• Blinking LEDs are great, but when we think of Morse code, we usually
think of beeping sounds, so replace the LED with a piezo speaker, which
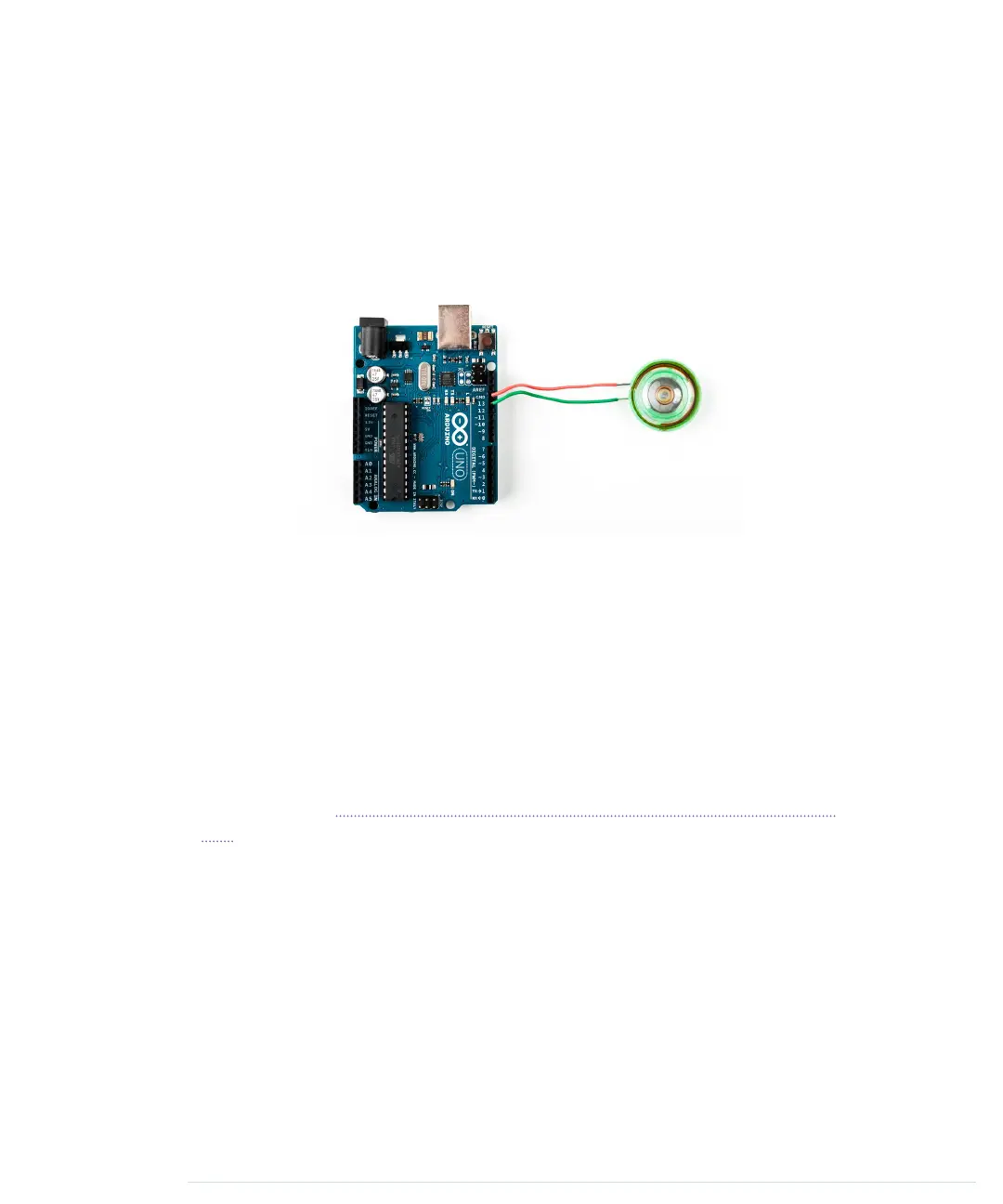
is cheap and easy to use. The following figure shows how you connect it
to an Arduino. Piezo speakers have a ground pin and a signal pin, so
connect the speaker’s ground to the Arduino’s ground, and connect the
signal pin to Arduino pin 13.
Then replace the
output_symbol
method with the following code:
void Telegraph::output_symbol(const int length) {
const int frequency = 131;
tone(_output_pin, frequency, length);
This sends a square wave to the speaker, and it plays a tone having a
frequency of 131 Hertz. (Look at the example under File > Examples >
02.Digital > toneMelody that comes with the Arduino IDE to learn more
about playing notes with a piezo speaker.)
• The Arduino IDE offers an alternative way to handle serial communication.
Have a look at Serial Communication Using Various Languages, on page
255, and rewrite the Morse code library so that it uses the new
serialEvent
function. Also, use
String
objects instead of character arrays.
• Improve the library’s design to make it easier to support different output
devices. You could pass some kind of
OutputDevice
object to the
Telegraph
constructor. Then derive a
LedDevice
and a
SpeakerDevice
from
OutputDevice
. It
could look as follows:
class OutputDevice {
public:
virtual void output_symbol(const int length);
};
class Led : public OutputDevice {
Chapter 4. Building a Morse Code Generator Library • 74
report erratum • discuss
www.it-ebooks.info

 Loading...
Loading...