92
Accuracy Calculation Examples
Example 1
Standard Capacitor Value: 10.004 nF @ 1 KHz
Measured value: 10.0046 nF @1 KHz
Dissipation Factor “D”: 0.00044
Test Signal Level: 1 V
Speed: Slow
Cable Length= 0 (no compensation needed)
D < 0.1 then: Ae is NOT multiplied by
Ae = Capacitance Accuracy = ± [(A
L
× A) + (K
a
+K
b
+K
c
)× 100 + K
d
+ K
f
] × K
e
[%]
Test voltage level was 1 Volt, according to the Table 12 of manual the
correction factor for this voltage level is 1.
Using Figure 30 of the manual, the Test Measurement Accuracy (A)
of a 10.004 nF @ 1 KHz is 0.05% (intersection of 10 nF and 1 KHz on
the chart).
Zm= Impedance of the DUT = 15.9057 KOhms
Impedance of the device under test is bigger than 500 ohms. Ka=0.
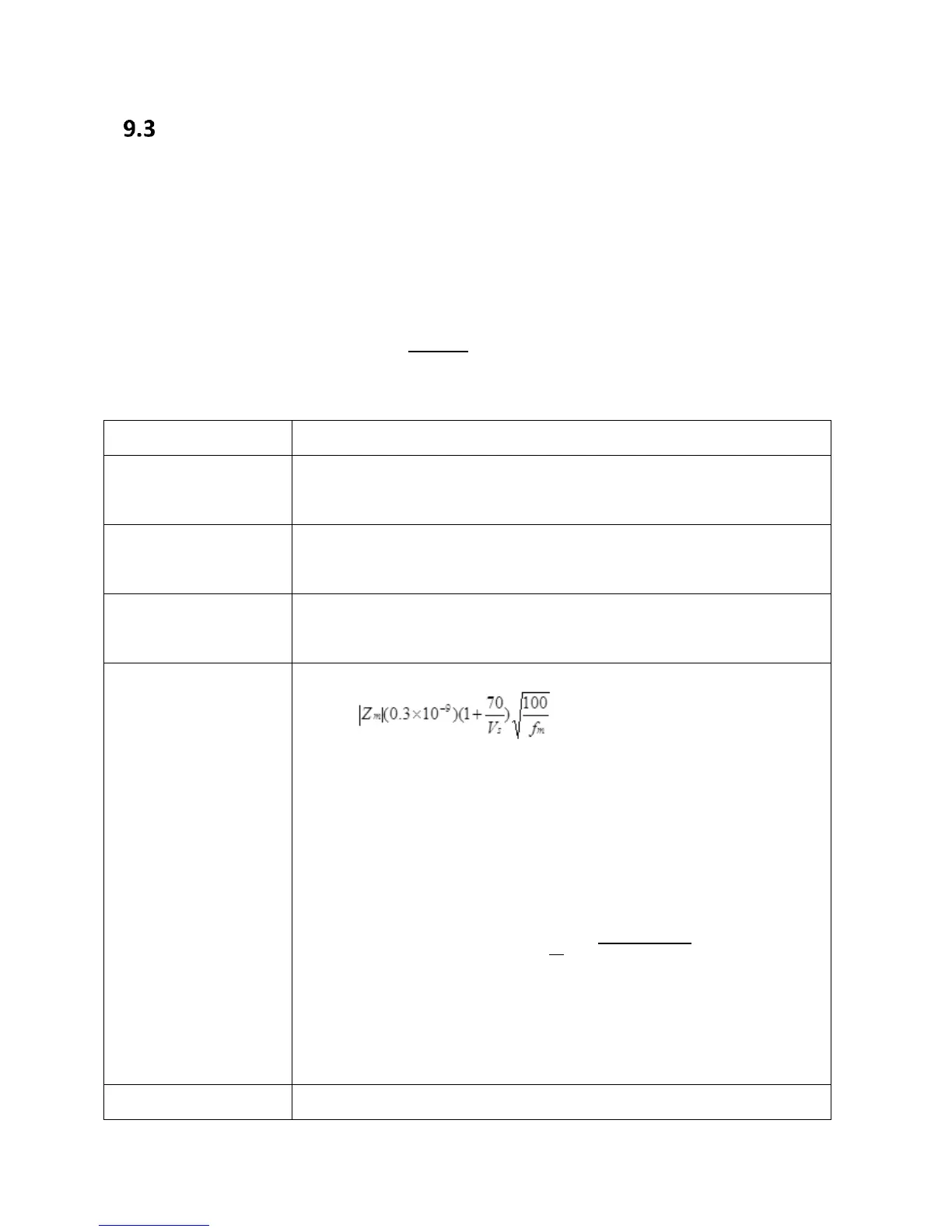
Use formula from Table 13 to find the
value of Kb.
Kb =
Kb is used because the impedance of DUT is bigger than 500 ohms.
Zm= Impedance of the DUT = 15.9057 KOhms
fm= 1 KHz (test frequency)
Vs= 1 (voltage test signal)
Kb=
Kb=0.00010713525
Cable Length =0. No Kb compensation (see Table 16)
Test frequency 1 KHz = Direct Calibrated Frequency= 0
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
 Loading...
Loading...