84
Proprietary Information: Not for use or disclosure except by written agreement with Calix.
© Calix. All Rights Reserved.
You also have the following options for determining the service-tag action P-bit for services
provisioned on xDSL ports:
Specify the P-bit value explicitly.
Enter the P-bit value to use for P-bit marking the outer tag.
Reference a Layer-3 Priority map.
Use a DSCP table or an IP Precedence table to map to a P-bit value. From the xDSL
port associated interface, you can select to use the system-default profiles ("access") or
specify another custom profile. See Layer 3 Priority to P-Bit Mapping (on page 96).
Only one service per port can use DSCP-Bit mapping function.
Works with Add-Tag and Add-2-Tags tag actions.
Either DSCP or IP Precedence can be used for a service, not both.
Provisioning sequence:
a. Create a DSCP-to-P-Bit map (on page 98) or create an IP Precedence to P-Bit Mask (on
page 100), if you do not want to use the system-default.
b. Assign the map to the xDSL port associated interface (on page 182), or leave the system-
default map "access" assignment.
c. Create a service-tag action with an Outer P-Bit Source of Map a layer-3 Priority.
d. Create a service using the defined service-tag action.
Preserve the existing P-bit value upstream.
Indicate that the E-Series preserves the P-bit value set in service provider-supplied CPEs
by specifying a P-bit value of "copy."
Note: The upstream traffic on a service VLAN must have the same priority value as is
set for downstream traffic.
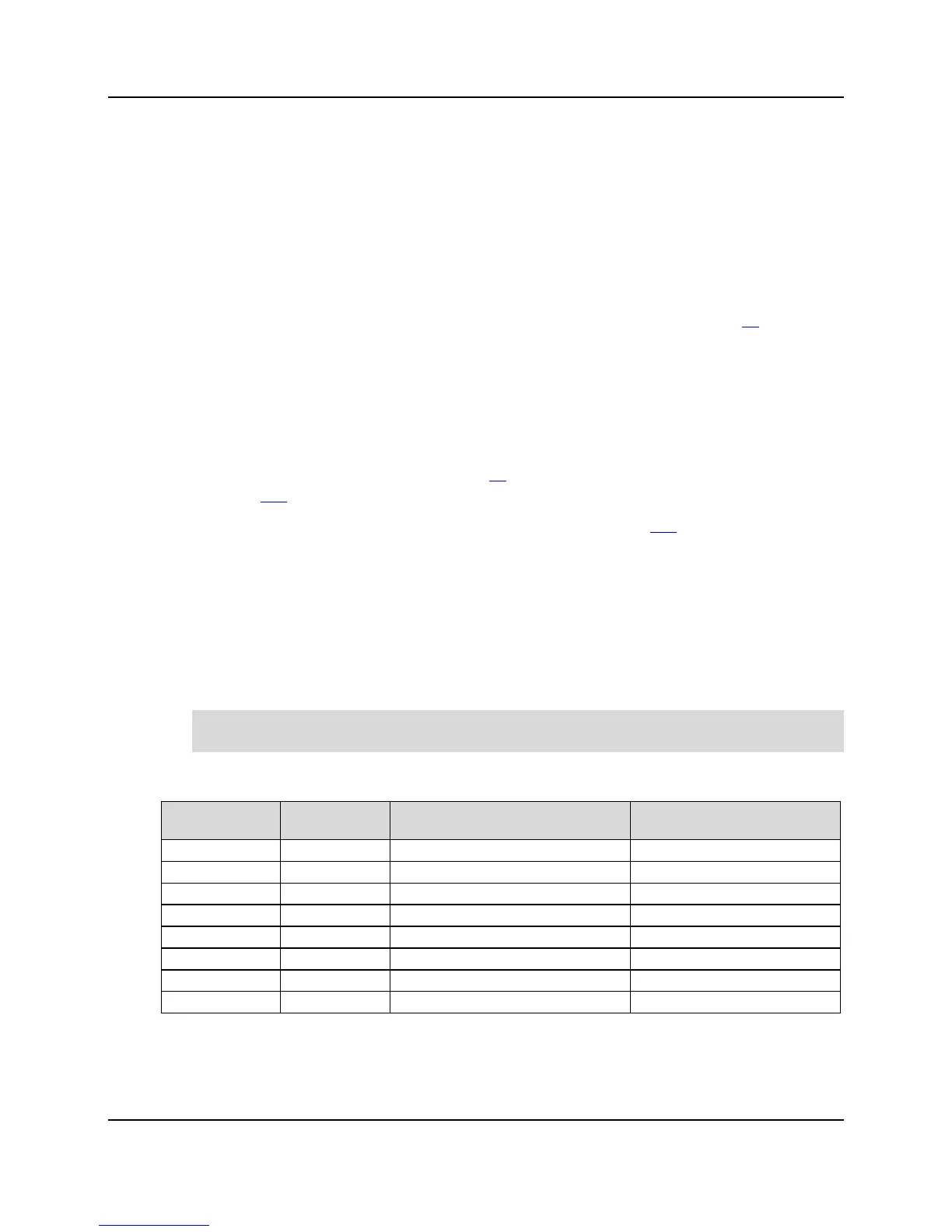
The table shows 802.1p to DiffServ DSCP system-default mapping table ("access").
Default
 Loading...
Loading...