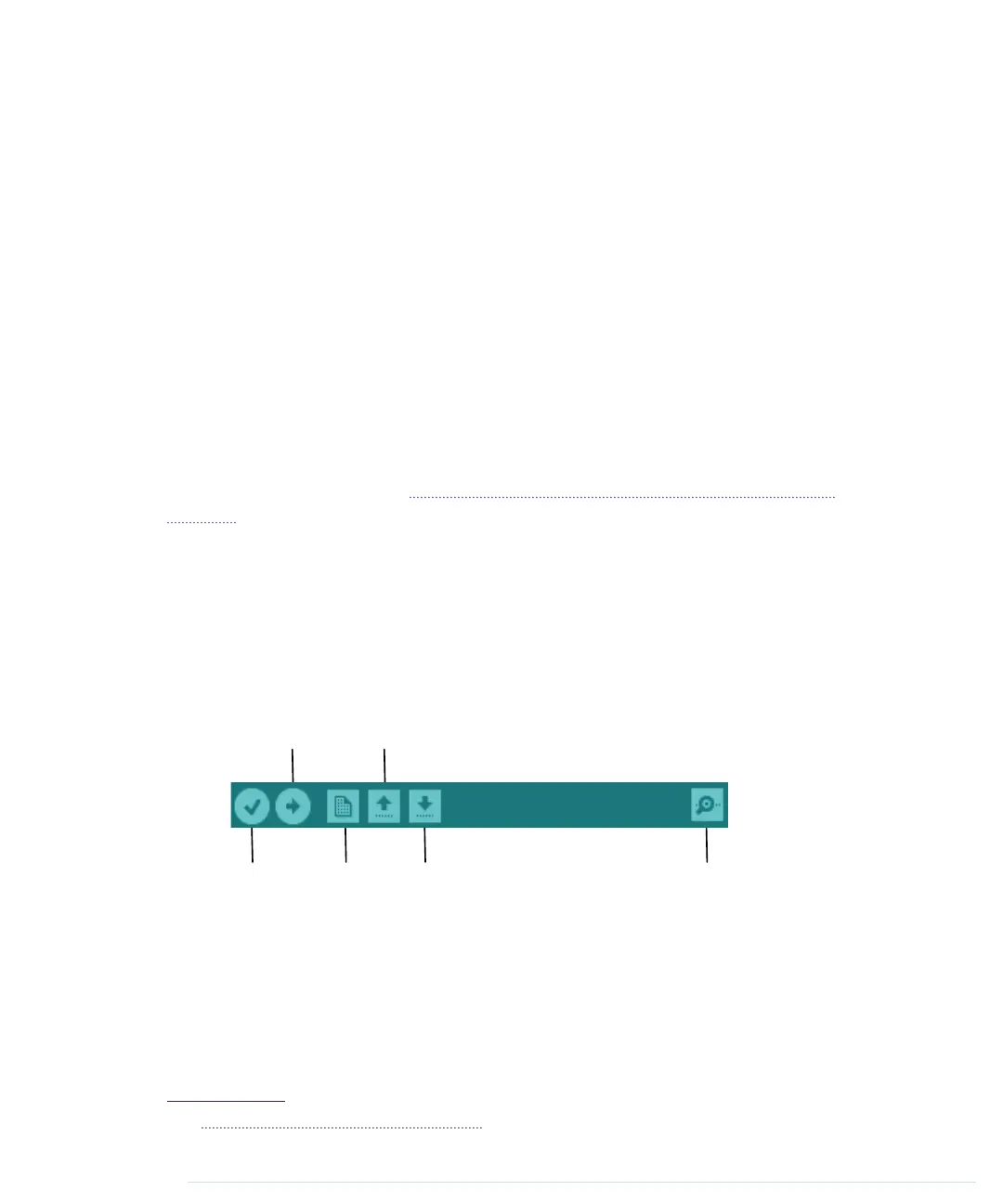 Loading...
Loading...