extending the minimum and maximum frame sizes from 64 and 1,518
bytes (octets) to 68 and 1,522 bytes. Two bytes are used for the tag
protocol identifier (TPID), the other two bytes for tag control
information (TCI). The TCI field is further divided into PCP, CFI,
and VID.
802.1q operation
Enable 802.1q” in the WAN configuration WEB page if IEEE 802.1q VLAN header is to
be inserted to the rfc2684 bridged encapsulated MAC frame in upstream direction.
In receiving downstream MAC frame, the 802.1q header will be stripped before it is
forwarded to the IP or the bridge module.
If the 802.1p marking is configured in the packet Quality of Service, it will only be effective if the
packet is forwarded to a PVC that has 802.1q VLAN enabled.
5.8.7. DSCP OVERVIEW
Quality of Service within the 6401 Rugged Router is provided by Differentiated Services Code Point
(DSCP). DiffServ uses the 6-bit field in the IP header for packet classification purposes.
DSCP replaces the outdated Type of Service (TOS) field.
Network traffic entering a DiffServ domain is subjected to classification and conditioning. Traffic may
be classified by many different parameters, such as source address, destination address or traffic type
and assigned to a specific traffic class. Traffic classifiers may honour any DiffServ markings in
received packets or may elect to ignore or override those markings.
Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP)
The DSCP is a number in the range 0 to 63 that is placed into an IP Packet to mark it according to the
class of traffic it belongs in. Half of these values are earmarked for standardized services the other half
are available for local definition
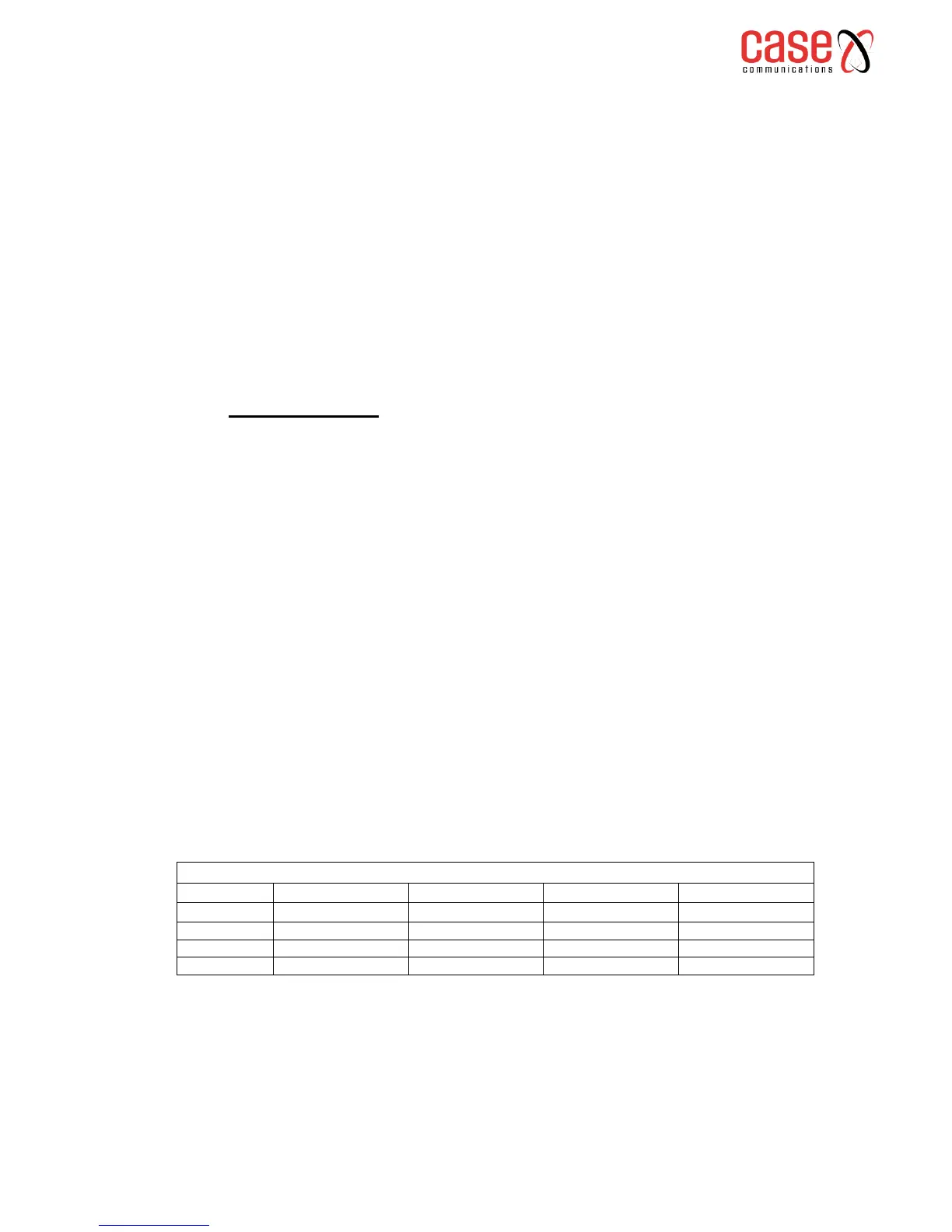
Assured Forwarding (AF) PHB group
Assured forwarding allows the operator to provide assurance of delivery as long as the traffic does not
exceed some subscribed rate. Traffic that exceeds the subscription rate faces a higher probability of
being dropped if congestion occurs.
The AF behaviour group defines four separate AF classes with Class 4 having the highest priority.
Within each class, packets are given drop precedence (high, medium or low). The combination of
classes and drop precedence yields twelve separate DSCP encodings from AF11 through AF43 (see
table below).
 Loading...
Loading...